St Kitts and Nevis facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto: "Country Above Self"
|
|
|
Anthem: "O Land of Beauty!"
|
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Basseterre 17°18′N 62°44′W / 17.300°N 62.733°W |
| Official languages | English |
| Vernacular language | Saint Kitts Creole |
| Ethnic groups
(2001)
|
|
| Religion
(2010)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Sir Tapley Seaton | |
| Terrance Drew | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
|
• Associated State
|
27 February 1967 |
|
• Independence declared
|
19 September 1983 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
261 km2 (101 sq mi) (188th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
Negligible |
| Population | |
|
• 2018 estimate
|
52,441 (213th) |
|
• 2011 census
|
46,204 |
|
• Density
|
164/km2 (424.8/sq mi) (64th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.758 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$31,095 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.058 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$18,714 |
| HDI (2019) | high · 74th |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (EC$) (XCD) |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +1 869 |
| ISO 3166 code | KN |
| Internet TLD | .kn |
|
|
Saint Kitts and Nevis, officially known as the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is a beautiful island country in the Caribbean Sea. It's part of the Leeward Islands chain. This country is special because it's the smallest independent nation in the Western Hemisphere. It has the smallest land area and population. It is also the world's smallest independent country made up of different states (a federation).
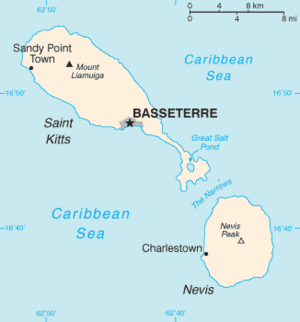
The capital city is Basseterre, located on the larger island of Saint Kitts. Basseterre is also the main port where cruise ships arrive and cargo is handled. The smaller island, Nevis, is about 3 kilometers (2 miles) southeast of Saint Kitts. A shallow channel called The Narrows separates the two islands.
Long ago, the island of Anguilla was also part of this country. It was called Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. However, Anguilla decided to become separate. It is now a British territory. Nearby islands include Sint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, Saint Martin, and Anguilla to the north. To the east are Antigua and Barbuda, and to the southeast is Montserrat.
Saint Kitts and Nevis were among the first Caribbean islands settled by Europeans. Saint Kitts was home to the first British and French colonies in the Caribbean. Because of this, it's sometimes called "The Mother Colony of the West Indies." It gained full independence from the United Kingdom in 1983.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The original people of Saint Kitts, the Kalinago, called it Liamuiga. This name means 'fertile land'.
It is believed that Christopher Columbus saw the islands in 1493. He might have named the larger island San Cristóbal, after his patron saint, Saint Christopher. Some newer studies suggest Columbus named it Sant Yago (Saint James). They think the name San Cristóbal was given to the island now known as Saba. Either way, by the 1600s, the island was known as San Cristóbal. English settlers later called it St. Christopher's Island. Since "Kit" was a common nickname for Christopher, it became known as Saint Kitts.
Columbus named Nevis San Martín (Saint Martin). The name Nevis comes from a Spanish name, Nuestra Señora de las Nieves. This means 'Our Lady of the Snows'. It refers to an old story about snow falling in Rome during summer. People think the white clouds often seen around Nevis Peak reminded someone of this story.
Today, the country's official document, the Constitution, uses both Saint Kitts and Nevis and Saint Christopher and Nevis. Saint Kitts and Nevis is used more often.
A Look at History

Early Inhabitants
The first people lived on these islands about 3,000 years ago. We don't know their name. Later, the Arawak people arrived around 1000 BC. Around 800 AD, the Island Caribs came to the islands.
European Settlers Arrive
Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands in 1493. The first English settlers arrived in 1623. They were led by Thomas Warner. They started a settlement on Saint Kitts at Old Road Town. They made an agreement with the Carib chief Ouboutou Tegremante. The French also settled on Saint Kitts in 1625. They were led by Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc. The English and French agreed to divide the island between them. From 1628, the English also began settling on Nevis.
The European settlers wanted to use the islands' resources. The native Caribs resisted them. In 1626, the English and French joined forces. They attacked the Kalinago at a place called Bloody Point. This was supposedly to stop a Carib plan to attack the Europeans. After this, the English and French started large sugar plantations. They brought many African slaves to work on these plantations. This made the plantation owners rich. It also changed the islands' population. Soon, black slaves outnumbered Europeans.
In 1629, a Spanish group destroyed the English and French colonies. They sent the settlers back to their home countries. But in 1630, Spain allowed the colonies to be rebuilt. Spain later officially agreed that Britain owned Saint Kitts. This was part of a deal to fight piracy.
As Spain's power weakened, Saint Kitts became an important base. It helped England and France expand in the Caribbean. From Saint Kitts, the British settled islands like Antigua and Montserrat. The French settled islands like Martinique and Guadeloupe. In the late 1600s, France and England fought over Saint Kitts and Nevis. They had wars in 1667, 1689–90, and 1701–13. France gave up its claim to the islands in 1713. The islands' economy was hurt by these wars. An earthquake in 1690 destroyed Jamestown, the capital of Nevis. A new capital, Charlestown, had to be built. A hurricane in 1707 caused more damage.
British Rule and Independence
By the 1700s, the colony had recovered. By the end of the 1700s, Saint Kitts was the richest British colony per person in the Caribbean. This was due to its sugar industry, which relied on slaves. Nevis, which used to be richer, became less important than Saint Kitts. Alexander Hamilton, who later became a famous American leader, was born on Nevis in 1755 or 1757.
When Britain was fighting its American colonies, the French tried to take Saint Kitts in 1782. However, Saint Kitts was given back to Britain in 1783.
The trade of African slaves was stopped in the British Empire in 1807. Slavery itself was completely outlawed in 1834. After this, slaves had a four-year "apprenticeship" period. They worked for their former owners for wages. On Nevis, 8,815 slaves were freed. On Saint Kitts, 19,780 were freed.
Saint Kitts and Nevis, along with Anguilla, joined together in 1882. In the early 1900s, people faced economic hardship. This led to the growth of groups fighting for workers' rights. During the Great Depression, sugar workers went on strike in 1935. In the 1940s, the Saint Kitts and Nevis Labour Party was founded. Robert Llewellyn Bradshaw led this party. He later became the colony's Chief Minister and Premier. He wanted the government to have more control over the sugar economy. The People's Action Movement party was founded in 1965.
After being part of the West Indies Federation for a short time (1958–62), the islands became an associated state in 1967. This meant they had full control over their own internal affairs. People in Nevis and Anguilla were not happy with Saint Kitts having too much power. Anguilla declared independence in 1967. In 1971, Britain took back control of Anguilla. It officially separated in 1980.
Then, attention turned to Nevis. The Nevis Reformation Party wanted to protect Nevis's interests in any future independent country. It was finally agreed that Nevis would have some self-rule. It would have its own Premier and Assembly. It also had the right to leave the federation if two-thirds of its people voted for it in a referendum. Saint Kitts and Nevis became fully independent on September 19, 1983. Kennedy Simmonds became the country's first Prime Minister. Saint Kitts and Nevis chose to remain part of the Commonwealth of Nations.
Recent Times
Kennedy Simmonds won elections in 1984, 1989, and 1993. In 1995, the Saint Kitts and Nevis Labour Party returned to power. Denzil Douglas became the new Prime Minister.
In Nevis, people were still unhappy about feeling left out. In 1998, there was a vote to separate from Saint Kitts. 62% voted to leave, but this was not enough for it to happen legally.
In 1998, Hurricane Georges caused a lot of damage. This affected the country's economy for years. The sugar industry had been struggling for a long time. It was only kept going by government money. In 2005, the government decided to close the state-owned sugar company completely.
In 2015, Timothy Harris became Prime Minister. He led the People's Labour Party. In June 2020, his party won the general elections again. In August 2022, Terrance Drew was elected as the current Prime Minister.
How the Government Works

Saint Kitts and Nevis is an independent country. It is a democracy and a federation. It is also a Commonwealth realm. This means the King of Saint Christopher and Nevis, Charles III, is its head of state. The King is represented in the country by a Governor-General. The Governor-General follows the advice of the Prime Minister and the Cabinet. The Prime Minister is the leader of the party with the most votes. The Cabinet manages the country's affairs.
Saint Kitts and Nevis has one main law-making body. It is called the National Assembly. It has fourteen members. Eleven members are elected by the people. Three of these are from Nevis. Three other members, called Senators, are chosen by the Governor-General. Two Senators are chosen based on the Prime Minister's advice. One is chosen based on the opposition leader's advice. Senators sit in the National Assembly with the elected members. All members serve for five years. The Prime Minister and Cabinet are responsible to the Parliament. Nevis also has its own Assembly with some self-rule.
Land and Nature
Saint Kitts and Nevis is made up of two main islands. They are Saint Kitts and Nevis. The Narrows strait separates them by about 3 kilometers (2 miles). Both islands were formed by volcanoes. They have tall central peaks covered in tropical rainforest. Most people live along the flatter areas near the coast. Saint Kitts has several mountain ranges in its center. The highest point in the country is Mount Liamuiga, which is 1,156 meters (3,793 feet) tall. On the east coast are the Canada Hills and Conaree Hills. The land becomes much narrower and flatter in the southeast. This area has the largest body of water, the Great Salt Pond. A small island called Booby Island is in The Narrows. Many rivers flow from the mountains, providing fresh water. Nevis, the smaller island, is round. It is dominated by Nevis Peak, which is 985 meters (3,232 feet) tall.
Saint Kitts and Nevis has two types of natural areas. These are moist forests and dry forests. The country's forests are important for its environment.
Animals of the Islands
The national bird of Saint Kitts and Nevis is the brown pelican. Many different kinds of birds, 176 species, have been seen in the country.
Plants of the Islands
The national flower is Delonix regia, also known as the flamboyant tree. Common plants include palmetto, hibiscus, bougainvillea, and tamarind. Pine trees are common in the dense forests. They are often covered by different types of ferns.
Weather and Climate
Saint Kitts has a tropical savanna climate. Nevis has a tropical monsoon climate. This means they are warm all year round. Average monthly temperatures in Basseterre are between 23.9°C (75°F) and 26.6°C (80°F). The country gets about 2,400 mm (94 inches) of rain each year.
| Climate data for Saint Kitts and Nevis (1991–2015) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 23.9 (75.0) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.5 (77.9) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.4 (77.7) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 150 (5.9) |
102 (4.0) |
99 (3.9) |
153 (6.0) |
219 (8.6) |
181 (7.1) |
214 (8.4) |
232 (9.1) |
222 (8.7) |
289 (11.4) |
286 (11.3) |
225 (8.9) |
2,372 (93.3) |
| Source: Climate Change Knowledge Portal | |||||||||||||
People and Sports
Population Numbers
The population of Saint Kitts and Nevis is about 53,000 people. This number has stayed about the same for many years. In the late 1800s, there were 42,600 residents. It slowly grew to over 50,000 by the mid-1900s. Between 1960 and 1990, the population dropped to 40,000. Then it rose again to its current level. About three-quarters of the people live on Saint Kitts. About 15,500 of them live in the capital, Basseterre. Other big towns on Saint Kitts are Cayon (3,000 people) and Sandy Point Town (3,000 people). On Nevis, Gingerland has 2,500 people and Charlestown has 1,900.
Popular Sports
Cricket is very popular in Saint Kitts and Nevis. Talented players can be chosen to play for the West Indies cricket team. Runako Morton, a famous cricketer, was from Nevis. Saint Kitts and Nevis was the smallest country to host matches for the 2007 Cricket World Cup.
Rugby and netball are also common sports.
The Saint Kitts and Nevis national football team, called the "Sugar Boyz," has done well internationally. They reached the semi-final round for the 2006 FIFA World Cup qualifiers. They beat the United States Virgin Islands and Barbados. Then they faced stronger teams like Mexico and Trinidad and Tobago.
The St Kitts and Nevis Billiard Federation (SKNBF) is in charge of cue sports. It is part of the Caribbean Billiards Union.
Kim Collins is the country's best track and field athlete. He won gold medals in the 100 metres at the World Championships and Commonwealth Games. He was the first athlete from the country to reach an Olympic final at the 2000 Summer Olympics. He and three other athletes represented Saint Kitts and Nevis at the 2008 Summer Olympics. The four by one hundred meter relay team won a bronze medal at the 2011 world championships. Jason Rogers, Antoine Adams, and Brijesh Lawrence were on the team with Collins.
The Economy of the Islands
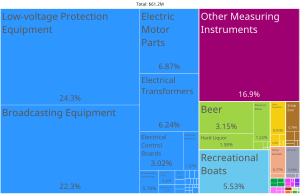
Saint Kitts and Nevis is a country with two islands. Its economy relies mostly on tourism, farming, and light manufacturing. Sugar used to be the main export since the 1940s. But making sugar became too expensive. Also, world prices for sugar were low. So, the government worked to rely less on sugar. They wanted to grow other crops. In 2005, the government closed the state-owned sugar company. It had been losing money.
Saint Kitts and Nevis depends a lot on tourism for its economy. This industry has grown a lot since the 1970s. In 2009, nearly 600,000 tourists visited Saint Kitts. This was a big increase from 2007. However, the tourism industry slowed down during the Global financial crisis. It has only recently returned to its previous levels. In recent years, the government has tried to make the economy more diverse. They are focusing on farming, tourism, making goods for export, and offshore banking.
In July 2015, Saint Kitts and Nevis signed a tax agreement with Ireland. This agreement helps countries share information about taxes. It helps with international cooperation.
Getting Around the Islands
Saint Kitts and Nevis has two international airports. The bigger one is Robert L. Bradshaw International Airport on Saint Kitts. It has flights to the Caribbean, North America, and Europe. The other airport is Vance W. Amory International Airport on Nevis. It has flights to other parts of the Caribbean.
The St. Kitts Scenic Railway is the last working railroad in the Lesser Antilles.
Images for kids
-
The Spanish capture of Saint Kitts in 1629 by Fadrique de Toledo, 1st Marquis of Villanueva de Valdueza
See also
 In Spanish: San Cristóbal y Nieves para niños
In Spanish: San Cristóbal y Nieves para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |