List of the prehistoric life of New Jersey facts for kids
Welcome to the amazing world of prehistoric creatures that once lived in New Jersey! Scientists have found many fossils here, showing us what life was like millions of years ago. This article will take you on a journey through time, exploring the ancient plants and animals whose remains have been discovered right here in New Jersey.
Ancient Life in New Jersey: A Timeline
Scientists divide Earth's long history into big chunks of time called eras. Each era had different kinds of life. Let's explore what we know about New Jersey's prehistoric past!
Precambrian Era: Earth's Earliest Life
The Precambrian Era was the very first and longest part of Earth's history. It lasted for billions of years! During this time, the first simple life forms appeared, like tiny bacteria. So far, scientists haven't found any fossils from the Precambrian Era in New Jersey. This means the rocks from that time might not be exposed, or they didn't preserve fossils well.
Paleozoic Era: The Age of Ancient Life
The Paleozoic Era came after the Precambrian, lasting from about 541 to 252 million years ago. This was a time when life really exploded! Many new types of animals appeared, especially in the oceans. In New Jersey, scientists have found fossils of some interesting creatures from this era:
- †Archaeocyathus: These were ancient, cone-shaped sea creatures that looked a bit like sponges. They were some of the first animals to build reefs.
- †Centroceras: A type of ancient cephalopod, related to modern-day squid and octopuses, but with a straight shell.
- †Cladopora: These were corals that grew in branching shapes, forming colonies on the seafloor.
- †Coenites: Another type of ancient coral, often found in fossil reefs.
- †Cordilleracyathus: Similar to Archaeocyathus, these were also early reef-building animals.
- †Favosites: Often called "honeycomb corals" because their fossilized skeletons look like honeycombs. They were very common in ancient oceans.
- †Leiorhynchus: A type of brachiopod, which are shelled marine animals that look a bit like clams but are different inside.
- †Leptodesma: An ancient type of bivalve, similar to modern clams or mussels.
- †Ophileta: This was a kind of ancient snail with a flat, coiled shell.
- †Styliolina: Tiny, cone-shaped fossils that were once part of plankton, drifting in ancient seas.
Mesozoic Era: The Age of Dinosaurs!
The Mesozoic Era, often called the "Age of Dinosaurs," lasted from about 252 to 66 million years ago. This was a time of giant reptiles, flying creatures, and the first birds and flowering plants. New Jersey has many important dinosaur and other reptile fossils from this time!
Dinosaurs and Other Land Animals
- †Anchisauripus: These are fossilized footprints of early dinosaurs, showing us how they walked.
- †Ankylosaurus: A famous armored dinosaur with a club tail.
- †Anomoepus: Another type of dinosaur footprint fossil, often found in New Jersey.
- †Apatopus: More dinosaur footprints, showing different kinds of dinosaurs that lived here.
- †Brontozoum: Large dinosaur footprints, possibly from a big plant-eating dinosaur.
- †Chirotherium: These are footprints made by large, crocodile-like reptiles, not dinosaurs.
- †Cimolomys: A small, ancient mammal that lived alongside dinosaurs.
- †Coelosaurus: A type of small, meat-eating dinosaur. Its fossils were among the first dinosaur remains found in North America.
- †Coelurosaurichnus: Footprints from small, two-legged meat-eating dinosaurs.
-
†Dryptosaurus: This was a large, meat-eating dinosaur, a relative of Tyrannosaurus rex. Its fossils were first found in New Jersey!
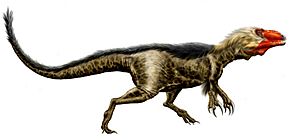 Life restoration of the Late Cretaceous primitive tyrannosaur Dryptosaurus
Life restoration of the Late Cretaceous primitive tyrannosaur Dryptosaurus - †Edmontosaurus: A large, duck-billed dinosaur that ate plants.
-
†Hadrosaurus: This famous duck-billed dinosaur was discovered in New Jersey! It was one of the first nearly complete dinosaur skeletons ever found, helping scientists understand what dinosaurs looked like.
 Life restoration of the Late Cretaceous dinosaur Hadrosaurus
Life restoration of the Late Cretaceous dinosaur Hadrosaurus - †Hypsibema: Another large, plant-eating dinosaur.
- †Hypsognathus: A small, plant-eating reptile with a short, broad head.
- †Hypuronector: A small, gliding reptile that lived in trees.
- †Icarosaurus: A small, lizard-like reptile that could glide using long ribs that supported a skin membrane.
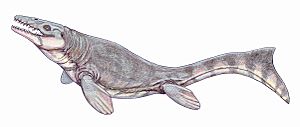
- †Rutiodon:
A large, crocodile-like reptile called a phytosaur. They lived in water and had long snouts.
 Fossilized skeleton of the Late Triassic phytosaur Rutiodon
Fossilized skeleton of the Late Triassic phytosaur Rutiodon - †Sauropus: Footprints from large, four-legged reptiles.
- †Semionotus: An ancient ray-finned fish.
- †Stegomus: A type of armored reptile, similar to a crocodile.
- †Tanytrachelos: A small, lizard-like reptile.
Marine Reptiles and Fish
- †Adocus: An ancient turtle.
-
†Amyda: Another type of ancient turtle.
 Shell and skeleton of Adocus beatus, Peabody Museum of Natural History
Shell and skeleton of Adocus beatus, Peabody Museum of Natural History - †Bottosaurus: An ancient crocodile.
- †Brachychampsa: A relative of modern alligators.
- †Cimoliasaurus: A type of plesiosaur, a long-necked marine reptile.
- †Clidastes: A type of mosasaur, a large marine reptile that looked like a giant lizard with flippers.
- †Corsochelys: An ancient sea turtle.
- †Cretoxyrhina: A very large, fast-swimming shark, sometimes called the "Ginsu shark."
- †Crocodilus: Ancient crocodiles.
-
†Deinosuchus: A giant crocodile relative, much larger than modern crocodiles.Mounted fossilized skeleton of the Late Cretaceous Alligator relative Deinosuchus
- †Diplocynodon: Another ancient crocodile.
- †Diplurus: An ancient fish.
- †Dasyatis: An ancient ray.
- †Edaphodon: A type of ancient fish with plate-like teeth.
- †Elasmosaurus: A very long-necked plesiosaur.
- †Enchodus: A fish with long, needle-like fangs.
- †Halisaurus: A type of mosasaur.
- †Hybodus: An ancient shark.
- †Hyposaurus: A type of ancient crocodile.
- †Ischyodus: A type of ancient fish related to modern chimaeras.
- †Ischyrhiza: A sawfish-like ray with a long, toothed snout.
- †Leidyosuchus: A relative of modern alligators.
- †Liodon: A type of mosasaur.
- †Lissodus: An ancient shark.
- †Megalocoelacanthus: A very large type of coelacanth, an ancient fish thought to be extinct until rediscovered alive.
-
†Mosasaurus: A giant marine reptile, one of the top predators of the Late Cretaceous seas.
 Life restoration of the Late Cretaceous Mosasaurus
Life restoration of the Late Cretaceous Mosasaurus - †Osteopygis: An ancient turtle.
- †Oxyrhina: An ancient shark.
- †Palaeoniscus: An ancient ray-finned fish.
- †Paralbula: An ancient fish.
- †Peritresius: An ancient sea turtle.
- †Plesiosaurus: A type of long-necked marine reptile.
- †Plioplatecarpus: A type of mosasaur.
- †Pristis: An ancient sawfish.
- †Procolpochelys: An ancient sea turtle.
- †Prognathodon: Another large, powerful mosasaur.
- †Pseudocorax: An ancient shark.
- †Ptychotrygon: An ancient ray.
- †Rhinobatos: An ancient guitarfish.
- †Rhombodus: An ancient ray.
- †Sargana: An ancient fish.
- †Scapanorhynchus: A goblin shark-like shark.
- †Sclerorhynchus: An ancient ray.
- †Serratolamna: An ancient shark.
- †Squalicorax: A crow shark, known for its serrated teeth.
- †Squatina: An ancient angelshark.
- †Stephanodus: An ancient fish.
- †Thoracosaurus: A crocodile relative that lived in marine environments.
- †Trionyx: An ancient softshell turtle.
-
†Xiphactinus: A very large, predatory bony fish.
 Life restoration of the Cretaceous bony fish Xiphactinus
Life restoration of the Cretaceous bony fish Xiphactinus
Other Mesozoic Life
- Acipenser: Ancient sturgeon fish.
- Acteon: A type of sea snail.
- †Aenona: An ancient bivalve.
- †Agerostrea: An ancient oyster.
- Amauropsis: A type of sea snail.
- Amia: An ancient bowfin fish.
- Arca: An ancient ark clam.
- Astarte: An ancient clam.
- Astrangia: An ancient coral.
- Atractosteus: An ancient gar fish.
- †Atreipus: Footprints from ancient reptiles.
- Attagenus: An ancient beetle.
- †Avellana: An ancient sea snail.
- †Axonoceras: An ancient ammonite, a shelled cephalopod.
- †Baculites: A straight-shelled ammonite.
- †Baikuris: An ancient ant.
- Barbatia: An ancient ark clam.
- †Belemnitella: An ancient belemnite, a squid-like creature with an internal shell.
- Bernaya: An ancient cowrie snail.
- Botula: An ancient mussel.
- Brachaelurus: An ancient carpet shark.
- †Brownimecia: An ancient ant, preserved in amber.
- Caestocorbula: An ancient clam.
- Callianassa: An ancient ghost shrimp.
- †Calliomphalus: An ancient sea snail.
- Cardita: An ancient clam.
- †Catopygus: An ancient sea urchin.
- †Ceratodus: An ancient lungfish.
- Cerithium: An ancient sea snail.
- Cheilotrichia: An ancient crane fly.
- †Chelone: An ancient plant.
- Chiloscyllium: An ancient carpet shark.
- Chlamys: An ancient scallop.
- †Cirroceras: An ancient ammonite.
- Clavagella: An ancient clam.
- Cliona: An ancient boring sponge.
- Corbula: An ancient clam.
- Crassostrea: An ancient oyster.
- †Crenella: An ancient mussel.
- †Cretolamna: An ancient shark.
- Cucullaea: An ancient ark clam.
- Culicoides: An ancient biting midge.
- Cuspidaria: An ancient clam.
- †Cylindracanthus: A fish with a long, pointed snout.
- †Cymella: An ancient clam.
- Cyzicus: An ancient clam shrimp.
- †Dentalium: An ancient tusk shell.
- †Didelphodon: An ancient marsupial mammal.
- †Didymoceras: A coiled ammonite.
- †Discoscaphites: A type of ammonite.
- †Dolicholatirus: An ancient sea snail.
- Dosinia: An ancient clam.
- †Epitonium: An ancient wentletrap snail.
- †Euspira: An ancient moon snail.
- †Eutrephoceras: An ancient nautilus.
- †Exogyra: A common fossil oyster with a twisted shell.
- Fasciolaria: An ancient spindle snail.
- †Gegania: An ancient sea snail.
- †Gervillia: An ancient bivalve.
- Ginglymostoma: An ancient nurse shark.
- Glossus: An ancient heart cockle.
- Glycimeris: An ancient ark clam.
- Glycymeris: An ancient ark clam.
- †Gonyaulax: An ancient dinoflagellate (microscopic marine organism).
- †Graculavus: An ancient bird.
- †Grallator: Dinosaur footprints.
- †Grimaldiella: An ancient insect.
- †Gryphaea: An ancient oyster.
- Hemiscyllium: An ancient carpet shark.
- Heterodontus: An ancient horn shark.
- †Hoploparia: An ancient lobster.
- †Hoploscaphites: An ancient ammonite.
- †Inoceramus: A very large, ancient clam.
- †Jeletzkytes: An ancient ammonite.
- †Jerseyempheria: An ancient insect.
- †Kouphichnium: Footprints from ancient horseshoe crabs.
- †Laornis: An ancient bird.
- Leptoconops: An ancient biting midge.
- Lima: An ancient file clam.
- Limatula: An ancient file clam.
- †Limonia: An ancient crane fly.
- †Linearis: An ancient clam.
- Linuparus: An ancient spiny lobster.
- Lithophaga: An ancient date mussel.
- Lopha: An ancient oyster.
- Lunatia: An ancient moon snail.
- Martesia: An ancient clam.
- †Menuites: An ancient ammonite.
- †Metoicoceras: An ancient ammonite.
- †Milnesium: An ancient tardigrade (water bear).
- †Modiolus: An ancient horse mussel.
- †Morea: An ancient sea snail.
- †Mytilus: An ancient mussel.
- †Neithea: An ancient scallop.
- †Nostoceras: A coiled ammonite.
- Nucula: An ancient nut clam.
- †Odaxosaurus: An ancient lizard.
- Odontaspis: An ancient sand tiger shark.
- Oecobius: An ancient spider.
- †Ophiomorpha: Fossil burrows made by ancient shrimp.
- Orchestina: An ancient spider.
- Ostrea: An ancient oyster.
- †Pachydiscus: A large, ancient ammonite.
- Pagurus: An ancient hermit crab.
- †Palaeopagurus: An ancient hermit crab.
- †Palaeotringa: An ancient bird.
- Panopea: An ancient geoduck clam.
- †Paracupes: An ancient beetle.
- †Paranomia: An ancient jingle shell.
- †Parrisia: An ancient plant.
- †Pecten: An ancient scallop.
- Pholadomya: An ancient clam.
- Pholas: An ancient piddock clam.
- †Pinna: An ancient pen shell.
- †Placenticeras: An ancient ammonite.
- †Plagiostoma: An ancient clam.
- Plicatula: An ancient oyster.
- †Plumalexius: An ancient wasp.
- Polinices: An ancient moon snail.
- †Protocardia: An ancient clam.
- †Pteria: An ancient wing oyster.
- †Pterotrigonia: An ancient clam.
- Pycnodonte: An ancient oyster.
- Rangia: An ancient clam.
- Ringicula: An ancient sea snail.
- †Scaphites: An ancient ammonite.
- Segestria: An ancient spider.
- Serpula: An ancient tube worm.
- †Spathopria: An ancient insect.
- †Sphecomyrma: An ancient ant, preserved in amber.
- †Sphenodiscus: An ancient ammonite.
- Spondylus: An ancient spiny oyster.
- †Stegobium: An ancient beetle.
- †Steropoides: Footprints from ancient reptiles.
- †Symmorphus: An ancient wasp.
- †Taphrosaurus: An ancient crocodile.
- Tellina: An ancient tellin clam.
- †Telmatornis: An ancient bird.
- Tenagodus: An ancient worm snail.
- †Tenea: An ancient clam.
- †Tomodon: An ancient snake.
- Trachycardium: An ancient cockle.
- †Trigonia: An ancient clam.
- Turbinella: An ancient chank snail.
- Turbonilla: An ancient sea snail.
- Turritella: An ancient sea snail with a tall, spiral shell.
- †Volviceramus: An ancient clam.
- Vulsella: An ancient clam.
- Xanthosia: An ancient plant.
Cenozoic Era: The Age of Mammals
The Cenozoic Era began about 66 million years ago and continues to the present day. This is the "Age of Mammals," as mammals grew larger and became the dominant land animals after the dinosaurs disappeared. New Jersey has many fossils from this more recent past, including ancient sharks, whales, and ice age mammals.
Mammals of the Cenozoic
- Bison: Ancient bison, related to modern buffalo.
- †Bootherium: An ancient musk ox.
- †Castoroides: A giant beaver, much larger than modern beavers.
- †Cervalces: A large, extinct deer, sometimes called the "stag moose."
- Equus: Ancient horses.
- †Mammut: The American mastodon, a large, elephant-like mammal.
- †Mammuthus: The mammoth, another large, hairy, elephant-like mammal.
- †Megalonyx: A giant ground sloth, much larger than modern sloths.
- †Menoceras: A small, ancient rhinoceros.
- Odobenus: Ancient walruses.
- Ovibos: Ancient musk oxen.
- Phoca: Ancient seals.
- Physeter: Ancient sperm whales.
- †Prosynthetoceras: An ancient hoofed mammal with horns.
- Rangifer: Ancient reindeer or caribou.
- †Squalodon: An ancient dolphin with shark-like teeth.
- †Tapiravus: An ancient tapir.
- Tapirus: Ancient tapirs.
- Trichechus: Ancient manatees.
- Tympanuchus: Ancient prairie chickens.
Marine Life of the Cenozoic
- †Acrodus: An ancient cartilaginous fish.
- Aetobatus: An ancient eagle ray.
- Carcharias: An ancient sand tiger shark.
- Carcharodon: Ancient great white sharks.
- †Carcharodon hastalis: A large, extinct shark.
-
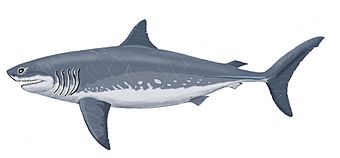
†Otodus megalodon: The famous Megalodon, the largest shark that ever lived! Its giant teeth are found in New Jersey.
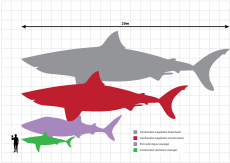 Diagram illustrating the largest (grey) and most conservative (red) size estimates of the Miocene-Pliocene shark Carcharocles megalodon (sometimes Carcharodon or Otodus megalodon) with a whale shark (violet), great white shark (green), and anachronistic human (black) to scale
Diagram illustrating the largest (grey) and most conservative (red) size estimates of the Miocene-Pliocene shark Carcharocles megalodon (sometimes Carcharodon or Otodus megalodon) with a whale shark (violet), great white shark (green), and anachronistic human (black) to scale -
Crocodylus: Ancient crocodiles.
 A living Crocodylus
A living Crocodylus - †Cylindracanthus: An ancient fish.
- Dasyatis: An ancient stingray.
- †Diatryma: A giant, flightless bird.
- †Eosphargis: An ancient sea turtle.
- †Eosuchus: An ancient crocodile relative.
-
Galeocerdo: Ancient tiger sharks.
 A living Galeocerdo cuvier, or tiger shark
A living Galeocerdo cuvier, or tiger shark - Hemipristis: An ancient weasel shark.
- Heptranchias: An ancient sevengill shark.
- Hexanchus: An ancient sixgill shark.
- †Hyposaurus: An ancient crocodile.
- †Ischyodus: An ancient chimaera fish.
- †Ischyrhiza: An ancient sawfish-like ray.
- Isurus: Ancient mako sharks.
- Lamna: Ancient porbeagle sharks.
- Libinia: An ancient spider crab.
- Myliobatis: Ancient eagle rays.
- Odontaspis: An ancient sand tiger shark.
- †Oxyrhina: An ancient shark.
- †Palaeocarcharodon: An ancient shark.
- †Palaeophis: A giant, ancient sea snake.
- †Pentacrinites: An ancient crinoid, or "sea lily."
- †Peritresius: An ancient sea turtle.
- Phyllodus: An ancient fish.
- Pristis: An ancient sawfish.
- †Puppigerus: An ancient sea turtle.
- Rhinoptera: An ancient cownose ray.
- †Rhizocrinus: An ancient crinoid.
- Scyliorhinus: An ancient catshark.
- Sphyraenodus: An ancient barracuda.
- Squalus: An ancient dogfish shark.
- Squatina: An ancient angelshark.
- †Striatolamia: An ancient shark.
- †Thecachampsa: An ancient crocodile relative.
- †Thoracosaurus: An ancient crocodile relative.
-
Xiphias: Ancient swordfish.
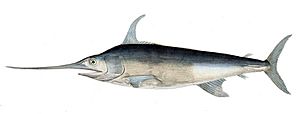 A living Xiphias, or swordfish
A living Xiphias, or swordfish - †Zygaena: An ancient hammerhead shark.
Other Cenozoic Life
- Acteocina: A type of sea snail.
- Anachis: A type of sea snail.
- Anadara: A type of ark clam.
- Angulus: A type of tellin clam.
- Anomia: A type of jingle shell.
- Architectonica: A type of sundial snail.
- Argopecten: A type of scallop.
- Argyrotheca: A type of brachiopod.
- Astrangia: A type of coral.
- Astyris: A type of sea snail.
- Athleta: A type of sea snail.
- Atrina: A type of pen shell.
- †Aturia: An ancient nautilus.
- Balanophyllia: A type of coral.
- Balanus: A type of barnacle.
- Barbatia: A type of ark clam.
- Barnea: A type of piddock clam.
- †Bonellitia: A type of sea snail.
- Buccinum: A type of whelk snail.
- Busycon: A type of whelk snail.
- Busycotypus: A type of whelk snail.
- Cadulus: A type of tusk shell.
- †Calappilia: An ancient crab.
- Callianassa: A type of ghost shrimp.
- Calliostoma: A type of sea snail.
- Calyptraea: A type of slipper snail.
- Cardita: A type of clam.
- Carditamera: A type of clam.
- Cardites: A type of clam.
- †Catopygus: An ancient sea urchin.
- Cerithiopsis: A type of sea snail.
- Chaetopleura: A type of chiton.
- Chama: A type of jewel box clam.
- Chelone: An ancient turtle.
- †Chesapecten: An ancient scallop.
- Chlamys: A type of scallop.
- Cidaris: A type of sea urchin.
- †Cistella: A type of brachiopod.
- Clavilithes: A type of sea snail.
- Clementia: A type of clam.
- Cliona: A type of boring sponge.
- Conus: A type of cone snail.
- Corbula: A type of clam.
- †Coscinopleura: A type of bryozoan.
- Crassinella lunulata: A type of clam.
- Crassostrea: A type of oyster.
- Crenella: A type of mussel.
- Crepidula: A type of slipper snail.
- †Cretolamna: An ancient shark.
- Crucibulum: A type of cup-and-saucer snail.
- Cucullaea: A type of ark clam.
- Cumingia: A type of clam.
- Cuspidaria: A type of clam.
- Cyclocardia: A type of clam.
- Cylichna: A type of sea snail.
- Cythara: A type of sea snail.
- Cytherea: A type of clam.
- Dentalium: A type of tusk shell.
- Diastoma: A type of sea snail.
-
†Diceratherium: An ancient rhinoceros.
 Restoration of the Oligocene-Miocene hornless rhinoceros Diceratherium. Robert Bruce Horsfall (1913).
Restoration of the Oligocene-Miocene hornless rhinoceros Diceratherium. Robert Bruce Horsfall (1913). - Diodora: A type of keyhole limpet.
- Diplodonta punctata: A type of clam.
- Discinisca: A type of brachiopod.
- †Dolicholatirus: A type of sea snail.
- Donax: A type of coquina clam.
- Dosinia: A type of clam.
- Echinarachnius: A type of sand dollar.
- †Echinocorys: A type of sea urchin.
- †Echinopsis: A type of sea urchin.
- †Ecphora: A type of sea snail with distinctive ridges.
- Ensis: A type of razor clam.
- Epitonium: A type of wentletrap snail.
- Ervilia: A type of clam.
- Eupleura: A type of sea snail.
- Euspira: A type of moon snail.
- †Eutrephoceras: An ancient nautilus.
- Fasciolaria: A type of spindle snail.
- Flabellum: A type of coral.
- Fossarus: A type of sea snail.
- Galeodea: A type of helmet snail.
- Gemma: A type of tiny clam.
- Geukensia: A type of ribbed mussel.
- Glans: A type of clam.
- †Glomerula: A type of tube worm.
- Glossus: A type of heart cockle.
- Glycymeris: A type of ark clam.
- †Gorgonella: A type of soft coral.
- †Gryphaea: A type of oyster.
- †Hamulus: A type of tube worm.
- Haustator: A type of sea snail.
- Hespererato: A type of sea snail.
- Hiatella: A type of rock borer clam.
- Hydroides: A type of tube worm.
- Ilyanassa: A type of mud snail.
- Ischadium: A type of mussel.
- Isognomon: A type of tree oyster.
- Kurtziella: A type of sea snail.
- Laevicardium: A type of cockle.
- Latirus: A type of sea snail.
- †Linthia: A type of sea urchin.
- Lithophaga: A type of date mussel.
- Littoraria: A type of periwinkle snail.
- Lunularia: A type of bryozoan.
- Macoma: A type of tellin clam.
- Macrocallista: A type of clam.
- Mactra: A type of surf clam.
- Melampus: A type of marsh snail.
- Melanella: A type of sea snail.
- Mercenaria: A type of quahog clam.
- Mesodesma: A type of clam.
- Mitrella: A type of sea snail.
- Modiolus: A type of horse mussel.
- Morus: An ancient gannet bird.
- Mulinia: A type of clam.
- Murex: A type of murex snail.
- Murexiella: A type of murex snail.
- †Mya: A type of softshell clam.
- Mytilus: A type of mussel.
- Nassarius: A type of dog whelk snail.
- Natica: A type of moon snail.
- Neptunea: A type of whelk snail.
- Neverita: A type of moon snail.
- Nucula: A type of nut clam.
- †Ophiocoma: A type of brittle star.
- Ophiomusium: A type of brittle star.
- Ostrea: A type of oyster.
- Paliurus: An ancient plant.
- Pandora: A type of pandora clam.
- Panopea: A type of geoduck clam.
- Panopeus: A type of mud crab.
- Pecten: A type of scallop.
- Penion: A type of sea snail.
- †Peronidella: A type of sponge.
- Petricola: A type of boring clam.
- Phyllonotus: A type of murex snail.
- Pinna: A type of pen shell.
- Pitar: A type of clam.
- †Plagiochasma: A type of sea urchin.
- Pleuromeris: A type of clam.
- Pleurotomaria: A type of slit snail.
- Plicatula: A type of oyster.
- Polinices: A type of moon snail.
- Protula: A type of tube worm.
- Psammechinus: A type of sea urchin.
- Pseudoliva: A type of sea snail.
- Pteria: A type of wing oyster.
- Pycnodonte: A type of oyster.
- Pyrgocythara: A type of sea snail.
- Rangia: A type of clam.
- †Rotularia: A type of tube worm.
- Scaphella: A type of volute snail.
- Seila: A type of sea snail.
- Semele: A type of clam.
- Serpula: A type of tube worm.
- Serpulorbis: A type of worm snail.
- Sinum: A type of moon snail.
- Siphonalia: A type of sea snail.
- †Solarium: A type of sundial snail.
- Solenosteira: A type of sea snail.
- Stellatoma: A type of sea snail.
- Stewartia: A type of clam.
- Stramonita: A type of rock snail.
- Strioterebrum: A type of sea snail.
- Tagelus: A type of razor clam.
- Tectonatica: A type of moon snail.
- Tellina: A type of tellin clam.
- Tenagodus: A type of worm snail.
- †Tenea: A type of clam.
- Teredo: A type of shipworm.
- Tibia: A type of sea snail.
- Triphora: A type of sea snail.
- Trochita: A type of slipper snail.
- Turbonilla: A type of sea snail.
- Turris: A type of sea snail.
- Turritella: A type of sea snail.
- Tylocidaris: A type of sea urchin.
- Urosalpinx: A type of oyster drill snail.
- †Veleda: A type of sea snail.
- Venericardia: A type of clam.
- Venus: A type of venus clam.
- Yoldia: A type of nut clam.
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |