Yemeni Civil War (2015–present) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Yemeni Civil War (2015–present) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Arab Winter, the Yemeni Crisis and the Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict/Qatar–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict | ||||||||||
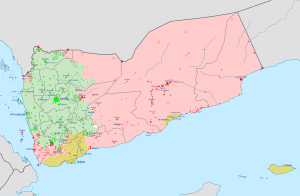 Military situation in Yemen on 13 February 2019 Controlled by the Supreme Political Council (Houthis)
Controlled by the Hadi-led government and allies Controlled by Southern Transitional Council Controlled by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) Controlled by Ansar al-Sharia and Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) (For a map of the military situation in Yemen and border areas in Saudi Arabia, see the detailed map here.) |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Main belligerents | ||||||||||
|
Alleged support:
|
Saudi-led coalition
Support:
Support:
|
|
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||||||
Casualties:
|
Under 1,000 troops
Casualties:
|
|
||||||||
| Strength | ||||||||||
|
|
1,800 security contractors |
|
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||||
| "Thousands" killed (per Al Jazeera; as of May 2018) 11,000+ killed (Arab Coalition claim; as of December 2017) |
Academi: 15 PMCs killed |
|||||||||
|
91,600+ killed overall in Yemen (11,700+ civilians) |
||||||||||
The Yemeni Civil War is a conflict that started in 2015 in the country of Yemen. It is mainly a fight between two groups. One group supports the government led by President Hadi. The other group is the Houthi movement, along with their allies. Both groups believe they are the rightful government of Yemen.
The Houthis took control of Yemen's capital city, Sanaʽa. They teamed up with forces loyal to former president Ali Abdullah Saleh. These groups have been fighting against Hadi's supporters, who are based in the city of Aden. Other groups like Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) have also been involved. They have carried out attacks and control some areas.
In March 2015, after taking Sanaʽa, the Houthis announced they would try to take over more areas. They started moving into southern parts of Yemen. By March 25, they reached the city of Aden, where Hadi's government was. President Hadi then left the country. At the same time, a group of countries led by Saudi Arabia started military actions. They used air strikes to try and bring back Hadi's government. The United States helped this group with information and supplies.
Contents
Impact of the Conflict
The war has caused a lot of suffering for people in Yemen. From 2015 to 2017, thousands of people were killed, including many regular citizens. Many more have been affected by a severe lack of food, which is called a famine. This has led to many deaths.
International Involvement
The conflict is often seen as a proxy war. This means bigger countries are supporting different sides without directly fighting each other. For example, Iran is believed to support the Houthis. Saudi Arabia is against the Houthis and is trying to stop Iran's influence in the region.
In 2018, the UN warned that millions of people in Yemen were at risk of starvation. They said it could become the worst famine in a century. Many countries have criticized the Saudi-led group for bombing areas where civilians live. These bombings have caused many injuries and deaths among regular people.
US Support and Concerns
The United States has provided bombs and other help to the Saudi forces. In March 2019, the US Senate tried to pass a resolution to stop this support. However, President of the United States Donald Trump stopped it. In May, the Senate was not able to overrule his decision.
Images for kids
-
President Hadi meets U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 7 May 2015
-
Registration of Indian citizens evacuating from Yemen in March 2015
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra civil yemení (2014-presente) para niños
In Spanish: Guerra civil yemení (2014-presente) para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |








