FIBA facts for kids
 |
|
| Abbreviation | FIBA |
|---|---|
| Predecessor | International Amateur Handball Federation |
| Formation | 18 June 1932 |
| Founded at | Geneva, Switzerland |
| Type | Sports federation |
| Headquarters |
|
|
Membership
|
212 national federations |
|
Official languages
|
English French |
|
President
|
Sheikh Saud Ali Al Thani |
|
Secretary-General
|
Andreas Zagklis |
|
Key people
|
George Vassilakopoulos Manfred Ströher |
|
Revenue (2018)
|
US$102.2 million |
| Expenses (2018) | US$107.74 million |

The International Basketball Federation (FIBA) is the main organization that runs the sport of basketball around the world. Think of it like the global boss for basketball! FIBA sets the rules, decides what equipment is needed, and organizes big international games.
It also manages how players move between countries and picks the international referees. FIBA has 212 national basketball groups as members. These groups are organized into five main areas: Africa, Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.
FIBA organizes important basketball events for both men and women. This includes the tournaments that help teams qualify for the Summer Olympics. The biggest event is the FIBA Basketball World Cup, where national men's teams compete every four years for the Naismith Trophy. This trophy is named after James Naismith, who invented basketball! There's also a similar event for women's teams, the FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup.
Contents
History of FIBA
How FIBA Started (1932–1949)
FIBA was created in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1932. This was two years after the IOC officially recognized basketball as a sport. Before FIBA, basketball was managed by a handball organization.
Eight countries were the first members of FIBA: Argentina, Czechoslovakia, Greece, Italy, Latvia, Portugal, Romania, and Switzerland. In 1934, FIBA became the only official group for basketball. During the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin, James Naismith, the inventor of basketball, was named FIBA's Honorary President.
FIBA's Growth (1950–2019)
FIBA started organizing the men's FIBA Basketball World Cup in 1950 and the women's FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup in 1953. For many years, these events happened every four years, taking turns with the Olympics. After 2014, the men's World Cup moved to a new schedule, happening the year before the Summer Olympics.
In 1989, FIBA made a big change. They voted to allow players from the NBA (the professional league in the USA) to play in international events like the World Cup and the Olympics. This made the competitions even more exciting!
FIBA's main office moved to Munich in 1956, then back to Geneva in 2002. In 2013, FIBA moved into its current headquarters, called "The House of Basketball," in Mies. Andreas Zagklis became the Secretary-General of FIBA in December 2018.
Recent Events (2020–Present)
In February 2022, two countries, Russia and Belarus, were temporarily stopped from playing in international basketball competitions. This was due to the conflict in Ukraine. They were also not allowed to host any basketball events.
FIBA Leaders: Presidents and Secretaries General
FIBA has had several leaders over the years. The President is like the head of the organization, and the Secretary-General handles the daily operations.
| Years | Name |
|---|---|
| 1932–1976 | |
| 1976–2003 | |
| 2003–2018 | |
| 2018–present |
How FIBA is Organized
FIBA's Five Zones
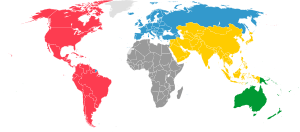
FIBA divides the world into five zones. These zones help manage basketball in different parts of the world through regional offices. Each country's national basketball group is a member of FIBA and belongs to one of these zones:
- FIBA Africa (54 members)
- FIBA Americas (42 members)
- FIBA Asia (44 members)
- FIBA Europe (50 members)
- FIBA Oceania (22 members)
FIBA works with 212 national basketball groups. For example, in Great Britain, the British Basketball Federation is the single group that manages basketball there. Some members from FIBA Oceania, like Australia and New Zealand, also play in Asian tournaments.
FIBA's Rules and Leadership
FIBA's main office is in Mies, Switzerland. It's called the Patrick Baumann House of Basketball, named after a former Secretary-General.
The highest decision-making group in FIBA is the FIBA Congress. This is where representatives from all the national groups meet. They meet every two years and are the only ones who can change FIBA's main rules. The Congress also elects the FIBA President and other important leaders.
The FIBA Central Board is the top executive group. It has 29 members, including the President, Secretary-General, and leaders from each of the five zones. This Board decides which countries will host the men's and women's FIBA World Cups. Sheikh Saud Ali Al Thani became the President in August 2023.
Basketball Competitions
FIBA organizes many exciting basketball competitions for national teams and clubs around the world.
National Team Competitions
- Men's Basketball
- FIBA Basketball World Cup
- Olympic Basketball Tournament
- Olympic Qualifying Tournaments
- FIBA U-19 Basketball World Cup (for players under 19)
- FIBA U-17 Basketball World Cup (for players under 17)
- 3x3 Men's Basketball (a faster, three-on-three version of basketball)
- FIBA 3x3 World Cup
- Olympic 3x3 Basketball Tournament
- FIBA 3x3 U-23 World Cup (for players under 23)
- FIBA 3x3 U-18 World Cup (for players under 18)
- Women's Basketball
- FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup
- Olympic Women's Basketball Tournament
- FIBA Women's Olympic Qualifying Tournament
- FIBA U-19 Women's Basketball World Cup
- FIBA U-17 Women's Basketball World Cup
- 3x3 Women's Basketball
- FIBA 3x3 Women's World Cup
- Olympic 3x3 Women's Basketball Tournament
- FIBA 3x3 U-23 Women's World Cup
- FIBA 3x3 U-18 World Cup
Club Competitions
- FIBA Intercontinental Cup (for top club teams)
- Esports
- EFIBA Esport (for video game basketball)
Current Champions
World Champions
These tables show the most recent winners of major FIBA tournaments.
| Tournament | FIBA World Cup | Year | Next edition | Olympics | Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 2023 | 2027 | 2024 | ||||
| Women | 2022 | 2026 | 2024 | ||||
| U-19 Men | 2025 | 2027 | 2018 | ||||
| U-19 Women | 2023 | 2025 | 2018 | ||||
| U-17 Men | 2024 | 2026 | N/A | ||||
| U-17 Women | 2024 | 2026 | |||||
^ A: The Youth Olympic Games are a U-19 event played in FIBA 3x3 format.
3x3 World Champions
| Tournament | FIBA 3x3 World Cup | Year | Olympics | Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 2025 | 2024 | ||||
| Women | 2025 | 2024 | ||||
| U-23 Men | 2024 | N/A | ||||
| U-23 Women | 2024 | |||||
| U-18 Men | 2024 | |||||
| U-18 Women | 2024 | |||||
World Club Champions
| Club competition | Year | Champion | Score | Runner-up | Next edition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIBA Intercontinental Cup | 2024 | 75–60 | 2025 |
eFIBA Esport World Champions
| Competitions | Year | Champion | Score | Runner-up | Next edition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eFIBA | 2023 | 2024 |
Continental Champions
These are the champions from the different FIBA zones (continents).
| National teams |
FIBA Africa | Year | Next edition | FIBA Americas | Year | Next edition | FIBA Asia | Year | Next edition | FIBA Europe | Year | Next edition | FIBA Oceania | Year | Next edition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 2021 | 2025 | 2022 | 2025 | 2022 | 2025 | 2022 | 2025 | 2015 | N/A | ||||||||||
| Women | 2023 | 2025 | 2023 | 2025 | 2023 | 2025 | 2023 | 2025 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| U-18 Men | 2024 | 2026 | 2024 | 2026 | 2024 | 2026 | 2024 | 2025 | 2023 | 2025 | ||||||||||
| U-18 Women | 2024 | 2026 | 2024 | 2026 | 2024 | 2026 | 2024 | 2025 | 2023 | 2025 | ||||||||||
| U-16 Men | 2023 | 2025 | 2025 | 2027 | 2023 | 2025 | 2024 | 2025 | 2024 | 2026 | ||||||||||
| U-16 Women | 2023 | 2025 | 2025 | 2027 | 2023 | 2025 | 2024 | 2025 | 2024 | 2026 |
^ B: FIBA Oceania no longer conducts senior-level championships for either sex. Since 2017, that region's members have competed for FIBA Asia senior championships. FIBA Oceania continues to hold age-grade championships.
Continental Club Champions
| Region | Competition | Year | Champion | Title | Runner-up | Next edition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men's club competitions | ||||||||
| Africa | Basketball Africa League | 2025 | 1st | 2026 | ||||
| Americas | Basketball Champions League Americas | 2024–25 | 2nd | 2025–26 | ||||
| Liga Sudamericana de Baloncesto | 2024 | 1st | 2025 | |||||
| Asia | Basketball Champions League Asia | 2025 | 1st | 2026 | ||||
| East Asia Super League | 2024–25 | 1st | 2025–26 | |||||
| West Asia Super League | 2024–25 | 2nd | 2025–26 | |||||
| Europe | Basketball Champions League | 2024–25 | 2nd | 2025–26 | ||||
| Europe Cup | 2024–25 | 1st | 2025–26 | |||||
| Euroleague Basketball Next Generation Tournament | 2024–25 | 3rd | 2025–26 | |||||
| Youth Basketball Champions League | 2025 | 2nd | 2026 | |||||
| Women's club competitions | ||||||||
| Africa | Africa Women's Basketball League | 2024 | 3rd | 2025 | ||||
| Americas | Women's Basketball League Americas | 2024 | 2nd | 2025 | ||||
| Liga Sudamericana de Baloncesto Femenino | 2024 | 1st | 2025 | |||||
| Asia | Women's Basketball League Asia | 2024 | Sichuan Yuanda Meile |
1st | 2025 | |||
| Europe | EuroLeague Women (1st-tier) | 2024–25 | 2nd | 2025–26 | ||||
| EuroCup Women (2nd-tier) | 2024–25 | 2nd | 2025–26 | |||||
| SuperCup Women | 2024 | 2nd | 2025 | |||||
^ C: The top-tier European professional basketball club competitions are complex. The EuroLeague run by Euroleague Basketball and its EuroCup are competing with the FIBA Europe organized competitions. The best European clubs have joined the closed league EuroLeague.
Awards
FIBA gives out awards to the best players in its tournaments. Here are some of the most recent Most Valuable Player (MVP) award winners:
Most Valuable Player Awards
| Tournament | Most Recent Awardee | Team | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Dennis Schröder | 2023 | |
| Women | A'ja Wilson | 2022 | |
| U-19 Men | Izan Almansa | 2023 | |
| U-19 Women | Iyana Martín Carrión | 2023 | |
| U-17 Men | Cameron Boozer | 2024 | |
| U-17 Women | Jerzy Robinson | 2024 |
World Rankings
FIBA keeps track of how well national teams perform in competitions. These rankings help show which teams are the strongest in the world.
Men's World Rankings
The table below shows the top 32 men's basketball countries. This number is important because the next FIBA Basketball World Cup is expected to have 32 teams competing.
| Rank | Change | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 784.8 | ||
| 2 | 773.9 | ||
| 3 | 759 | ||
| 4 | 757.9 | ||
| 5 | 756.3 | ||
| 6 | 750.6 | ||
| 7 | 746.2 | ||
| 8 | 743.2 | ||
| 9 | 737.1 | ||
| 10 | 713.1 | ||
| 11 | 703.6 | ||
| 12 | 660.4 | ||
| 13 | 655.7 | ||
| 14 | 641.6 | ||
| 15 | 611.7 | ||
| 16 | 608.4 | ||
| 17 | 607.7 | ||
| 18 | 560.5 | ||
| 19 | 556.3 | ||
| 20 | 537.4 | ||
| 21 | 507.2 | ||
| 22 | 502.7 | ||
| 23 | 465.9 | ||
| 24 | 445.8 | ||
| 25 | 440.9 | ||
| 26 | 432.2 | ||
| 27 | 427.8 | ||
| 28 | 423.3 | ||
| 29 | 420.4 | ||
| 30 | 420.2 | ||
| 31 | 375.5 | ||
| 32 | 374.6 | ||
| *Change from 9 August 2021 | |||
Women's World Rankings
This table shows the top 16 women's basketball countries. The next FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup is expected to have 16 teams.
| Rank | Change | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 834.8 | ||
| 2 | 686 | ||
| 3 | 668.8 | ||
| 4 | 658.1 | ||
| 5 | 653.4 | ||
| 6 | 652.8 | ||
| 7 | 649.2 | ||
| 8 | 598 | ||
| 9 | 594.2 | ||
| 10 | 580.3 | ||
| 11 | 495.1 | ||
| 12 | 490.1 | ||
| 13 | 444.8 | ||
| 14 | 405.5 | ||
| 15 | 378.4 | ||
| 16 | 357.7 | ||
| *Change from 9 August 2021 | |||
FIBA Sponsors
FIBA works with several global partners and suppliers who help support basketball around the world.
FIBA Global Partners
Other Partners
- Global Supplier: Kuehne + Nagel
See also
 In Spanish: Federación Internacional de Baloncesto para niños
In Spanish: Federación Internacional de Baloncesto para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |