Geography of Indiana facts for kids
The geography of Indiana is all about its land, rivers, and where it is on the map. Indiana is a state in the north-central United States. It touches Lake Michigan in the north. Other states around Indiana are Michigan (north and northeast), Illinois (west), Kentucky (south), and Ohio (east). The entire southern border of Indiana is the Ohio River.
Contents
Quick Facts About Indiana
- Indiana covers about 36,420 square miles (94,321 square kilometers). This makes it the 38th largest state in the U.S.
- Lake Michigan is the biggest body of water partly or fully inside Indiana.
- The highest spot in Indiana is Hoosier Hill in Wayne County. It's about 1,257 feet (383 meters) above sea level.
- The lowest natural point is on the Ohio River. This is where Indiana, Illinois, and Kentucky meet. It's about 333 feet (101 meters) above sea level.
Indiana's Borders and Rivers
Indiana shares its northern border with Lake Michigan and the state of Michigan. To the east is Ohio, and to the south is Kentucky, with the Ohio River forming the border. Illinois is to the west. Indiana is one of the states near the Great Lakes.
When Indiana became a state in 1816, its northern border was moved. This gave Indiana a useful part of the Lake Michigan shoreline.
The Wabash River is 475 miles (764 kilometers) long. It flows through Indiana from the northeast to the southwest. Then it goes south, mostly along the border with Illinois. This river is so important that it's mentioned in famous Indiana songs. The Wabash is the longest river east of the Mississippi River that flows freely. The White River is another important river that winds through central Indiana.
Indiana has 24 state parks, nine man-made reservoirs, and hundreds of lakes. There are also special areas protected by the U.S. government, like:
- George Rogers Clark National Historical Park in Vincennes
- Indiana Dunes National Park near Michigan City
- Lincoln Boyhood National Memorial in Lincoln City
- Hoosier National Forest in Bedford
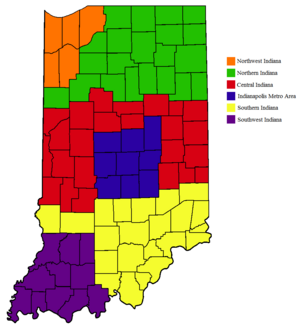
Exploring Indiana's Regions
Indiana can be split into three main parts, each with its own special features.
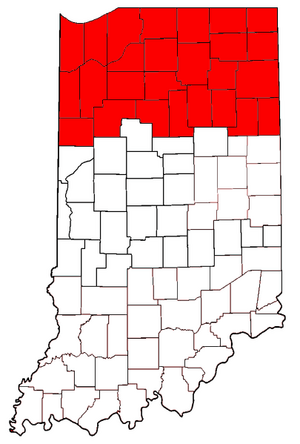
Northern Indiana
Northern Indiana includes 26 counties in the top third of the state. The land here is mostly flat or gently rolling. It ranges from 600 to 1,000 feet (183 to 305 meters) above sea level. You can find higher, hillier areas called terminal moraines and many glacial kettle lakes. Along Lake Michigan, there are sand dunes and sand ridges, some almost 200 feet (61 meters) tall.
Besides some cities, much of Northern Indiana is farmland. Heavy industry is also a big part of the economy, especially in the eastern two-thirds of the region. This area is often linked to the "Rust Belt" because of its industrial history. Northern Indiana is also the most diverse part of the state.
The northwest corner of Indiana is part of the Chicago metropolitan area. Almost a million people live here. Cities like Gary and others near Lake Michigan are like suburbs of Chicago. These areas are in the Central Time Zone, just like Chicago. The South Shore Line is a train that connects South Bend to Chicago. Along the Lake Michigan shore, you'll find both factories and beautiful parks. The Indiana Dunes National Park and Indiana Dunes State Park are famous natural spots.
Northwest Indiana has a unique landscape with "swells" (higher ground) and "swales" (lower, marshy areas). These are left over from ancient Lake Michigan beaches. Different plants and animals live in these different areas. Marsh plants are in the swales, while forests or even cactus can be found in the drier swells.

The Kankakee River flows through northern Indiana. It helps separate the Chicago suburbs from the rest of the state. Before it was drained for farming, the Kankakee Marsh was one of the biggest freshwater marshes in the country. South of the Kankakee, there's a large area of prairie land. This is the eastern edge of the huge Grand Prairie that covers Iowa and Illinois.
The South Bend area is in north central Indiana. It's the main business center for the Michiana region. Other cities here include Elkhart, Mishawaka, and Goshen. Fort Wayne, Indiana's second largest city, is in the northeast. It's a major transportation hub. East of Fort Wayne, the land is very flat.
Northeastern Indiana has many lakes, most of which are kettle lakes. These were formed by glaciers thousands of years ago. Some famous lakes include Lake James, Lake Maxinkuckee, Lake Wawasee, and Lake Tippecanoe. Lake Wawasee is Indiana's largest natural lake. Lake Tippecanoe is the deepest, going down over 120 feet (37 meters). Both are in Kosciusko County. Chain O'Lakes State Park has 11 lakes, with 8 connected by natural channels.
Michiana Area
The middle part of Northern Indiana is known as the Indiana section of Michiana. South Bend is the main city for culture and business in this area.
Maumee River Valley
The eastern part of Northern Indiana is centered around Fort Wayne and the Maumee River basin.
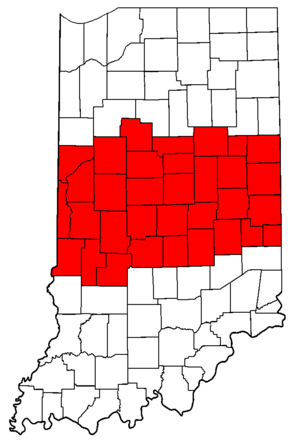
Central Indiana
Central Indiana includes 33 counties in the middle of the state. Many people in Indiana think of Central Indiana as the Indianapolis metropolitan area. The biggest city here is Indianapolis, which is the state capital. Other important cities are Anderson, Kokomo, and Muncie. About 3.3 million people live in Central Indiana, making it the most populated region.
The land in Central Indiana has low, gently rolling hills and shallow valleys. Some counties are quite flat, while others are more rugged. Elevations range from 600 to 1,000 feet (183 to 305 meters) above sea level. Forests and farms cover these plains and river valleys. The highest point in Indiana, Hoosier Hill, is in northern Wayne County. Many areas have a mix of farm fields and forests. You can find sandstone ravines carved by glaciers in west-central Indiana, especially in Turkey Run and Shades state parks.
Central Indiana's economy relies on healthcare, education, farming, and manufacturing. Many major universities are located here, such as Ball State University, Purdue University, and Indiana State University.
Southern Indiana
Southern Indiana has a mix of farmland, forests, and very hilly areas. This is especially true near Louisville and in the south-central limestone hills. These hills stretch from the Ohio River north to Greencastle. There are also wide, flat valleys along the Wabash and Ohio rivers. The Hoosier National Forest is a large nature preserve of 200,000 acres (809 square kilometers) in south-central Indiana.
Evansville, the third largest city in Indiana, is in the southwest corner. It's part of a "tri-state area" that includes Illinois and Kentucky. Cities like Clarksville and New Albany are part of the Louisville metropolitan area. Bloomington, home to Indiana University, is in the northern part of this region. Vincennes is the oldest settlement in Indiana, founded by French traders in 1732. It was also Indiana's first capital.
Southern Indiana has more varied land than the north. It generally has more hills and different landforms. For example, the ""Knobs"" are a series of 1,000-foot (305-meter) hills that run along the Ohio River. The flat, flood-prone areas where the Wabash, White, and Ohio Rivers meet have many plants and animals usually found further south. Brown County is famous for its colorful autumn leaves and its charming town of Nashville. Harrison and Crawford Counties have popular commercial caves like Wyandotte and Marengo.
The limestone rock in Southern Indiana has created many caves. It's also one of the biggest limestone quarry regions in the U.S. Many famous buildings in Indiana, like the Indiana Statehouse, are made with Indiana limestone. This limestone has also been used in other famous structures across the United States, such as the Empire State Building and the Pentagon.
Indiana's Landforms
Indiana is divided into three main physical regions:
- The Great Lakes Plain in the northern third of the state.
- The Tipton Till Plain in the central third.
- The Southern Hills and Lowlands region in the southern third.
Indiana's Geology
Two-thirds of Indiana is covered by glacial till, which is rock and soil left by glaciers. This layer can be from a few feet to hundreds of feet thick. So, the visible geology of the state is mostly from the Quaternary period. The southern third of the state was not covered by glaciers, so the older bedrock is visible there.
The oldest bedrock is from the Ordovician period. These layers of shale and limestone are only seen on the surface in the southern parts. Next are bands of Silurian age bedrock, mostly limestone. Then come Devonian rocks, which pass under cities like Lafayette and Indianapolis. The youngest bedrock is from the Carboniferous age. It covers almost a third of the state's southwestern area. This is where Indiana's "coal measures" are found, and coal mining is a big part of the local economy.
Coal Mining Areas
Indiana's main coal mining areas are in the southwest corner of the state. Here, the bedrock is from the Pennsylvanian era.
Indiana's Rivers and Waterways
The Wabash River is the longest river in Indiana. It flows across the state from east to west. The Wabash and its main branches, like the White River and Tippecanoe River, drain Central Indiana. The Iroquois and Kankakee Rivers start in Indiana and flow west into Illinois.
The St. Joseph River flows from Michigan through northern Indiana at South Bend. It then returns to Michigan and ends at Lake Michigan. The Maumee River in the northeast is formed by two other rivers joining in Fort Wayne. It then flows into Ohio and ends at Lake Erie. The Ohio River forms the southern border of the state. It drains the lower counties.
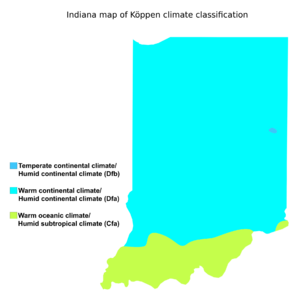
Climate in Indiana
Indiana has a humid continental climate. This means it has warm, humid summers and cold winters. The state experiences all four seasons clearly.