Economy of California facts for kids
 |
|
| Statistics | |
|---|---|
| GDP | $3.89 trillion (2023) |
|
GDP per capita
|
$100,042 (2023) |
|
Population below poverty line
|
13.3% (absolute) 19.0% (relative) |
|
Labor force
|
19,254,000 (November 2022) |
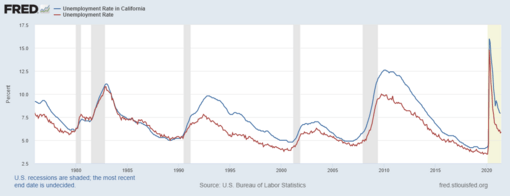
| Unemployment | 4.8% (Oct. 2023) |
| Public finances | |
| Revenues | $195.7 billion (2022-23) |
| Expenses | $286.4 billion (2022-23) |
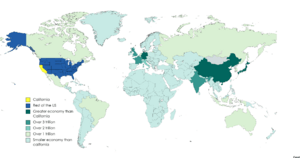
The economy of California is the largest in the United States. In 2023, its total economic output, called gross state product (GSP), was about $3.89 trillion. This makes California the biggest economy of any state or region in the world.
If California were its own country, its economy would be the fifth largest globally in 2022. It would be bigger than India and just behind Japan. California is also home to Silicon Valley, where many of the world's biggest technology companies are located. These include Apple, Alphabet (which owns Google), and Nvidia. Many large companies, including 11 of the Fortune 100, have their main offices in California.
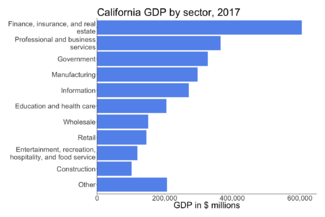
California is the most populated U.S. state and has many different climates. Because of this, its economy is very diverse. Important parts of the economy include finance, business services, government, and manufacturing. A lot of the economic activity happens in cities along the coast. Los Angeles is famous for its media and entertainment, especially Hollywood. The San Francisco Bay Area is a major center for technology.
Both Los Angeles and the San Francisco Bay Area, along with other big ports like San Diego, are important for trade. They help goods move in and out of the United States. Also, California's farming industry produces more than any other U.S. state. The Central Valley is one of the most productive farming areas on Earth. It grows more than half of the country's fruits, vegetables, and nuts. However, recent droughts in California have been affecting farming and other businesses.
Contents
California's Economic Journey
Early History and the Gold Rush
California has seen many people move there over time. After the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo was signed in 1848, the U.S. gained California and other lands from Mexico. This led to quick growth and development. In 1848, gold was discovered, starting the famous California gold rush.
Cities like San Francisco, San Jose, and Sacramento grew fast. They worked hard to provide supplies for the many gold miners. Los Angeles was much smaller back then, with fewer than 5,000 people.
Becoming a State and Education Growth
By 1850, California's population had grown to over 110,000 people. Because of this rapid growth and the gold being found, California was able to become a state in 1850. It joined the U.S. as a free state, which means it did not allow slavery.
Soon after becoming a state, California started offering widespread elementary school education. In the 1930s, California also led the way in providing high school education. The state has a long history of supporting college education too. Today, there are three public college systems:
- The California State University (CSU) system, started in 1857. It is the largest university system in the U.S.
- The University of California (UC) system, started in 1868.
- The California Community College System (CCCS), started in 1967.
California also has many private colleges and universities, like California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Stanford University.
Connecting the State: Transportation
In the early days, about half of the new settlers came to California by wagon trains on the California Trail. This trip took about 140-160 days. The other half came by paddle steamers, traveling through Panama or Nicaragua. This sea trip took about 40 days.
The Panama Railroad was built in 1855, making the sea route much faster for passengers. Most goods, however, traveled by sailing ship around Cape Horn at the tip of South America. This long journey took 120 to 200 days. Shipping by sea was slow but cheap.
In 1861, the First Transcontinental Telegraph allowed fast communication with the East Coast. Then, in 1869, the First transcontinental railroad was finished. This cut the travel time across the country to about 7 days. This rail link helped California's trade grow much faster. In 1886, the first refrigerated train cars started operating. This made it possible to send fresh fruits and vegetables, like oranges, from California to the eastern U.S. This helped the citrus industry in Southern California boom.
Farming and Water in California
Early farming in California was mostly near the coast and in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta. Winter wheat was an early crop that grew well without much water. By the 1880s, many grape fields were planted for making wine.
Chinese workers and others built many miles of levees in the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta. This helped control floods and turn wet land into farms. Today, this area grows a lot of rice. Later, big irrigation projects brought water to more parts of the Central Valley.
The Central Valley Project (1935) and the even larger California State Water Project (1950s) were built. These projects collect water from melting snow in the Sierra Nevada (U.S.) mountains. They use a huge system of dams and canals, like the California Aqueduct, to move water to farms and cities. The Colorado River Aqueduct and the Los Angeles Aqueduct also bring water from other rivers. California needs a lot of water, and managing it is a big challenge.

Farming is a very important part of California's economy. The state leads the U.S. in growing fruits, vegetables, grapes for wine, and nuts. California produces most of the wine in the U.S. Dairy products, like milk, also bring in a lot of money for farms. California's farms are very productive because of good soil, a long growing season, and modern farming methods. Irrigation is key because the long, dry summers mean most crops would not grow without it.
| Top 30 Publicly Traded Companies in California for 2022 (by revenue) |
|||||
| State Rank | Corporation | U.S. Rank | |||
| 1 | Apple | 4 | |||
| 2 | Alphabet | 8 | |||
| 3 | Chevron | 10 | |||
| 4 | Meta | 31 | |||
| 5 | Wells Fargo | 47 | |||
| 6 | Disney | 48 | |||
| 7 | Intel | 62 | |||
| 8 | HP Inc. | 63 | |||
| 9 | TD Synnex | 64 | |||
| 10 | Cisco | 82 | |||
| 11 | Qualcomm | 98 | |||
| 12 | Broadcom | 123 | |||
| 13 | Molina | 126 | |||
| 14 | Uber | 127 | |||
| 15 | Netflix | 129 | |||
| 16 | Salesforce | 133 | |||
| 17 | Visa | 137 | |||
| 18 | PayPal | 148 | |||
| 19 | Gilead Sciences | 150 | |||
| 20 | Nvidia | 152 | |||
| 21 | Amgen | 154 | |||
| 22 | Applied Materials | 155 | |||
| 23 | AMD | 167 | |||
| 24 | PG&E | 180 | |||
| 25 | Western Digital | 221 | |||
| 26 | Ross | 223 | |||
| 27 | Adobe | 233 | |||
| 28 | Block | 234 | |||
| 29 | Lam Research | 240 | |||
| 30 | Edison | 241 | |||
| Further information: List of California companies Source: Fortune/Patch |
|||||
Shipping and Entertainment Industries
California's location on the Pacific coast led to the building of major seaports. These include ports in San Francisco, Sacramento, Long Beach, Los Angeles, and San Diego. These ports helped California trade with other parts of the U.S. and with countries in South America, Asia, and Oceania. During World War II, many military bases and factories were built in California to support the war effort.
California also became a leader in the movie industry. In the early 1900s, film companies started moving to Southern California. They liked the cheap land, good weather all year, and many talented people. Since the 1920s, California, especially Hollywood and Burbank, has been a major center for movies, TV shows, and cartoons.
Technology and Tourism Boom
After 1945, manufacturing of electronics, computers, and other machinery grew quickly. Stanford University played a big role in developing California's high-tech industry. Leaders at Stanford encouraged professors and students to start their own companies. This led to the growth of companies like Hewlett-Packard, Intel Corporation, Apple Inc., and Google in what is now known as Silicon Valley.
Silicon Valley is still a top place for new technology ideas and development. It receives a large share of all venture capital (money invested in new businesses) in the U.S.
Tourism is another important part of California's economy. Yosemite National Park, established in 1890, and other national parks attract many visitors. Disneyland, which opened in 1955, and other theme parks also bring millions of tourists each year.
California has also created many new ideas in retail. Famous fast food restaurant chains like McDonald's and Taco Bell started here. Also, credit cards like Visa Inc. (originally BankAmericard) and MasterCard were first developed in California.
Key Economic Sectors
The U.S. government uses a system called North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) to group economic activities. This helps to understand today's economy better.
The largest industry in California, like in most states, is government. It employs about 2.5 million people. The second largest industry is Healthcare and Social Assistance.
Global Trade and Visitors

California earns a lot of money from international trade and tourism. In 2007, California exported $134 billion worth of goods. A large part of this was computers and electronics. These exports create many high-paying jobs for Californians.
Foreign companies also invest a lot in California. In 2005, companies controlled by foreign investors employed over 542,600 workers in California. Major investors came from Japan, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, France, and Germany. Tourism also brings in a lot of money, with total travel spending reaching $96.7 billion in 2008. Los Angeles County gets the most tourists in the state.
Farming and Energy
California has a very large agriculture industry. This includes growing fruits, vegetables, dairy farming, and making wine. The state's farming industry generates over $100 billion in related economic activity. California's farm sales first went over $30 billion in 2004, making it twice as big as any other state's agriculture industry.
Milk is California's top farm product. The state's almond industry sells the most products to other countries, with $4.5 billion in foreign sales in 2016. California also leads the U.S. in strawberry production, growing over 80% of the nation's strawberries.
Oil drilling has been important for California's growth. Major oil discoveries happened in areas like Bakersfield, Long Beach, Los Angeles, and off the coast. Solar power in California is also a growing industry, employing over 43,000 people. Many of these jobs are in the San Francisco Bay Area, Los Angeles, San Diego, and the Central Valley.
Personal Income and Housing
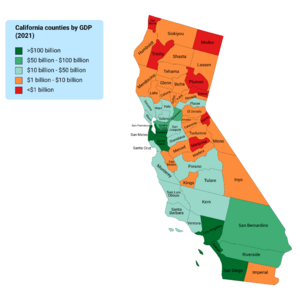
In 2017, the average income per person in California was $58,272. This ranked 6th in the nation. However, income varies a lot depending on where people live and what job they have. The counties with the highest incomes are Marin County and San Francisco County. These areas have average incomes over $100,000 per person. Some coastal cities in the San Francisco Bay Area and Greater Los Angeles Area are among the wealthiest places in the U.S.
California has some of the most expensive housing markets in the U.S. In some communities, average house prices are between $1 million and $2 million. The Central Valley in northern California and the Inland Empire in Southern California are generally less expensive. However, even in these areas, prices are still much higher than in most other parts of the country. Some farming counties in the Central Valley have higher poverty rates.
In the early 2000s, housing prices in California increased very quickly. But then, in 2007 and 2008, prices dropped sharply as a housing bubble burst. Many homes went into foreclosure (when a bank takes back a property because the owner can't pay).
Taxes in California
| California State and Local Tax Revenue 2011 (in thousands) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Revenue type |
State and local revenue |
State revenue |
Local revenue |
| General revenue from own sources | 268,224,2941 | 142,927,463 | 125,296,8312 |
| Various taxes | 185,218,208 | 116,695,284 | 68,522,924 |
| Property taxes | 53,506,490 | 3,207,301 | 50,299,189 |
| Sales and gross receipts tax | 59,179,135 | 45,147,657 | 14,031,478 |
| General sales tax | 40,101,659 | 30,996,372 | 9,105,287 |
| Selective sales tax | 19,077,476 | 14,151,285 | 4,926,191 |
| Motor fuel tax | 5,705,527 | 5,705,527 | (X) |
| Alcoholic beverage tax | 334,178 | 334,178 | (X) |
| Tobacco products tax | 905,245 | 905,245 | (X) |
| Public utilities | 3,974,053 | 790,501 | 3,183,552 |
| Other selective sales tax | 8,158,473 | 6,415,834 | 1,742,639 |
| Individual income tax | 50,508,441 | 50,508,441 | (X) |
| Corporate income tax | 9,613,594 | 9,613,594 | (X) |
| Vehicle license tax | 3,131,975 | 3,090,610 | 41,365 |
| Other taxes | 9,278,573 | 5,127,681 | 4,150,892 |
| Charges and misc. general revenue | 83,006,086 | 26,232,179 | 56,773,907 |
| Current charges | 60,339,164 | 16,701,739 | 43,637,425 |
| Education K-14 | 10,168,290 | 7,258,220 | 2,910,070 |
