Downtown Los Angeles facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Downtown Los Angeles
|
|
|---|---|
|
Clockwise, from top: Skyline from the southwest, the Arts District, City Hall, the Jewelry District and the Financial District in 2001
|
|
| Nicknames:
"Downtown L.A.", "DTLA", "Downtown"
|
|
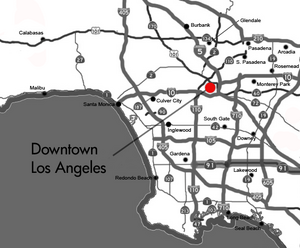
Freeway map of the Los Angeles area showing Downtown LA
|
|
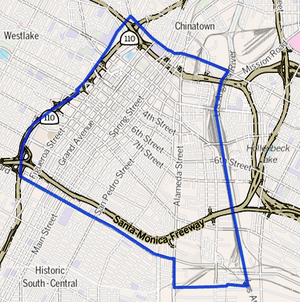
Downtown map as delineated by the Los Angeles Times
|
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | |
| City | |
| Downtown neighborhoods | |
| Elevation | 305 ft (93 m) |
Downtown Los Angeles (often called DTLA) is the main business area of Los Angeles, California. It's also a home for about 85,000 people and covers an area of about 5.84 square miles. In 2013, a study showed that over 500,000 jobs were located here. It is a key part of Central Los Angeles.
Downtown Los Angeles is split into many smaller neighborhoods and districts. Many of these are named after what they are known for, like the Arts, Civic Center, Fashion, and Jewelry districts. It's also the main hub for the city's train system and other regional trains.
Years ago, banks, big stores, and movie theaters brought many people downtown. However, after the 1950s, the area faced some tough times. It still remained important for government work in the Civic Center and for banking on Bunker Hill. Broadway continued to be a lively place for shopping and fun, especially for Hispanic people living in Los Angeles. Since the early 2000s, Downtown has been making a big comeback. The Crypto.com Arena is a major spot at the south end of downtown. Older buildings along Broadway are being fixed up and turned into fancy apartments, shared workspaces, and cool shops.
Contents
What is the History of Downtown LA?
How Downtown LA Started
The first people known to live in the area of Downtown Los Angeles were the Tongva, a Native American group. Later, in 1769, a Spanish explorer named Father Juan Crespí thought the area would be perfect for a large settlement. On September 4, 1781, a group of settlers from what is now Mexico officially founded the city.
In the 1880s, more and more people wanted to buy land here. This caused the city's population to grow very quickly. It went from 11,000 people in 1880 to almost 100,000 by 1896. As the city grew, new roads and a street plan helped develop areas like the Civic Center and Historic Core.
Downtown's Golden Age
By 1920, Los Angeles had one of the biggest and best train systems in the world. It even had more miles of track than New York City. With many new residents and active land developers, Downtown LA became the busy center of a large city. Train lines connected four counties with over 1,100 miles of track.
In the early 1900s, many banks gathered around South Spring Street. This area became known as the Spring Street Financial District. People sometimes called it the "Wall Street of the West" because so many important financial companies were there. The Los Angeles Stock Exchange was also located here for many years.
As businesses grew, new hotels were built. Grand hotels like the Alexandria (1906), the Rosslyn (1911), and the Biltmore (1923) opened. There was also a need for places to entertain the growing population. Broadway became the main spot for nightlife, shopping, and shows. Over a dozen theaters and movie palaces were built there before 1932.
Big department stores also opened their main shops downtown. These included The Broadway, May Company, and Bullock's. They served the wealthy people living in the Bunker Hill neighborhood. Many special stores also did well, especially those selling jewelry, which led to the Downtown Jewelry District.
The Los Angeles Union Passenger Terminal (Union Station) opened in May 1939. It brought together train services from different companies. It was built to be very grand and was one of the last big railway stations built in the United States.
Challenges and Comeback

After World War II, more people moved to the suburbs and bought cars. This meant less money was invested in downtown. Many company headquarters moved to new areas. The once-wealthy Bunker Hill neighborhood became less cared for, and its beautiful old houses were not kept up. Many very old buildings in the Plaza area were torn down to make parking lots. This was because parking was in high demand and more profitable. With fewer people living downtown, many street-level shops struggled. For most people in Los Angeles, downtown became a place they would drive to for a quick visit and then leave.
To help bring businesses back, the city started the Bunker Hill Redevelopment Project in 1955. This big project cleared land for new tall buildings. During this time, the entire neighborhood was changed, and the Angels Flight funicular railway closed in 1969. Angels Flight reopened in 1996 but closed again in 2001 due to safety issues. After major safety upgrades, it reopened for passengers on March 15, 2010.
As new, modern office spaces became available on Bunker Hill, many of Downtown LA's remaining financial companies moved to these newer buildings. This left the old Spring Street Financial District empty above the ground floor. After companies moved, the large department stores on Broadway also closed, mostly in the 1980s.
However, the Broadway theaters found new life as Spanish-language movie houses. This started when the Million Dollar Theater was changed into a Spanish-language theater in the 1950s.
Downtown Today

By mid-2013, Downtown was seen as a neighborhood with more and more trendy and well-off residents.
Because many offices moved to Bunker Hill and the Financial District, many old office buildings were left empty. In 1999, the Los Angeles City Council passed a special rule. This rule made it easier for developers to turn old, empty office buildings into new apartments and luxury condos.
By early 2009, over 14,500 new homes were created this way. This led to a big increase in the number of people living downtown. The population grew from 28,878 residents in 2006 to 39,537 in 2008, a jump of almost 37%. Downtown Los Angeles is seeing lots of new life and investment.
Here are some key things that have helped Downtown LA grow:
- The Staples Center, which opened in 1999, has greatly helped the area. It brings in 250 events and nearly 4 million visitors each year. Next to it, the L.A. Live complex was built. This includes the Microsoft Theatre and the Grammy Museum.
- The Los Angeles County Metro Rail, a train system centered downtown, makes it easy to get to the city center.
- Developers planned a huge $1.8 billion project along Grand Avenue. This included building Grand Park, a large city park. It also involved building major landmarks like the Frank Gehry-designed Walt Disney Concert Hall and the modern art museum The Broad, which opened in 2015.
- In 2007, the Los Angeles City Council changed building rules for downtown. These changes allow for bigger and denser buildings. Developers who set aside 15% of their homes for lower-income residents can build larger buildings.
- In 2009, Bottega Louie opened in the historic Brockman Building. It helped create a "restaurant row" that brought many new restaurants and shops to the area.
- In October 2015, an outdoor shopping and lifestyle center called The Bloc Los Angeles opened. It replaced the old enclosed Macy's Plaza.
Where is Downtown Los Angeles?
Downtown Los Angeles is surrounded by other neighborhoods. To the north and northwest is Echo Park. Chinatown is to the northeast. Boyle Heights is to the east. Vernon is to the south. Historic South Central and University Park are to the southwest. Pico-Union and Westlake are to the west.
Downtown is bordered by Cesar Chavez Avenue to the northeast. The Los Angeles River is to the east. The Los Angeles city line with Vernon is to the south. East Washington Boulevard is to the southwest. The 110 Freeway or Beaudry Avenue is to the west. This includes the entire Four Level Interchange with Highway 101.
Nearby Neighborhoods
Here's how Downtown Los Angeles relates to other communities:
 |
Echo Park | Echo Park | Chinatown |  |
| Pico-Union & Westlake | Boyle Heights | |||
| Historic South Central & University Park | Vernon | Vernon, Maywood & Bell |
Downtown Districts
Downtown Los Angeles includes these smaller areas:
Who Lives in Downtown Los Angeles?

In 2000, about 27,849 people lived in Downtown's 5.84 square miles. This was a lower population density compared to the rest of Los Angeles. However, the number of residents grew to 34,811 by 2008. By 2014, the population had reached 52,400 residents, with many new homes being built. The average age of residents was 39.
Downtown Los Angeles has a very diverse population. In 2010, the population was almost equally split among four main groups: Asian Americans (23%), African Americans (22%), Latinos (25%), and non-Hispanic Whites (26%).
A study in 2000 showed that Downtown was one of the most diverse neighborhoods in Los Angeles. Most residents (93.4%) rented their homes. In 2000, about 2,400 military veterans lived Downtown.
A 2013 study found that 52.7% of Downtown residents were Caucasian, 20.1% Asian, 17.0% Latino, and 6.2% African-American. Most residents (74.8%) were between 23 and 44 years old. The average age was 34.
How to Get Around Downtown LA?
Local and Regional Transport
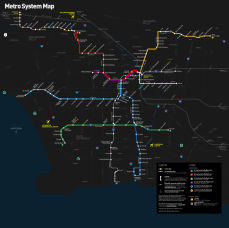
Downtown Los Angeles is the main hub for the region's growing train system. Six commuter lines are run by Metrolink. Five rapid-transit rail lines and local bus services are run by Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro).
Important Metro stations in Downtown include Los Angeles Union Station, Civic Center/Grand Park station, Pershing Square station, 7th Street/Metro Center station, Pico station, and Little Tokyo/Arts District station.
- The Los Angeles Metro Rail System has five train lines that serve Downtown Los Angeles: the A Line, B Line, D Line, E Line, and the L Line.
- In late 2009, the Metro J Line bus rapid transit project opened. It replaced two separate bus lines with a single service through downtown.
- In 2006, part of the Metro Red Line (now the B Line) was renamed the Metro Purple Line (now the D Line). This subway line runs from Union Station to Wilshire/Western station in Koreatown. An extension of this line to Westwood is currently being built.
- Metro also runs a large bus network. This includes local buses, express commuter lines, and rapid buses that get signal priority.
- The Los Angeles Department of Transportation runs seven local DASH shuttle lines downtown on weekdays. Weekend service is available on some lines.
Amtrak Train Service

Amtrak runs long-distance passenger train services on five routes through Los Angeles Union Station. These routes include the Coast Starlight, Pacific Surfliner, Southwest Chief, Sunset Limited, and Texas Eagle.
Greyhound Bus Service
Greyhound Lines has a major bus station in Downtown Los Angeles. It is located at the corner of Seventh and Alameda streets.
Getting to Los Angeles International Airport
Los Angeles World Airports runs a direct shuttle bus called LAX FlyAway Bus. It runs every 30–60 minutes between Union Station and Los Angeles International Airport.
Future Transit Plans
- The Metro E Line was built in two parts and finished in 2016. The first part connected 7th Street/Metro Center Station downtown with Culver City. The second part extended the line to Santa Monica. The E Line shares tracks and stations with the Metro A Line.
- Los Angeles Union Station will be a major stop for the new California High-Speed Rail system. This project will connect Northern and Southern California. Trains will travel at an average speed of 220 miles per hour.
- The Regional Connector Transit Corridor is currently being built. It will connect the A, E, and L Lines between the Little Tokyo/Arts District and 7th Street/Metro Center stations.
- There are plans to bring streetcar-style trolley service to Downtown Los Angeles along Broadway. This would connect the L.A. Live area with the Grand Avenue cultural spots and Bunker Hill.
Parks and Green Spaces
Downtown Los Angeles has many public parks, plazas, gardens, and other open spaces:
- Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels meditation garden and olive garden
- Grand Park
- La Placita Olvera
- Pershing Square
- Los Angeles City Hall South Lawn
- Los Angeles Police Department's Police Administration Building South Lawn
- Los Angeles State Historic Park
- Los Angeles Union Station gardens
- Walt Disney Concert Hall Community Park
- The Water Court at California Plaza, an outdoor area for performances and dining.
- Japanese Garden and plaza at the Little Tokyo Cultural and Community Center Plaza
- Japanese Garden at the Kyoto Grand Hotel and Gardens
- Garden at Bank of America Plaza
There are also plans for new parks in the future. These include a public park at the proposed Nikkei Center in Little Tokyo. Another plan is for a 1-acre park at the Medallion development in the Historic Core. A small "pocket park" is also planned at the Wilshire Grand Hotel replacement project.
The city of Los Angeles recently finished a new park. It is located on the 400 block of South Spring Street in the Historic Core neighborhood.
What Does the Downtown LA Skyline Look Like?
Los Angeles has one of the largest skylines in the United States. Until 1958, buildings could not be taller than the 27-story City Hall building. Since then, the skyline has grown quickly. This is thanks to better building designs that make skyscrapers very resistant to earthquakes. Many new tall buildings now include homes or hotels.
Here are some current and upcoming skyscraper projects:
- 1340 Figueroa: A 43-story apartment building designed by architect Daniel Libeskind.
- 705 Ninth Street: A 35-story apartment building finished in 2009.
- 717 Olympic: A 26-story apartment building finished in mid-2008.
- 888 Olive: A 32-story apartment building that opened in 2015.
- Concerto: A 28-story apartment building finished in early 2009.
- The Grand Avenue Project: Designed by architect Frank Gehry, this project includes a 48-story hotel tower and a civic park.
- L.A. Live: A large dining, entertainment, and hotel complex. It includes a Ritz-Carlton and JW Marriott Hotel, plus Ritz-Carlton condos. It was finished in 2010.
- Marriott International finished a 24-story hotel tower near L.A. Live in 2014. They also plan to build another hotel.
- Metropolis: A project with four towers (60, 50, 38, and 19 stories) that is currently being built.
- South: A complex of three towers called Elleven, Luma, and Evo. It was finished in phases by early 2009.
- The Wilshire Grand Tower is being rebuilt. It will be a 900-room hotel and office project. It is currently the tallest tower west of the Mississippi River, at 1,100 feet.
Building Height Limits: 1904-1957
Los Angeles first set a height limit for buildings after the 13-story Continental Building was finished. The goal was to prevent the city from becoming too crowded. Many cities at the time worried about skyscrapers causing too much traffic. In 1911, the city set a specific height limit of 150 feet. Some decorative towers, like those on the Eastern Columbia Building, were allowed to be taller.
This height limit was removed in 1957. The first private building to go over the old limit was the 18-story United California Bank Building.
What is the Economy of Downtown LA Like?
DTLA is a growing center for technology companies. In 2015, one company found 78 tech-focused businesses in DTLA. These included companies making mobile apps, hardware, digital media, and clean energy tech. There are also shared workspaces and places that help new businesses get started.
The Arts District has become a popular place for companies looking for different kinds of offices. Its central location makes it easy to reach from many parts of Los Angeles. The lively cultural scene also attracts young tech employees.
Anschutz Entertainment Group has its main offices in Downtown Los Angeles.
BYD Company, a Chinese technology company, has its North American headquarters in Downtown Los Angeles.
Cathay Bank has its main offices in the Los Angeles Chinatown.
Education in Downtown LA
In 2000, about 17.9% of Downtown residents aged 25 and older had a four-year college degree. This was about average for the city.
Here are some of the schools in the Downtown area:
- Ramon C. Cortines School of Visual and Performing Arts, a high school at 450 N. Grand Ave.
- Downtown Business High School, an alternative school at 1081 W. Temple St.
- California Academy for Liberal Studies Early College High School, a charter school at 700 Wilshire Blvd.
- Alliance Dr. Olga Mohan High School, a charter school at 644 W. 17th St.
- Abram Friedman Occupational School, an adult education school at 1646 S. Olive St.
- Metropolitan Continuation School, at 727 S. Wilson St.
- Para Los Ninos Middle School, a charter school at 1617 E. Seventh St.
- Jardin de la Infancia, a charter elementary school at 307 E. Seventh St.
- Saint Malachy Catholic Elementary School, a private school at 1200 E. 81st St.
- Tri-C Community Day School, at 716 E. 14th St.
- City of Angels School, an alternative school at 1449 S. San Pedro St.
- San Pedro Street Elementary School, at 1635 S. San Pedro St.
- Saint Turibius Elementary School, a private school at 1524 Essex St.
- American University Preparatory School, a private school at 345 S. Figueroa St.
The Fashion Institute of Design & Merchandising is at 800 S. Hope St. The Colburn School for music and performing arts is at 200 S. Grand Ave.
Images for kids
-
1894 drawing of the Victorian-era business district, now the eastern half of the Civic Center district
-
Looking northeast on Spring Street from First Street, 1880s. Asher Hamburger's Peoples Store at center. Towers of the Baker Block are visible in the distance.
-
The Last Bookstore, which was founded in 2005.
-
Downtown Los Angeles with Dodger Stadium
-
St Vincent Court in 2017. European-style decorations date to 1957.
See also
 In Spanish: Downtown Los Angeles para niños
In Spanish: Downtown Los Angeles para niños
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |