Eiffel Tower facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Eiffel Tower |
|
|---|---|
|
Tour Eiffel (French)
|
|

Seen from the Champ de Mars
|
|
| Record height | |
| Tallest in the world from 1889 to 1930 | |
| Preceded by | Washington Monument |
| Surpassed by | Chrysler Building |
| General information | |
| Type | Observation tower Broadcasting tower |
| Location | 7th arrondissement, Paris, France |
| Coordinates | 48°51′29.6″N 2°17′40.2″E / 48.858222°N 2.294500°E |
| Construction started | 28 January 1887 |
| Completed | 31 March 1889 |
| Opening | 15 May 1889 |
| Owner | City of Paris, France |
| Management | Société d'Exploitation de la Tour Eiffel (SETE) |
| Height | |
| Architectural | 300 m (984 ft) |
| Tip | 330 m (1,083 ft) |
| Top floor | 276 m (906 ft) |
| Technical details | |
| Floor count | 4 (3 accessible, 1 residual) |
| Lifts/elevators | 8 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect | Stephen Sauvestre |
| Structural engineer | Maurice Koechlin Émile Nouguier |
| Main contractor | Compagnie des Etablissements Eiffel |
|
Monument historique
|
|
| Official name | Tour Eiffel |
| Type | Classé |
| Designated | 1964 |
| References | |
| I. | |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Part of | Paris, Banks of the Seine |
| Criteria | Cultural: i, ii, iv |
| Inscription | 1991 (15th Session) |
The Eiffel Tower (pronounced EYE-fuhl) is a famous wrought-iron tower in Paris, France. It stands on the Champ de Mars and is named after Gustave Eiffel. His company designed and built the tower between 1887 and 1889.
Locally, people call it "La dame de fer" (which means "Iron Lady"). It was built for the 1889 World's Fair. This fair celebrated 100 years since the French Revolution. At first, some artists didn't like its design. But now, it's a global symbol of France. It's one of the most recognized buildings in the world.
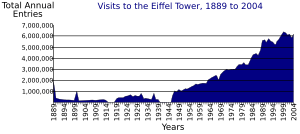
The tower is very popular. In 2022, almost 6 million people visited it. It's the most visited monument in the world that charges an entrance fee. In 2015, over 6.9 million people went up the tower. In 1964, it became a French historical monument. In 1991, it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list.
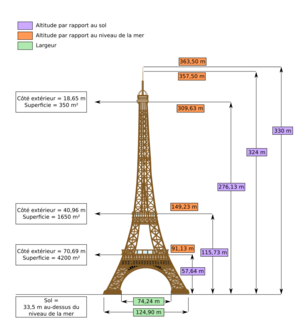
The Eiffel Tower is about 330 meters (1,083 feet) tall. This is like an 81-story building. It's the tallest structure in Paris. Its base is square, with each side measuring 125 meters (410 feet). When it was built, it was the tallest human-made structure. It held this record for 41 years. The Chrysler Building in New York City became taller in 1930.
The tower has three levels for visitors. There are restaurants on the first and second levels. The top level's platform is 276 meters (906 feet) high. This is the highest public observation deck in the European Union. You can buy tickets to go up by stairs or lift. Climbing to the first level takes over 300 steps. From the first to the second level is another 300 steps. The top level is usually only reached by lift. On the third level, there's a private apartment. Gustave Eiffel built it for himself. He invited friends like Thomas Edison there.
Contents
History of the Eiffel Tower
How the Tower Began
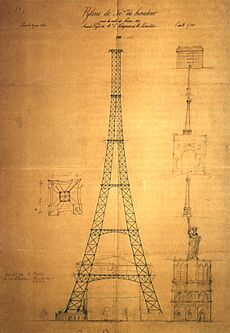
Maurice Koechlin and Émile Nouguier first designed the Eiffel Tower. They were engineers for Gustave Eiffel's company. They imagined it as a centerpiece for the 1889 World's Fair. This fair celebrated 100 years of the French Revolution. In 1884, Koechlin sketched their idea. He described it as a "great pylon" with four lattice girders.
Eiffel wasn't very excited at first. But he allowed more studies. The engineers then asked Stephen Sauvestre to help. Sauvestre was the head architect. He added decorative arches to the base. He also designed a glass pavilion for the first level.
This new design won Eiffel's support. He bought the rights to the design. It was shown at an exhibition in 1884. In 1885, Eiffel presented his plans. He said the tower would show "the art of the modern engineer." It would also represent the "century of Industry and Science." He said it would express France's thanks for the 1789 Revolution.
In 1886, the project moved forward. A competition was held for the fair's centerpiece. It basically ensured Eiffel's design would be chosen. Entries had to include a 300-meter metal tower. A commission reviewed the plans. They found Eiffel's design was the only practical one.
A contract was signed in January 1887. Eiffel received 1.5 million francs for construction. This was less than a quarter of the total cost. He would get all income from the tower during the fair and for 20 years after. He later created a company to manage the tower.
Artists' Protest Against the Tower
Many people debated the tower's design. Some thought it was impossible to build. Others disliked it for artistic reasons. No one had ever built a structure 300 meters tall before. A group called the "Committee of Three Hundred" formed. They protested the tower. Famous artists like Charles Garnier and Guy de Maupassant were part of it.
They sent a petition to the Minister of Works. It was published in a newspaper in 1887. They called the tower "useless and monstrous." They imagined it "crushing" Paris's beautiful monuments. They said it would be a "ghastly dream."
Gustave Eiffel replied to these critics. He compared his tower to the Egyptian pyramids. He asked, "Why would something admirable in Egypt become hideous and ridiculous in Paris?" The Minister of Trade, Édouard Lockroy, also supported Eiffel. He said the protest was too late. Construction had already begun.
Some protesters changed their minds after the tower was built. Others never did. It's said that Guy de Maupassant ate lunch in the tower's restaurant every day. He did this because it was the only place in Paris where he couldn't see the tower.
By 1918, the tower became a symbol of France. Guillaume Apollinaire wrote a poem shaped like the tower. Today, it's seen as a remarkable piece of art. It often appears in movies and books.
Building the Giant Tower

Construction of the foundations began on January 28, 1887. The east and south legs were simple. Each rested on four concrete slabs. The west and north legs were closer to the Seine river. They needed deeper foundations. Workers used compressed-air caissons to install piles. These piles supported thick concrete slabs.
The foundations were finished on June 30. Then, the ironwork began. A lot of detailed work happened behind the scenes. The drawing office made 1,700 general drawings. They also made 3,629 detailed drawings for 18,038 different parts. Precision was key. Rivet holes were specified to within 1 millimeter.
Parts arrived from a factory in Levallois-Perret. They were first bolted together. Then, bolts were replaced with rivets. No drilling or shaping was done on site. If a part didn't fit, it went back to the factory. In total, 18,038 pieces were joined. They used 2.5 million rivets.
At first, the legs were built like cantilevers. Halfway to the first level, construction paused. A large wooden scaffold was built. This made some people worry about the tower's safety. Newspapers even printed silly headlines. Small "creeper" cranes were installed in each leg. They moved up the tower as it grew.
Joining the legs at the first level was a big step. It was finished by March 1888. Workers used hydraulic jacks to align the legs perfectly. Despite the huge project, only one person died during construction. This was due to Eiffel's strong safety rules.
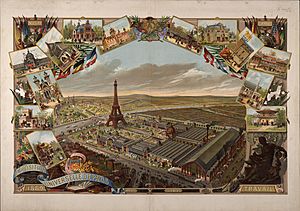
Opening Day and the 1889 World's Fair
The main structure was finished in March 1889. On March 31, Eiffel celebrated. He led officials and reporters to the top. The lifts weren't ready, so they walked. It took over an hour. Eiffel explained different parts of the tower.
Most people stopped at lower levels. But a few, including Eiffel, reached the top. At 2:35 PM, Eiffel raised a large French flag. A 25-gun salute fired from the first level.
The tower opened to the public nine days after the fair began on May 6. The lifts were still not ready. Almost 30,000 visitors climbed the 1,710 steps to the top. The lifts started working on May 26. By the end of the exhibition, nearly 1.9 million people had visited.
At night, hundreds of gas lamps lit the tower. A beacon sent out red, white, and blue light beams. Searchlights lit up other buildings at the fair. A cannon at the top announced the fair's daily opening and closing.
The French newspaper Le Figaro had an office on the second level. They printed a special souvenir edition there. At the top, there was a post office. Visitors could send postcards from there. Gustave Eiffel even collected visitors' written impressions. He called them "truly curious."
Famous visitors included the Prince of Wales and Thomas Edison. Eiffel invited Edison to his private apartment. Edison gave him a phonograph, a new invention. Edison wrote a message in the guestbook. He praised Eiffel as a "brave builder."
Eiffel used his apartment for science. He made weather observations. He also did experiments on how air affects falling objects.
Later Years and Changes
Eiffel's permit for the tower was for 20 years. It was supposed to be taken down in 1909. But the tower became useful for new technologies. Especially for radio telegraphy. So, it was allowed to stay. From 1910, it also helped with the International Time Service.
For the 1900 World's Fair, new lifts were installed. These lifts went to the second level. They had a special system to keep the floor level. The original lift in the north pillar was replaced by stairs.
In 1901, Alberto Santos-Dumont flew his airship around the tower. He won a 100,000-franc prize for it.
From 1910, the tower sent time signals to ships. This helped unify Universal Time. In 1912, a conference about radio time was held. This led to the creation of the International Time Bureau.
In 1910, Theodor Wulf measured radiant energy at the tower. He found more at the top than expected. This led to the discovery of cosmic rays. In 1912, Franz Reichelt died trying to test a parachute from the first level.
During World War I, the tower's radio station was very important. In 1914, it jammed German radio messages. This helped France win the First Battle of the Marne. In 1917, it intercepted a coded message. This helped catch Mata Hari, a famous spy.
From 1925 to 1934, Citroën car ads lit up three sides of the tower. It was the tallest advertising space then. In 1935, the tower was used for early television broadcasts.

In 1925, a con artist named Victor Lustig "sold" the tower for scrap metal twice! In 1926, pilot Leon Collet died trying to fly under the tower. His plane got caught in a radio aerial. In 1930, the tower lost its title as the world's tallest structure. The Chrysler Building was finished.
When Germany occupied Paris in 1940, the French cut the lift cables. German soldiers had to climb the tower to raise their flag. Hitler ordered the tower to be destroyed in 1944. But General Dietrich von Choltitz disobeyed the order. French forces later replaced the German flag with the French Tricolour.
A fire damaged the top of the tower in 1956. Repairs took a year. In 1957, a new radio aerial was added. In 1964, the tower became a historical monument.
In 1982, the old lifts to the third level were replaced. The new ones were faster. In 1983, a new lift was added for the Jules Verne restaurant. The lifts in the east and west legs were updated in 1986.

In 1984, Robert Moriarty flew a plane under the tower. In 1987, A. J. Hackett did one of his first bungee jumps from the tower. He was arrested by police.
For the "Countdown to the Year 2000" party, flashing lights were added. They sparkled for five minutes every hour at night. These sparkling lights were turned on again in 2003.
The tower welcomed its 200 millionth visitor in 2002. Since 2003, it has hosted about 7 million visitors each year. In 2004, a seasonal ice rink was added to the first level. A glass floor was installed on the first level during a 2014 renovation.
Tower Design and Features
Materials Used
The Eiffel Tower is made of 7,300 tons of wrought iron. With lifts, shops, and antennas, its total weight is about 10,100 tons. The top of the tower can move up to 18 centimeters (7 inches) away from the sun. This happens because the metal expands when it gets hot.
Wind and Weather
When it was built, some thought Eiffel ignored engineering rules. But Eiffel and his team were expert bridge builders. Eiffel said that the tower's curved shape was chosen for strength. It was designed to resist wind. He believed this also made it beautiful.
Eiffel used special methods to ensure the tower's strength. He made sure all parts could handle strong winds. The tower sways up to 9 centimeters (3.5 inches) in the wind.
Levels of the Tower
Ground Floor Access
Each of the tower's four legs has stairs and lifts. These go to the first two floors. The south leg's lift goes to the second-floor restaurant.
First Floor Fun
The first floor is open to everyone. You can reach it by lift or stairs. When first built, it had three restaurants and a bar. Today, it has the Le 58 Tour Eiffel restaurant and other shops.
Second Floor Views
The second floor is also open to visitors. It has a famous restaurant called Le Jules Verne. This fancy restaurant has its own lift from the south leg. It's named after the science-fiction writer Jules Verne.
Third Floor Top
The third floor is the highest level. You can only reach it by lift.
Originally, this floor had laboratories for experiments. Gustave Eiffel also had a small private apartment here. It's now open to the public. It's decorated with old furniture and lifelike figures of Eiffel and his guests.
From 1937 to 1981, there was a restaurant near the top. It was removed because it was too heavy. Today, there is a champagne bar on the third floor.
Lifts to the Top
The lifts have changed over the years. A round trip usually takes about 8 minutes and 50 seconds. The original hydraulic machinery is on display at the base of the east and west legs.
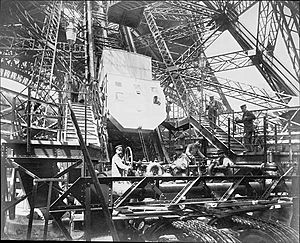
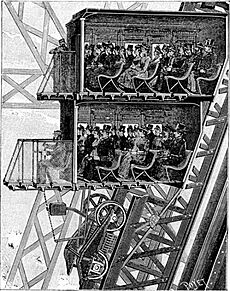
Building safe lifts was a big challenge. For the first level, the legs were wide enough for straight tracks. A French company, Roux, Combaluzier & Lepape, installed two lifts. They used endless chains to push the cars up.
Lifts to the second level were harder. A straight track wasn't possible. An American company, Otis Brothers & Company, got the contract. Their lifts had two compartments, each holding 25 passengers. They used a hydraulic system powered by water.
The original lifts for the second to third levels were from Léon Edoux. They used hydraulic rams. Passengers had to switch lifts halfway up.
Names Engraved on the Tower
Gustave Eiffel had the names of 72 French scientists, engineers, and mathematicians engraved on the tower. He did this to honor their work. He wanted to show the tower was a symbol of science. These engravings were painted over in the early 1900s. But they were restored in 1986–87.
How the Tower Looks
The tower is painted in three shades of brown. It's lighter at the top and darker at the bottom. This helps it blend with the Parisian sky. It was first reddish-brown. In 1968, it changed to "Eiffel Tower Brown." For the 2024 Summer Olympics in Paris, it was painted gold.
After the 2024 Olympics, the Mayor of Paris suggested keeping the Olympic rings on the tower. The rings are 95 feet wide and 43 feet high. This idea has caused some debate.
The four decorative arches at the base are not structural. They were added to make the tower look grander. They also created an impressive entrance to the fair.
In movies, you often see the Eiffel Tower from Parisian windows. In real life, most buildings in Paris are not tall enough to have a clear view.
Keeping the Tower Strong
The tower needs a lot of care. Workers apply 60 tons of paint every 7 years. This prevents it from rusting. The tower has been repainted at least 19 times. The most recent repaint was in 2010.
Communications Hub
The tower has been used for radio since the early 1900s. In 1909, a permanent underground radio center was built. In 1913, the tower exchanged wireless signals with the US. This helped measure the distance between Paris and Washington, D.C. Today, the Eiffel Tower sends out radio and digital television signals.
FM Radio Stations
| Frequency | kW | Service |
|---|---|---|
| 87.8 MHz | 10 | France Inter |
| 89.0 MHz | 10 | RFI Paris |
| 89.9 MHz | 6 | TSF Jazz |
| 90.4 MHz | 10 | Nostalgie |
| 90.9 MHz | 4 | Chante France |
Digital Television Channels
A TV antenna was added in 1957. This made the tower 18.7 meters (61 feet) taller. More work in 2000 added another 5.3 meters (17 feet). The total height became 324 meters (1,063 feet). Analogue TV signals stopped in 2011.
| Frequency | VHF | UHF | kW | Service |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 182.25 MHz | 6 | N/A | 100 | Canal+ |
| 479.25 MHz | N/A | 22 | 500 | France 2 |
| 503.25 MHz | N/A | 25 | 500 | TF1 |
| 527.25 MHz | N/A | 28 | 500 | France 3 |
| 543.25 MHz | N/A | 30 | 100 | France 5 |
| 567.25 MHz | N/A | 33 | 100 | M6 |
Tower Height Over Time
The Eiffel Tower's height has changed several times. This is usually due to new antennas.
| From | To | Height (m) | Height (ft) | What was added | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1889 | 1956 | 312.27 | 1,025 | Flagpole | Tallest freestanding structure until 1930. |
| 1957 | 1991 | 320.75 | 1,052 | Antenna | Became the tallest tower in the world until 1958. |
| 1991 | 1994 | 317.96 | 1,043 | Antenna change | |
| 1994 | 2000 | 318.7 | 1,046 | Antenna change | |
| 2000 | 2022 | 324 | 1,063 | Antenna change | |
| 2022 | Current | 330 | 1,083 | Antenna change | A new digital radio antenna was added on March 15, 2022. |
Other Tall Structures
The Eiffel Tower was the world's tallest structure when it was finished in 1889. It kept this title until 1929. That's when the Chrysler Building in New York City was completed. It also lost its title as the world's tallest tower to the Tokyo Tower in 1958. But it is still the tallest freestanding structure in France.
Lattice Towers Taller Than the Eiffel Tower
| Name | Height | Year Built | Country | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo Skytree | 634 m | 2011 | Japan | Tokyo | |
| Kyiv TV Tower | 385 m | 1973 | Ukraine | Kyiv | |
| Dragon Tower | 336 m | 2000 | China | Harbin | |
| Tokyo Tower | 333 m | 1958 | Japan | Tokyo |
Structures in France Taller Than the Eiffel Tower
| Name | Height | Year Built | Type | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longwave transmitter Allouis | 350 m | 1974 | Guyed mast | Allouis | |
| Viaduc de Millau | 343 m | 2004 | Bridge pillar | Millau | |
| TV Mast Niort-Maisonnay | 330 m | 1978 | Guyed mast | Niort |
Visiting the Tower
Getting There
The closest Paris Métro station is Bir-Hakeim. The nearest RER train station is Champ de Mars-Tour Eiffel. The tower is located where the quai Branly and the Pont d'Iéna meet.
How Popular Is It?
Over 300 million people have visited the tower since 1889. In 2015, there were 6.91 million visitors. It's the most-visited paid monument in the world. About 25,000 people go up the tower every day. This can mean long queues!
Night Lights and Copyright
The tower itself has been in the public domain since 1993. This is 70 years after Eiffel's death. But a special lighting display from 1989 is protected by copyright. The company that runs the tower, SETE, says any photo of the lit tower at night needs permission for commercial use. This is why you might not see many night photos of the tower on stock image sites.
This copyright rule has caused some debate. SETE says it helps manage how the image is used. They made over €1 million from copyright fees in 2002. However, it could also affect tourists sharing their photos online.
The copyright claim has never been fully tested in court. But for commercial uses, like in magazines or on product packaging, permission might be needed. The person who designed the 1989 lighting died in 2021. So, the lighting display will be under copyright until 2091.
Mini Eiffel Towers Around the World
The Eiffel Tower has inspired many replicas. One early example is Blackpool Tower in England. Its mayor saw the Eiffel Tower in 1889 and wanted a similar one. It opened in 1894 and is 158.1 meters (519 feet) tall. The Tokyo Tower in Japan, built in 1958, was also inspired by it. The Petřín Lookout Tower in Prague is another example.
There are many smaller versions in the United States. There's a half-size one at Paris Las Vegas. Another is in Paris, Texas. Two 1:3 scale models are at Kings Island in Ohio and Kings Dominion in Virginia. You can also find replicas in China and Mexico.
In 2011, a TV show estimated the cost to build a full-size replica. It would be about US$480 million. This is much more than the original cost.
See also
 In Spanish: Torre Eiffel para niños
In Spanish: Torre Eiffel para niños
- List of tallest buildings and structures in the Paris region
- List of tourist attractions in Paris
- List of the 72 names on the Eiffel Tower
- Lattice tower