| Institutions of higher education | 9,104,750 | 7,252,680 | 1,852,070 |
| School lunch sales (gross) | 426,647 | (X) | 426,647 |
| Hospital fees | 17,007,989 | 6,542,258 | 10,465,731 |
| Highway fees | 651,115 | 38,490 | 612,625 |
| Airport fees | 2,498,811 | (X) | 2,498,811 |
| Parking facilities | 435,455 | 12,261 | 423,194 |
| Sea and inland port facilities | 1,334,929 | (X) | 1,334,929 |
| Natural resources | 2,137,297 | 1,297,670 | 839,627 |
| Parks and recreation | 1,416,246 | 96,167 | 1,320,079 |
| Housing and community development | 951,021 | 487 | 950,534 |
| Sewerage | 6,485,827 | (X) | 6,485,827 |
| Solid waste management | 2,469,196 | (X) | 2,469,196 |
| Other charges & fees | 14,782,988 | 1,456,186 | 13,326,802 |
| Miscellaneous general revenue | 22,666,922 | 9,530,440 | 13,136,482 |
| Interest earnings | 6,253,309 | 2,374,030 | 3,879,279 |
| Special assessments | 1,466,292 | (X) | 1,466,292 |
| Sale of property | 333,326 | 14,168 | 319,158 |
| Other general revenue | 14,613,995 | 7,142,242 | 7,471,753 |
| Utility revenue | 25,316,003 | 2,496,154 | 22,819,849 |
| Water supply | 10,334,952 | (X) | 10,334,952 |
| Electric power | 12,795,350 | 2,496,154 | 10,299,196 |
| Gas supply | 242,213 | (X) | 242,213 |
| Transit | 1,943,488 | (X) | 1,943,488 |
| Insurance trust revenue3 | 149,964,876 | 120,379,020 | 29,585,856 |
| Unemployment compensation | 17,009,070 | 17,009,070 | (X) |
| Employee retirement | 124,640,863 | 95,055,007 | 29,585,856 |
| Workers' compensation | 2,077,574 | 2,077,574 | (X) |
| Other insurance trust revenue | 6,237,369 | 6,237,369 | (X) |
| Notes: 1. Federal transfers add $75.876 billion to state and local funds. |
|||
Taxes in California are collected by the California Franchise Tax Board. California is divided into 58 California counties, 480 cities, and about 3,400 special districts. These local governments have their own taxes and fees. Most taxes are collected by the state and then shared with cities, counties, and school districts.
Income Tax
California has a state personal income tax. The highest rate is 13.3%, but this only applies to incomes over $1 million. For a married couple, the first $15,164 of taxable income is taxed at 1.0%. The tax rate increases as income goes up. For example, income between $99,548 and $508,500 is taxed at 9.3%. A married couple earning less than $18,182 pays no income tax.
Sales Tax
The average sales tax in California is about 8.4%. This is one of the highest in the nation. The sales tax rate changes slightly depending on the city and county, from 7.25% to 10.0%. Some things are exempt from sales tax, like food, prescription drugs, and services. The state collects sales taxes and then gives a portion to local governments.
Property Tax
California's property tax rates are capped by Proposition 13, which was passed in 1978. Property taxes in California were over $54 billion in 2011. These taxes are mainly used to fund local governments, especially schools. When a property is sold, it is taxed at 100% of its value. The maximum tax on real estate is 1.0% plus any local voter-approved fees for things like school improvements or flood control.
Property tax increases are limited to 2.0% of the previous year's value or the inflation rate, whichever is lower. This means older properties are often taxed at a lower rate than newly sold ones. This rule was put in place to encourage people to stay in their homes longer.
Other Taxes
California has high gasoline and diesel taxes. Gasoline is taxed at $0.719 per gallon, and diesel at $0.749 per gallon. These are the highest fuel taxes in the U.S.
Cigarette excise taxes in California are $2.87 per pack. When you add the federal tax, the total excise tax is $3.88 per pack. Sales tax is also added to the price of cigarettes, which means you pay a tax on a tax.
California also has taxes on alcoholic beverages. The tax varies by drink, from 20 cents per gallon for wine or beer to $6.60 per gallon for strong spirits.
Employers pay unemployment insurance based on their company's turnover. The rate is usually between 1.0% and 6.0% of the first $7,000 of a worker's income.
See also
 In Spanish: Economía de California para niños
In Spanish: Economía de California para niños