Mecklenburg County, North Carolina facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Mecklenburg County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Uptown Charlotte skyline
Old Mecklenburg County Courthouse
First Presbyterian Church
Pineville Historic District
President James K. Polk Historic Site
Charlotte Research Institute campus at UNC Charlotte
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Meck County
|
|||
Location within the U.S. state of North Carolina
|
|||
 North Carolina's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | December 11, 1762 | ||
| Named for | Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz | ||
| Seat | Charlotte | ||
| Largest municipality | Charlotte | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 546.09 sq mi (1,414.4 km2) | ||
| • Land | 523.61 sq mi (1,356.1 km2) | ||
| • Water | 22.48 sq mi (58.2 km2) 4.12% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 1,115,482 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
1,163,701 |
||
| • Density | 2,042.671/sq mi (788.680/km2) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Mecklenburger | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| Congressional districts | 12th, 14th | ||
Mecklenburg County is a county in the southwestern part of North Carolina, in the United States. It was named after Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, who was the Queen of the United Kingdom. Her name came from the Mecklenburg region in Germany, meaning "large castle."
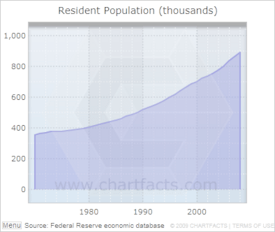
As of 2020, over 1.1 million people live here. This makes it the second-most populated county in North Carolina. It was also the first county in the Carolinas to have more than a million people. The main city and county seat is Charlotte, which is the largest city in North Carolina. Mecklenburg County is also the center of the larger Charlotte-Concord-Gastonia metropolitan area.
Contents
- History of Mecklenburg County
- Geography of Mecklenburg County
- Population and People
- Economy and Jobs
- Transportation in Mecklenburg County
- Education in Mecklenburg County
- Healthcare Services
- Arts and Culture
- Communities of Mecklenburg County
- Notable People from Mecklenburg County
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Mecklenburg County
Mecklenburg County was created in 1762 by English colonists. It was formed from the western part of Anson County. The county was named to honor the marriage of King George III to Queen Charlotte. The city of Charlotte is also named after her.
At first, the county's borders were not clear. Some areas that are now part of South Carolina were once considered part of Mecklenburg County. In 1768, a large western part of Mecklenburg County became Tryon County. Over the years, more parts of Mecklenburg County were used to form other counties. In 1792, Cabarrus County was created from its northeastern part. Later, in 1842, Union County was formed from its southeastern part and part of Anson County.
Important Declarations and Gold Rush
The Mecklenburg Declaration of Independence was supposedly signed on May 20, 1775. If it is real, Mecklenburg County was the first place in the Thirteen Colonies to declare independence from Great Britain. The "Mecklenburg Resolves" were adopted on May 31, 1775. Mecklenburg County still celebrates this declaration every May. The date is even on the flag of North Carolina.
The first gold rush in the United States happened nearby. A 12-year-old boy found a gold nugget in a stream in Cabarrus County. This led many miners and merchants to settle in Mecklenburg County. The first U.S. branch mint was built in Charlotte in 1837. It made coins until 1913. The original building is now a museum.
Growth and Development
During World War I in 1917, Camp Greene was set up west of Charlotte as an army training camp. It closed after the war in 1919. In the 1930s and 1940s, the county's population grew quickly. New places like Carolinas Medical Center and Charlotte College (now University of North Carolina at Charlotte) were built. Lake Norman was finished in 1964 after five years of building.
The county kept growing fast in the mid-1900s. Many new government buildings were constructed. Charlotte Douglas International Airport was also made bigger in 1954. By 1960, a quarter-million people lived in the county. By 1990, the population reached half a million. Today, the Charlotte metropolitan area includes 11 counties in North and South Carolina. It had an estimated population of over 2.8 million people in 2023.
In 2020, a large gasoline leak happened from the Colonial Pipeline near Huntersville. About 2 million gallons of gasoline leaked. This was one of the biggest gasoline spills in U.S. history. Cleanup efforts are still ongoing.
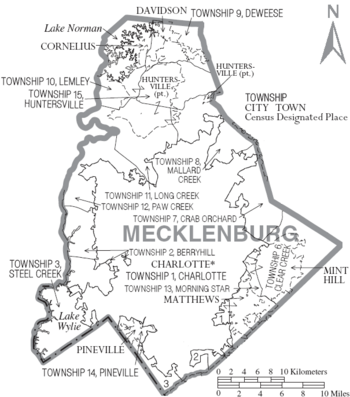
Geography of Mecklenburg County
Mecklenburg County covers about 546 square miles. Most of this area, about 523 square miles, is land. The rest, about 22 square miles, is water.
Protected Areas and Sites
Mecklenburg County has many protected areas and historical sites. These include:
- Carolina Raptor Center
- Charlotte Museum of History
- Historic Latta Place
- Little Sugar Creek Greenway
- Mint Museum Randolph (in the old Charlotte Mint building)
- Mint Museum Uptown
- President James K. Polk Historic Site
There are also several nature preserves in Charlotte:
- Auten Nature Preserve
- Big Rock Nature Preserve
- Latta Nature Preserve
- McDowell Nature Preserve
- Reedy Creek Nature Preserve
Major Water Bodies
Important rivers and lakes in the county include:
Neighboring Counties
Mecklenburg County shares borders with these counties:
- Iredell County (north)
- Cabarrus County (northeast)
- Union County (southeast)
- Lancaster County, South Carolina (south)
- York County, South Carolina (southwest)
- Gaston County (west)
- Lincoln County (northwest)
Population and People
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 11,395 | — | |
| 1800 | 10,439 | −8.4% | |
| 1810 | 14,272 | 36.7% | |
| 1820 | 16,895 | 18.4% | |
| 1830 | 20,073 | 18.8% | |
| 1840 | 18,273 | −9.0% | |
| 1850 | 13,914 | −23.9% | |
| 1860 | 17,374 | 24.9% | |
| 1870 | 24,299 | 39.9% | |
| 1880 | 34,175 | 40.6% | |
| 1890 | 42,673 | 24.9% | |
| 1900 | 55,268 | 29.5% | |
| 1910 | 67,031 | 21.3% | |
| 1920 | 80,695 | 20.4% | |
| 1930 | 127,971 | 58.6% | |
| 1940 | 151,826 | 18.6% | |
| 1950 | 197,052 | 29.8% | |
| 1960 | 272,111 | 38.1% | |
| 1970 | 354,656 | 30.3% | |
| 1980 | 404,270 | 14.0% | |
| 1990 | 511,433 | 26.5% | |
| 2000 | 695,454 | 36.0% | |
| 2010 | 919,628 | 32.2% | |
| 2020 | 1,115,482 | 21.3% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 1,163,701 | 26.5% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 |
|||
In 2020, Mecklenburg County had 1,115,482 people. There were 426,313 households and 254,759 families living in the county. The population is very diverse, with people from many different backgrounds.
Economy and Jobs
The main industries in Mecklenburg County are banking, manufacturing, and professional services. These services often support banking and medicine. Many large companies have their headquarters here. For example, Bank of America, Nucor (a steel company), and Duke Energy (an electric power company) are based in Mecklenburg County.
The largest employers in the county include Atrium Health (healthcare), Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools (education), and Bank of America. Other big employers are American Airlines, Harris Teeter (a grocery store), and Duke Energy.
Transportation in Mecklenburg County
Mecklenburg County has many ways to get around, from air travel to trains and buses.
Air Travel
The main airport for the county is Charlotte Douglas International Airport. It is located in Charlotte.
Train Services
Mecklenburg County is a busy place for freight trains. This is because it's on a major train line between Washington and Atlanta.
Three Amtrak passenger train routes serve Mecklenburg County daily:
- The Crescent connects Charlotte to cities like New York, Philadelphia, Washington D.C., and Atlanta.
- The Carolinian connects Charlotte to New York, Washington D.C., and Raleigh.
- The Piedmont connects Charlotte to Raleigh, Durham, and Greensboro.
The main train station is at 1914 North Tryon Street. A new station, Gateway Station, is planned. It will include light rail, a bus station, and the Crescent train line. There are also plans for a high-speed rail line connecting Charlotte to Washington, D.C.
Local Transit
LYNX Rapid Transit Services provides light rail service. The Lynx Blue Line runs for about 19 miles. It goes from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte, through Uptown Charlotte, to Pineville. The CityLynx Gold Line is a streetcar line. It runs through Uptown Charlotte.
The Charlotte Area Transit System (CATS) offers bus service. It covers all of Mecklenburg County, including Charlotte and nearby towns. There are also plans for a new light rail line, the Lynx Silver Line. This line would connect Charlotte to surrounding towns like Belmont and Matthews.
Freight Transport
Mecklenburg County is a major hub for the trucking industry. This is due to its manufacturing base and its central location. The Inland Port of Charlotte is also here. It is a key rail corridor for freight.
Major Roads
Many important highways run through Mecklenburg County:
 I-77
I-77 I-85
I-85 I-277
I-277 I-485
I-485 US 21
US 21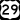 US 29
US 29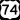 US 74
US 74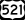 US 521
US 521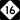 NC 16
NC 16 NC 24
NC 24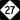 NC 27
NC 27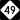 NC 49
NC 49 NC 51
NC 51 NC 73
NC 73 NC 115
NC 115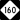 NC 160
NC 160 NC 218
NC 218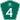 Charlotte Route 4
Charlotte Route 4
Education in Mecklenburg County
School System
The Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools (CMS) system serves all of Mecklenburg County. North Carolina also has approved several charter schools in the county. These are independently run schools funded by taxes.
Colleges and Universities
Mecklenburg County is home to many colleges and universities:
- Central Piedmont Community College
- Davidson College
- Johnson C. Smith University
- Johnson & Wales University
- Pfeiffer University
- Queens University of Charlotte
- Union Presbyterian Seminary
- University of North Carolina at Charlotte
- Wake Forest University Charlotte Center
Libraries
The Public Library of Charlotte and Mecklenburg County serves all residents. You can use a library card from any of its 20 locations. The library has over 1.5 million items, including books, DVDs, and audiobooks.
The Billy Graham Library holds papers and items related to the famous evangelist, Billy Graham.
Healthcare Services
Mecklenburg County has two main healthcare providers: Atrium Health and Novant Health. Together, they offer 14 emergency departments. These include special emergency departments for mental health and for children. Two hospitals in the area provide trauma services. Atrium Health is the county's public hospital authority.
MEDIC, the Mecklenburg EMS Agency, provides emergency medical services. They handle all emergency ambulance calls in the county. In 2024, MEDIC responded to over 157,000 calls.
Arts and Culture
Mecklenburg County offers many cultural and entertainment options.
Museums and Libraries
- Bechtler Museum of Modern Art
- Billy Graham Library
- Carolinas Aviation Museum
- Charlotte Museum of History
- Charlotte Nature Museum
- Discovery Place
- Discovery Place Kids-Huntersville
- Harvey B. Gantt Center for African-American Arts + Culture
- ImaginOn
- Levine Museum of the New South
- Mint Museum Randolph
- Mint Museum Uptown
- NASCAR Hall of Fame
- Public Library of Charlotte and Mecklenburg County
Sports and Entertainment
The county is home to several professional sports teams and venues:
- Carolina Panthers (NFL football)
- Charlotte Hornets (NBA basketball)
- Charlotte FC (MLS soccer)
- Charlotte Checkers (AHL hockey)
- Charlotte Knights (Minor League Baseball)
- Charlotte Motor Speedway (NASCAR racing)
- Bank of America Stadium
- Truist Field
Music and Performing Arts
- Actor's Theatre of Charlotte
- Bojangles' Coliseum
- ImaginOn
- Knight Theater
- North Carolina Blumenthal Performing Arts Center
- Ovens Auditorium
- PNC Music Pavilion
- Spectrum Center
Amusement Parks
- Carowinds
- Great Wolf Lodge (in nearby Cabarrus County)
- Ray's Splash Planet
Other Attractions
- Carolina Place Mall
- Carolina Raptor Center
- Concord Mills Mall (in nearby Cabarrus County)
- Lake Norman
- Lake Wylie
- Little Sugar Creek Greenway
- President James K. Polk Historic Site
- SouthPark Mall
- U.S. National Whitewater Center
Communities of Mecklenburg County
Mecklenburg County has seven main towns and cities. These include the City of Charlotte and the towns of Cornelius, Davidson, and Huntersville to the north. To the south and southeast are Matthews, Mint Hill, and Pineville. A small part of Stallings is also in Mecklenburg County.
City
- Charlotte (the county seat and largest city)
Towns
Unincorporated Communities
These are areas that are not part of any city or town:
Notable People from Mecklenburg County
Many famous people have come from Mecklenburg County:
- Nathaniel Alexander (1756–1808), a U.S. Congressman and governor of North Carolina.
- Romare Bearden (1911–1988), a famous African-American artist.
- Brigadier General William Lee Davidson (1746–1781), a general during the American Revolutionary War.
- Ric Flair (born 1949), a retired professional wrestler.
- Anthony Foxx (born 1971), a former U.S. Secretary of Transportation and mayor of Charlotte.
- Billy Graham (1918–2018), a world-famous speaker.
- Anthony Hamilton (born 1971), an American R&B/soul singer.
- James K. Polk (1795–1849), the 11th president of the United States. He was born in Mecklenburg County.
- Shannon Spake (born 1976), an ESPN sports reporter.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Mecklenburg (Carolina del Norte) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Mecklenburg (Carolina del Norte) para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |