Kyoto facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kyoto
京都市
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
From top left: Kiyomizu-dera, Bamboo Forest of Arashiyama, Kinkaku-ji, Dry garden of Ryōan-ji, Katsura Imperial Villa, Senbon torii gates of Fushimi Inari-Taisha, Heian Shrine and Kyoto Imperial Palace
|
|||
|
|||
Location of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Region | Kansai | ||
| Prefecture | Kyoto Prefecture | ||
| Founded | 794 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Mayor–council | ||
| • Body | Kyoto City Assembly | ||
| Area | |||
| • Designated city | 827.83 km2 (319.63 sq mi) | ||
| Highest elevation | 971 m (3,186 ft) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 9 m (30 ft) | ||
| Population
(October 1, 2020)
|
|||
| • Designated city | 1,463,723 | ||
| • Rank | 9th, Japan | ||
| • Density | 1,768.144/km2 (4,579.473/sq mi) | ||
| • Metro | 3,783,014 | ||
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) | ||
| - Tree | Weeping Willow, Japanese Maple and Katsura | ||
| - Flower | Camellia, Azalea and Sugar Cherry | ||
| Kyoto | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

"Kyoto" in kanji
|
|||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||
| Kanji | 京都 | ||||||
|
|||||||
Kyoto (/ˈkjoʊtoʊ/; Japanese: 京都, Kyōto [kʲoꜜːto]), officially Kyoto City (京都市 (Kyōto-shi, [kʲoːtoꜜɕi])), is a famous city in Japan. It is the capital of Kyoto Prefecture and is located on Honshu, Japan's largest island. As of 2020, about 1.46 million people live here.
Kyoto is one of Japan's oldest cities. It became the home of Japan's imperial court in 794. The original city, called Heian-kyō, was designed like ancient Chinese capitals. Japanese emperors ruled from Kyoto for over 1,000 years until 1869. The city was not heavily damaged during World War II, so many old buildings and cultural sites are still preserved.
Today, Kyoto is known as Japan's cultural heart and a top tourist spot. It has many Buddhist temples, Shinto shrines, palaces, and gardens. Some of these are even World Heritage Sites recognized by UNESCO. Famous places include Kiyomizu-dera, Kinkaku-ji, and the Kyoto Imperial Palace. The well-known video game company Nintendo is also based in Kyoto.
Contents
Understanding the Name Kyoto
In Japanese, Kyoto has had several names over time. It was once called Kyō or Miyako, both meaning "capital." When it became the capital in 794, it was named Heian-kyō, meaning "tranquility and peace capital." Later, people just called it "Kyōto," which means "capital city."
After the emperor moved to Edo (which was renamed Tokyo, meaning "eastern capital"), Kyoto was briefly called "Saikyō," meaning "western capital." Because it was Japan's capital for so long (from 794 to 1868), Kyoto is sometimes called the "thousand-year capital."
Kyoto's Rich History
Kyoto's story goes back a long way. People lived in this area even in ancient times. The Shimogamo Shrine is thought to have been built around the 6th century.
Early Beginnings
In the 8th century, Emperor Kanmu decided to move the capital. He wanted to keep the government separate from powerful Buddhist groups in Nara. So, in 794, the new capital, Heian-kyō, was built. It was designed like the Chinese capital Chang'an. This marked the start of the Heian period in Japanese history. Kyoto remained Japan's capital until 1869, even when military leaders ruled from other cities.
Feudal Times and Rebuilding
During the Sengoku period (a time of civil war), Kyoto faced huge destruction in the Ōnin War (1467–1477). Samurai battles filled the streets, and many buildings were burned. The city took a long time to recover.
In the late 1500s, Toyotomi Hideyoshi helped rebuild Kyoto. He added new streets and built earth walls called odoi around the city. He also moved many Buddhist temples to Teramachi Street.
- Gallery
-
Rakuchū rakugai zu, a 16th-century painting of central Kyoto, showing Gion Matsuri floats and Kiyomizu-dera.
