List of seas on Earth facts for kids
Our planet Earth is mostly covered by water! This huge body of water is called the World Ocean. But this ocean isn't just one big, plain area. It's divided into many smaller parts, which we call seas. This article will help you learn about these different seas, including large areas of water like gulfs, bays, and straits. Sometimes, a body of water is called a "sea" just because of old traditions, even if it's technically a bay or gulf.
Contents
What are Seas and Oceans?
Let's learn some important words to understand our watery world better:
- Ocean: These are the biggest parts of the World Ocean. There are usually four to seven main oceans, like the Pacific Ocean or the Atlantic Ocean.
- Sea: A sea is a part of an ocean. It's often partly surrounded by land, like islands or peninsulas. Think of it like a room in a very big house. For example, the Sargasso Sea is special because it's defined by ocean currents, not land!
- Marginal Sea: This is a type of sea that is next to a big ocean. It's often partly closed off by islands or land, but still open to the main ocean.
- River: A narrow stream of water that flows over land, usually from higher ground to lower ground.
- Strait: A narrow channel of water that connects two larger bodies of water. Imagine a tiny hallway connecting two big rooms.
- Channel: Similar to a strait, but usually wider.
- Canal: A waterway built by people to connect different bodies of water.
There are also different names for parts of the ocean that push into the land:
- Bay: This is a general word for a part of the ocean that curves into the land. Bays can be small or very large.
- Gulf: A very large bay. It's often a major part of an ocean or sea.
- Bight: A bay that is usually shallower than a sound.
- Sound: A large, wide bay that is typically deeper than a bight, or it can be a strait.
- Cove: A very small bay, often sheltered and with a narrow entrance.
These terms can sometimes be confusing because they are used differently in different places. This list includes all large areas of water, no matter what they are called.
Biggest Seas by Size
Here are some of the largest seas in the world, listed by their size. The numbers show how many square kilometers (km2) they cover:
- Philippine Sea – 5.695 million km2
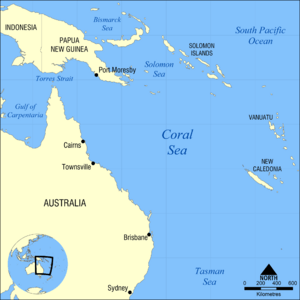
- Coral Sea – 4.791 million km2
- American Mediterranean Sea – 4.200 million km2
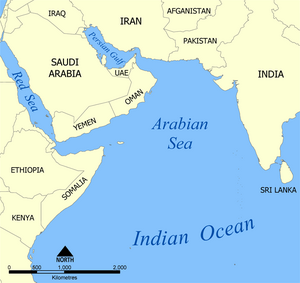
- Arabian Sea – 3.862 million km2
- Sargasso Sea – 3.5 million km2
- South China Sea – 3.5 million km2
- Weddell Sea – 2.8 million km2
- Caribbean Sea – 2.754 million km2
- Mediterranean Sea – 2.510 million km2
- Gulf of Guinea – 2.35 million km2
- Tasman Sea – 2.3 million km2
- Bay of Bengal – 2.172 million km2
- Bering Sea – 2 million km2
- Sea of Okhotsk – 1.583 million km2
- Gulf of Mexico – 1.550 million km2
- Gulf of Alaska – 1.533 million km2
- Barents Sea – 1.4 million km2
- Norwegian Sea – 1.383 million km2
- East China Sea – 1.249 million km2
- Hudson Bay – 1.23 million km2
- Greenland Sea – 1.205 million km2
- Somov Sea – 1.15 million km2
- Mar de Grau – 1.14 million km2
- Riiser-Larsen Sea – 1.138 million km2
- Sea of Japan – 1.05 million km2
- Argentine Sea – 1 million km2
- East Siberian Sea – 987,000 km2
- Lazarev Sea – 929,000 km2
- Kara Sea – 926,000 km2
- Scotia Sea – 900,000 km2
- Labrador Sea – 841,000 km2
- Andaman Sea – 797,700 km2
- Laccadive Sea – 786,000 km2
- Irminger Sea – 780,000 km2
- Solomon Sea – 720,000 km2
- Mozambique Channel – 700,000 km2
- Cosmonauts Sea – 699,000 km2
- Banda Sea – 695,000 km2
- Baffin Bay – 689,000 km2
- Laptev Sea – 662,000 km2
- Arafura Sea – 650,000 km2
- Ross Sea – 637,000 km2
- Chukchi Sea – 620,000 km2
- Timor Sea – 610,000 km2
- North Sea – 575,000 km2
- Bellingshausen Sea – 487,000 km2
- Beaufort Sea – 476,000 km2
- Red Sea – 438,000 km2
- Black Sea – 436,000 km2
- Gulf of Aden – 410,000 km2
- Yellow Sea – 380,000 km2
- Baltic Sea – 377,000 km2
- Caspian Sea – 371,000 km2
- Libyan Sea – 350,000 km2
- Mawson Sea – 333,000 km2
- Levantine Sea – 320,000 km2
- Java Sea – 320,000 km2
- Gulf of Thailand – 320,000 km2
- Celtic Sea – 300,000 km2
- Gulf of Carpentaria – 300,000 km2
- Celebes Sea – 280,000 km2
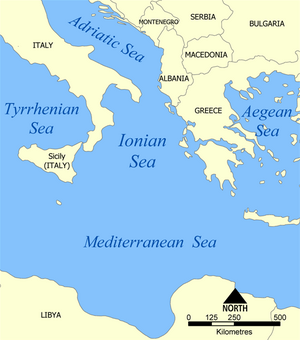
- Tyrrhenian Sea – 275,000 km2
- Sulu Sea – 260,000 km2
- Cooperation Sea – 258,000 km2
- Persian Gulf – 251,000 km2
- Flores Sea – 240,000 km2
- Gulf of St. Lawrence – 226,000 km2
- Bay of Biscay – 223,000 km2
- Aegean Sea – 214,000 km2
- Gulf of Anadyr – 200,000 km2
- Molucca Sea – 200,000 km2
- Oman Sea – 181,000 km2
- Ionian Sea – 169,000 km2
- Gulf of California – 160,000 km2
- Balearic Sea – 150,000 km2
- Adriatic Sea – 138,000 km2
Marginal Seas by Ocean
Seas can be "marginal" when they are between a big ocean and land. They can also be between two oceans. There isn't one single rule for how they are named.
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is at the very top of the world. Here are some of its marginal seas:
- Chukchi Sea
- East Siberian Sea
- Laptev Sea
- Kara Sea
- Barents Sea (connected to the Kara Sea by the Kara Strait)
- Greenland Sea
- Baffin Bay
- Hudson Bay
- Beaufort Sea
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is a huge ocean that separates Europe and Africa from the Americas.
Seas Near Africa and Eurasia
- Norwegian Sea
- North Sea
- Baltic Sea
- Gulf of Bothnia
- Gulf of Finland
- Gulf of Riga
- Baltic Sea
- English Channel
- Irish Sea
- Celtic Sea
- Bay of Biscay
- Mediterranean Sea (a very large and important sea)
- Alboran Sea
- Balearic Sea
- Ligurian Sea
- Tyrrhenian Sea
- Adriatic Sea
- Ionian Sea
- Aegean Sea
- Sea of Marmara
- Levantine Sea
- Libyan Sea
- Black Sea
- Gulf of Guinea
Seas Near the Americas
- Baffin Bay
- Labrador Sea
- Gulf of St. Lawrence
- Gulf of Maine
- Long Island Sound
- New York Bay
- Delaware Bay
- Chesapeake Bay
- American Mediterranean Sea (includes the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea)
- Argentine Sea
Seas Near Northern Islands
- Irish Sea (between Great Britain and Ireland)
- Denmark Strait (between Greenland and Iceland)
- Irminger Sea
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean.
- Andaman Sea
- Arabian Sea
- Bay of Bengal
- Gulf of Aden
- Gulf of Oman
- Laccadive Sea
- Mozambique Channel
- Persian Gulf
- Red Sea
- Timor Sea
- Palk Strait
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's oceanic divisions.
Seas Near the Americas
- Bering Sea
- Chilean Sea
- Gulf of Alaska
- Salish Sea
- Gulf of California (also known as the Sea of Cortés)
- Gulf of Panama
- Grau Sea
- San Francisco Bay
Seas Near Australia and Eurasia
- Arafura Sea
- Banda Sea
- Bismarck Sea
- Bohai Sea
- Celebes Sea
- Coral Sea
- East China Sea
- Flores Sea
- Gulf of Carpentaria
- Gulf of Thailand
- Java Sea
- Philippine Sea
- Sea of Japan
- Sea of Okhotsk
- Seto Inland Sea
- Solomon Sea
- South China Sea
- Sulu Sea
- Tasman Sea
- Tokyo Bay
- Yellow Sea
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean surrounds Antarctica.
- Amundsen Sea
- Bellingshausen Sea
- Cooperation Sea
- Cosmonauts Sea
- Davis Sea
- D'Urville Sea
- Drake Passage
- Lazarev Sea
- Mawson Sea
- Ross Sea
- Scotia Sea
- Somov Sea
- Weddell Sea
Seas Defined by Ocean Currents
Most seas are defined by land around them. But one sea is special because it's defined only by the way ocean currents move:
- Sargasso Sea: This sea is in the Atlantic Ocean. It's unique because it has no land borders. Instead, it's surrounded by four strong ocean currents that form a giant circle.
What's Not Included?
This list only includes parts of the World Ocean. It does not include:
- Lakes that have "Sea" in their name, like the Dead Sea or Sea of Galilee. These are inland bodies of water, not connected to the ocean.
- Imaginary seas from stories or myths.
See also