Blue facts for kids
| This box shows the color blue. |
|---|
Blue is one of the amazing colors we can see, like in a rainbow. It is one of the three main, or primary colors, along with red and yellow. Blue light has the shortest wavelength of these primary colors, usually around 470 nanometers.
Blue is the color of our Earth's sky and the huge oceans. When astronauts look at Earth from outer space, it looks like a beautiful blue marble!
We often think of blue as a cold color. Have you ever noticed your lips might turn a bit blue if you are really chilly? That is why blue is often used to show coldness.
You can also find blue in nature, like the feathers of a bluebird or a blue jay.
Contents
What Makes Blue a Special Color?
Blue is a truly unique color that surrounds us every day. It is not just a color; it is a feeling, a part of nature, and even a key player in how we see the world.
Discovering Different Shades of Blue
Just like there are many shades of green or red, blue comes in a huge variety of tones! From the lightest sky blue to the deepest navy blue, each shade has its own feel. Some blues might look a bit green, like cyan or turquoise. Others might lean towards purple, like indigo or ultramarine. Darker blues often have a bit of black or grey mixed in. Lighter blues have more white.
Here are just a few examples of blue shades:
- Sky Blue: A light, bright blue like a clear daytime sky.
- Navy Blue: A very dark blue, often seen in uniforms.
- Cobalt Blue: A strong, vibrant blue.
- Azure: A bright, slightly greenish-blue, like a Mediterranean sky.
- Indigo: A deep, rich blue that is almost purple.
Blue in Nature: Sky, Sea, and More
Blue is everywhere in our natural world. You can see it from the vastness of space to the tiny details of a flower.
Why the Sky Looks Blue
Have you ever wondered why the sky is blue? It is because of something called Rayleigh scattering. Sunlight is made up of all the colors of the rainbow. When sunlight travels through Earth's atmosphere, tiny bits of oxygen and nitrogen gas scatter the blue light more than other colors. This happens because blue light has a shorter wavelength. This scattered blue light spreads across the sky, making it look blue to our eyes.
At sunrise and sunset, the sun's light has to travel through much more of the atmosphere to reach us. Most of the blue and even green light gets scattered away. This leaves behind the longer wavelengths of red and orange. That is why sunsets and sunrises can be so fiery and colorful!
Why the Ocean Looks Blue
The sea also looks blue for a similar reason. Water absorbs longer wavelengths of light, like red, more easily than shorter wavelengths, like blue. So, when sunlight hits the ocean, the red light gets absorbed. The blue light is reflected and scattered back to our eyes.
The color of the sea can also change depending on other things. For example, the color of the sky reflecting on its surface can change it. Or if there is lots of algae (tiny plants) in the water, it can make it look greener. If there is a lot of dirt or sediment in the water, it might even look brownish.
Blue in the Distance
Have you ever noticed that distant mountains or objects often look a bit blue? This is called atmospheric perspective. The farther away something is, the more air and tiny particles are between you and that object. This air scatters blue light, making distant things appear bluer and lighter. In art, painters use this trick to make things look farther away!
How We See Blue: Light and Wavelengths
Our eyes are amazing tools that help us see colors. Blue is a special part of the visible spectrum of light.
Blue Light and Your Eyes
Our eyes see blue when they detect light with a wavelength between about 450 and 495 nanometers. If the wavelength is a bit shorter, it starts to look more like violet. If it is a bit longer, it starts to look more like green. A pure blue color has a wavelength of about 470 nanometers.
Long ago, a scientist named Isaac Newton was one of the first to describe the visible spectrum of light. He saw seven main colors, including blue and indigo (which is a deep blue-violet).
Mixing Colors: Art vs. Screens
In art and traditional colour theory, blue is one of the three primary colors for pigments (red, yellow, blue). Artists mix these three colors to create almost any other color. For example, mixing blue and yellow makes green. Mixing blue and red makes violet. If you mix all three primary colors together, you get a dark grey or black. This system, called RYB, has been used by painters for centuries.
But on your TV or computer screen, colors are made differently! Screens use something called additive colour or the RGB color model. This system uses red, green, and blue light. If you combine all three of these lights at full brightness, you get white light! Your screen is made of tiny dots called pixels. Each pixel has tiny red, green, and blue lights. By turning these lights on and off at different brightnesses, your screen can create millions of colors.
Blue Pigments and Dyes Through History
For thousands of years, people have found ways to make blue colors for painting, clothing, and art.
Ancient Blue Pigments
In ancient times, blue pigments (colors for painting) were often made from special minerals.
- Lapis lazuli: This beautiful blue stone, mined in Afghanistan for over 3,000 years, was crushed into a powder to make ultramarine pigment. It was very expensive, especially during the Renaissance. It was often used for important paintings, like the robes of the Virgin Mary.
- Azurite: Another mineral, found in Europe and Asia, was also crushed to make blue pigment. It was a cheaper option than lapis lazuli. However, it could sometimes change color over time.
- Egyptian blue: This was the very first man-made blue pigment, created around 2500 BC! It was made by heating sand, copper, and other ingredients.

Blue Dyes for Clothing
Before modern chemistry, blue dyes for clothes came from plants.
- Woad: This plant was used in Europe to make a blue dye.
- True indigo: This plant, common in Asia and Africa, produced a much stronger and more vibrant blue dye. When indigo arrived in Europe in the 15th century, it changed the world of fashion! It is the color that makes denim jeans blue.
Today, most blue pigments and dyes are made through chemical processes. This makes them more affordable and widely available. For example, Prussian blue was invented around 1706 and became popular for uniforms. Phthalocyanine blue, created in the 1930s, is used in many inks and dyes today.

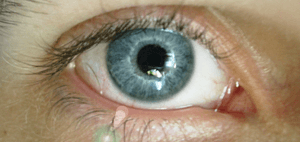
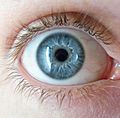
Blue Eyes: A Cool Fact
It might surprise you, but blue eyes do not actually contain any blue pigment! The color of your eyes depends on two things: the amount of dark melanin pigment in the iris (the colored part of your eye) and how light scatters within the iris.
People with blue eyes have less dark melanin in their irises compared to those with brown eyes. This means less blue light is absorbed. More of it is reflected and scattered back out. This scattering effect, similar to what makes the sky blue, makes the eyes appear blue! Eye color can even look a bit different depending on the lighting.
Blue eyes are most common in places like Ireland, the Baltic Sea area, and Northern Europe. They are also found in parts of Western Asia. For example, in Estonia, almost everyone (99%) has blue eyes! In the United States, blue eyes have become less common over the years, but they are still a beautiful and unique trait.
Amazing Blue Animals and Plants
While blue pigments are rare in nature, many animals and plants show off stunning blue colors.
- Blue Morpho Butterfly: The Morpho peleides butterfly has incredibly bright blue wings. This blue is not from pigment. It is from tiny scales on its wings that scatter light, creating an iridescent effect. This bright color helps scare away predators!
- Blue Whales: The blue whale is the largest animal ever known to exist. Its back is a pale blue-grey.
- Blue Poison Dart Frog: The Dendrobates azureus from Brazil is a bright blue frog with black spots. Its skin contains powerful chemicals that can paralyze or even kill predators. It warns them with its bright color.
- Blue Jay: These birds are famous for their vibrant blue and white feathers.
- Blueberries: These delicious fruits are named for their deep blue color.
- Flowers: Many beautiful flowers come in shades of blue, like cornflowers, forget-me-nots, and blue anemones.
- Sapphire: This precious gemstone is a type of mineral called corundum. Small amounts of iron inside the stone give it its beautiful blue color. If it has traces of chromium instead, it turns red and is called a ruby!
-
The Indigo milk cap, a blue mushroom
-
A beautiful Cornflower
-
Myosotis, or forget-me-not flowers
-
A blue Linckia starfish
-
A Blue jay
-
A blue whale, the largest animal on Earth.
Related pages
- List of colors
- Aqua
- Azure
- Blue-green
- Blue-violet
- Cerulean
- Cyan
- Electric blue
- Indigo
- Navy blue
- Prussian blue
- Teal blue
More Blue Images
-
Blue eyes, showing the effect of Tyndall scattering.
-
Red, green, and blue subpixels on an LCD display.
-
Prussian blue, a popular blue pigment.
-
The Blue Boy (1770), a famous painting using blue pigments.
-
The Great Wave off Kanagawa (1831), a famous Japanese print using Prussian blue.
-
Morning glory (Ipomoea acuminata) flowers.
-
Vaccinium corymbosum (blueberries).
-
An Indigo bunting bird.
-
The blue facial ridges of a mandrill.
-
The mandarin fish, one of the few animals with true blue pigment.
-
A Lapis lazuli bowl from ancient Iran.
-
A stained glass window at Saint Denis Basilica (1130-1140), colored with cobalt blue.
-
Detail of the Blue Virgin Window, Chartres Cathedral (12th century).
-
The Wilton Diptych (1395–1399), showing the Virgin Mary in traditional blue robes.
-
An urn by Josiah Wedgewood (1780s).
-
Blue conveys sadness in Picasso's The Old Guitarist (1903-1904).
-
"The Conversation" by Henri Matisse (1908-1912).
-
Officers of the London Metropolitan Police.
-
Sailors of the Royal Navy.
-
Blue domes of a church in Santorini, Greece.
-
A blue mosque in Herat, Afghanistan (15th century mosaic).
-
The Italian national football team in their blue jerseys.
See also
 In Spanish: Azul para niños
In Spanish: Azul para niños