Modern Changes
When the emperor moved to Tokyo in 1869, Kyoto's economy struggled. To help the city, the Lake Biwa Canal was built in 1890. Kyoto officially became a modern city on April 1, 1889. By 1932, its population grew to over one million people.
Kyoto in Recent History
During World War II, the United States considered bombing Kyoto with an atomic bomb. However, the Secretary of War, Henry L. Stimson, insisted that Kyoto be saved. As a result, Kyoto was largely spared from bombing. This means many of its old buildings, like traditional machiya townhouses, are still standing.
In 1994, 17 historic sites in Kyoto became UNESCO World Heritage Sites. In 1997, Kyoto hosted a big meeting that led to the Kyoto Protocol, an agreement about reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Kyoto's Location and Weather
City Landscape
Kyoto is in a valley called the Yamashiro Basin. Mountains surround it on three sides: Higashiyama, Kitayama, and Nishiyama. These mountains can be up to 1,000 meters high. This location means Kyoto has hot, humid summers and cold winters with some snow.
Three rivers flow through the basin: the Uji River, the Katsura River, and the Kamo River. Kyoto City covers about 827.9 square kilometers. The city also has a large natural water supply underground.
Kyoto's Climate
Kyoto has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has clear changes in temperature and rainfall throughout the year. Summers are hot and humid. Winters are cold, with occasional snowfall.
The East Asian rainy season usually starts in mid-June and ends in late July. After that, summer becomes hot and sunny. Like many parts of Japan, Kyoto can experience typhoons in summer and autumn.
| Climate data for Kyoto (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1880−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.9 (67.8) |
22.9 (73.2) |
25.7 (78.3) |
30.7 (87.3) |
34.9 (94.8) |
36.8 (98.2) |
39.8 (103.6) |
39.8 (103.6) |
38.1 (100.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
26.9 (80.4) |
22.8 (73.0) |
39.8 (103.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.1 (48.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
14.1 (57.4) |
20.1 (68.2) |
25.1 (77.2) |
28.1 (82.6) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
29.2 (84.6) |
23.4 (74.1) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.8 (40.6) |
5.4 (41.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
14.4 (57.9) |
19.5 (67.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
28.5 (83.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
18.4 (65.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.2 (45.0) |
16.2 (61.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
1.6 (34.9) |
4.3 (39.7) |
9.2 (48.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.2 (66.6) |
23.6 (74.5) |
24.7 (76.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
14.4 (57.9) |
8.4 (47.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −11.9 (10.6) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
4.9 (40.8) |
10.6 (51.1) |
11.8 (53.2) |
7.8 (46.0) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 53.3 (2.10) |
65.1 (2.56) |
106.2 (4.18) |
117.0 (4.61) |
151.4 (5.96) |
199.7 (7.86) |
223.6 (8.80) |
153.8 (6.06) |
178.5 (7.03) |
143.2 (5.64) |
73.9 (2.91) |
57.3 (2.26) |
1,522.9 (59.96) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 5 (2.0) |
7 (2.8) |
1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2 (0.8) |
15 (5.9) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 8.1 | 8.9 | 11.2 | 10.6 | 10.8 | 13.2 | 12.6 | 9.3 | 11.1 | 9.4 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 120.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67 | 65 | 61 | 59 | 60 | 66 | 69 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 68 | 68 | 65 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 123.5 | 122.2 | 155.4 | 177.3 | 182.4 | 133.1 | 142.7 | 182.7 | 142.7 | 156.0 | 140.7 | 134.4 | 1,793.1 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
City Layout and Districts
Kyoto has about 2,000 temples and shrines. The main business area is south of the Kyoto Imperial Palace. In the city center, you can find covered shopping streets like Teramachi Street and Shinkyōgoku Street.
The old city was planned using Chinese feng shui ideas. The Imperial Palace faced south. This meant the "right sector" (Ukyō) was on the west, and the "left sector" (Sakyō) was on the east. Even today, many streets in the central areas follow a grid pattern.
Kyoto City is divided into eleven areas called ku (wards). The central wards are smaller and have more people. The city hall is in Nakagyō-ku.
Population and People
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1873 | 238,663 | — |
| 1889 | 279,165 | +17.0% |
| 1900 | 371,600 | +33.1% |
| 1910 | 470,033 | +26.5% |
| 1920 | 736,462 | +56.7% |
| 1925 | 860,878 | +16.9% |
| 1930 | 987,777 | +14.7% |
| 1935 | 1,117,439 | +13.1% |
| 1940 | 1,127,870 | +0.9% |
| 1945 | 1,041,700 | −7.6% |
| 1950 | 1,130,185 | +8.5% |
| 1955 | 1,229,808 | +8.8% |
| 1960 | 1,295,012 | +5.3% |
| 1965 | 1,374,159 | +6.1% |
| 1970 | 1,427,376 | +3.9% |
| 1975 | 1,468,833 | +2.9% |
| 1980 | 1,473,065 | +0.3% |
| 1985 | 1,486,402 | +0.9% |
| 1990 | 1,461,103 | −1.7% |
| 1995 | 1,470,902 | +0.7% |
| 2000 | 1,467,785 | −0.2% |
| 2005 | 1,474,811 | +0.5% |
| 2010 | 1,474,015 | −0.1% |
| 2015 | 1,475,183 | +0.1% |
| 2020 | 1,463,723 | −0.8% |
Kyoto was once the biggest city in Japan. Its population was later passed by Osaka and Edo. After World War II, it was the third-largest city in 1947. Today, it is the ninth-largest city in Japan.
More than half of all people in Kyoto Prefecture live in Kyoto City. This is the highest percentage for any city in Japan.
Kyoto's Economy and Industries

Technology and electronics are very important to Kyoto's economy. Many big companies have their main offices here. These include Nintendo, Omron, Kyocera, and Shimadzu.
Tourism also brings a lot of money to Kyoto. Many people from Japan and other countries visit the city. Traditional Japanese crafts are a big industry too. Kyoto is famous for its kimono weavers. Sake brewing is another important traditional business.
Learning and Education
Kyoto is a major center for education in Japan. It has 40 colleges and universities. Kyoto University is one of the top universities in the country. Many famous scientists and even two Prime Ministers of Japan have studied there.
Other well-known private universities like Doshisha University and Ritsumeikan University are also in Kyoto. There are also programs for students from other countries to study Japanese language and culture.
Getting Around Kyoto
Train Travel

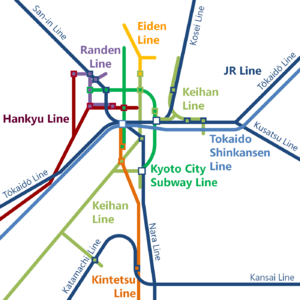
Kyoto has a great train system. Kyōto Station is the main hub. You can catch the Tokaido Shinkansen (bullet train) here. It connects Kyoto to cities like Nagoya, Yokohama, and Tokyo in the east. It also connects to Osaka and other cities like Kobe and Fukuoka in the west.
Many other train lines run through Kyoto. These include lines from JR West, Kintetsu Railway, Keihan Electric Railway, and Hankyu Railway. These lines connect Kyoto to nearby cities and suburbs. If you fly into Kansai International Airport, a special train called Haruka can take you to Kyoto Station in about 73 minutes.
The Kyoto Railway Museum shows many old and new trains used in Japan.
Subway System
Kyoto has a subway system with two lines: the Karasuma Line and the Tōzai Line. They meet at Karasuma Oike Station in the city center.
The Karasuma Line runs north to south. It connects to other train lines at Kyoto Station. The Tōzai Line runs east to west through downtown Kyoto. It also connects to other train lines.
Tramways
Kyoto also has tram lines, which are like streetcars. These include the Eizan Electric Railway and the Keifuku Electric Railroad.
Buses and Roads
Kyoto has a large bus network. Both city buses and private buses operate here. Many tourists use the buses to get around. Bus stops often have announcements and signs in English.
Many older streets in Kyoto are narrow. This means they are often one-way and don't have sidewalks. Cycling is a popular way to get around. Kyoto has several national highways and expressways that connect it to other parts of Japan.
Kyoto's Unique Culture

Kyoto is known as Japan's cultural heart. It has many National Treasures and Important Cultural Properties. The Japanese government even moved its Agency for Cultural Affairs to Kyoto in 2023.
The city has about 2,000 religious sites. These include 1,600 Buddhist temples and 400 Shinto shrines. Many palaces and gardens are also well-preserved. Famous temples include Kiyomizu-dera (a wooden temple on a mountain slope), Kinkaku-ji (the Golden Pavilion), and Ginkaku-ji (the Silver Pavilion). Ryōan-ji is famous for its rock garden.
The Heian Jingū is a Shinto shrine built in 1895. It honors the imperial family. Important imperial sites include the Kyoto Imperial Palace, Katsura Imperial Villa, and Shugakuin Imperial Villa.
Other popular spots are Arashiyama (a bamboo forest), the Gion and Ponto-chō geisha areas, and the Philosopher's Walk.
World Heritage Sites
The "Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto" are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This list includes 14 temples, shrines, and castles in Kyoto. They date from the 6th to the 17th centuries.
Food and Entertainment
Kyoto is famous for its delicious food. Because it's not by the sea and has many Buddhist temples, it developed special local vegetables called kyō-yasai. The oldest restaurant in Kyoto, Honke Owariya, opened in 1465.
Kyoto is also a center for Japan's TV and film industry. Many jidaigeki (samurai action films) are shot at Toei Uzumasa Eigamura. This is a film set and theme park where you can see traditional Japanese buildings. Sometimes, you can even watch movies being filmed!
The local way of speaking in Kyoto is called Kyō-kotoba or Kyōto-ben. It was once the standard Japanese language.
Festivals and Celebrations
Kyoto is well-known for its traditional festivals. Some have been held for over 1,000 years! They are a big draw for tourists.
- The Aoi Matsuri is held on May 15.
- The Gion Matsuri in July is one of Japan's three greatest festivals. It ends with a huge parade on July 17.
- During the Bon Festival, Kyoto celebrates with the Gozan no Okuribi. Fires are lit on mountains to guide spirits home (August 16).
- The Jidai Matsuri, or Festival of the Ages, on October 22, celebrates Kyoto's long and famous history.
Museums to Explore
Kyoto has many interesting museums. Here are a few:
- Kyoto International Manga Museum (for manga fans!)
- Kyoto Botanical Garden (a beautiful place to see plants)
- Kyoto National Museum (for Japanese art and history)
- Kyoto Railway Museum (for train lovers)
- Toei Kyoto Studio Park (where movies are made)
Sports in Kyoto

Kyoto hosts many sports events. These range from the 400-year-old Tōshiya archery competition to the Kyoto Marathon.
The city has professional sports teams. The Kyoto Sanga FC is a professional soccer team. They won the Emperor's Cup in 2002. The Kyoto Hannaryz is a professional basketball team. They play in the B.League.
Kyoto Racecourse is one of Japan's major horse racing tracks. It hosts important races like the Kikuka-shō.
Global Connections
Kyoto has "sister-city" relationships with several cities around the world. These partnerships help foster friendship and cooperation.
- Boston, United States
- Cologne, Germany
- Florence, Italy
- Guadalajara, Mexico
- Kyiv, Ukraine
- Prague, Czech Republic
- Xi'an, China (a friendship city)
- Zagreb, Croatia
Kyoto also has "partner cities." These partnerships focus on specific areas of cooperation.
See also
 In Spanish: Kioto para niños
In Spanish: Kioto para niños
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |