Lake Michigan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Michigan |
|
|---|---|

Lake Michigan seen from space (August 19, 2019). Chicago is at the southwest end.
|
|
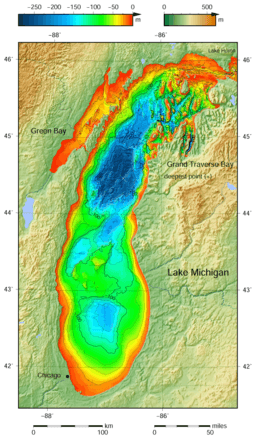
Map showing Lake Michigan's depths. The deepest spot is marked with "×".
|
|
| Location | United States |
| Group | Great Lakes |
| Coordinates | 44°N 87°W / 44°N 87°W |
| Lake type | Formed by glaciers |
| Primary inflows | Straits of Mackinac, Fox River, Grand River, Menominee River, Milwaukee River, Muskegon River, Kalamazoo River, St. Joseph River |
| Primary outflows | Straits of Mackinac; also, controlled flow through locks on the Chicago River (and its North Shore Channel), and Calumet River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 307 mi (494 km) |
| Max. width | 118 mi (190 km) |
| Min. width | 91 mi (146 km) |
| Surface area | 22,300 sq mi (58,000 km2) |
| Average depth | 279 ft (85 m) |
| Max. depth | 923 ft (281 m) |
| Water volume | 1,183 cu mi (4,930 km3) |
| Residence time | 99 years |
| Shore length1 | 1,400 mi (2,300 km) plus 238 mi (383 km) for islands |
| Surface elevation | 577 ft (176 m) |
| Islands | see list |
| Settlements | see list |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake Michigan is one of the five amazing Great Lakes in North America. It's like a giant freshwater sea! This lake is the second-largest of the Great Lakes in terms of how much water it holds and how deep it is. It's also the third-largest by its surface area.
Lake Michigan is special because it's the only Great Lake that is entirely within the United States. The other four Great Lakes are shared with Canada. It's the biggest lake in the world that is completely inside one country. Lake Michigan touches four U.S. states: Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan. Many important cities, like Chicago and Milwaukee, are located along its beautiful shores. The name Michigan comes from the Ojibwe language, meaning "great water."
Contents
Lake Michigan: A Great North American Lake
A Look Back: Lake Michigan's Past
Early People and European Explorers
Long ago, different groups of Native Americans lived around Lake Michigan. The Hopewell people were some of the earliest known inhabitants. Later, the Late Woodland Native Americans lived here. When European explorers first arrived in the early 1600s, they met descendants of these groups. These included the Ojibwe, Menominee, Potawatomi, and other peoples.
The French explorer Jean Nicolet is thought to be the first European to see Lake Michigan, possibly around 1634. Early maps sometimes called it "Lake Illinois." In the 1640s and 1650s, conflicts over the fur trade caused many Native American groups to move around the lake.
Trade Routes and Growing Cities
The Straits of Mackinac, which connect Lake Michigan to Lake Huron, were very important. They were a key travel route for Native Americans and a busy place for fur trading. French explorers like Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet used Lake Michigan as part of their journey to find the Mississippi River in 1673.
By the 1800s, Lake Michigan became vital for the growth of cities like Chicago. Ships carried huge amounts of grain and other goods across the lake, helping the Midwestern United States develop. Even after railroads became popular, shipping on the lake remained very important.
Modern Discoveries and Environmental Changes
In 1985, scientist J. Val Klump was the first person to reach the deepest part of Lake Michigan using a special underwater vehicle. More recently, scientists have studied how the lake is changing. A 2018 report from Purdue University showed that the surface temperature of Lake Michigan has been slowly getting warmer since 1980. This warming can affect the homes of native fish and other animals.
How Lake Michigan Works: Hydrology
Lake Facts and Figures
Lake Michigan is divided into two main parts by an underwater ridge called the Milwaukee Reef. Water in each part tends to flow in a clockwise direction, influenced by rivers and winds. Strong westerly winds push surface water towards the east. This helps keep the climate milder on Michigan's western side.
Even though they have different names, Lake Michigan and Lake Huron are actually connected by the wide and deep Straits of Mackinac. This means they have the same water level and are considered one large body of water by scientists. Together, they form the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface area! The Mackinac Bridge is often seen as the dividing line between them.
Lake Michigan has a surface area of about 22,404 sq mi (58,030 km2). It is 307 miles (494 km) long and 118 miles (190 km) wide. The lake's average depth is 279 feet (85 m), and its deepest point is 923 feet (281 m). It holds an enormous 1,183 cu mi (4,930 km3) of water. Green Bay in the northwest and Grand Traverse Bay in the northeast are its largest bays.
Islands to Explore
Most of Lake Michigan's islands are found in its northern part.
- Beaver Island is the largest, covering 55.8 sq mi (145 km2). It's part of an archipelago that includes islands like Garden Island and High Island.
- The Fox Islands include North Fox Island and South Fox Island.
- The Manitou Islands are made up of North Manitou Island and South Manitou Island.
- Other islands are found in places like Grand Traverse Bay and near the Door Peninsula in Wisconsin. Washington Island is a well-known island in Wisconsin.
- Northerly Island in Chicago is a human-made peninsula that is home to the Adler Planetarium.
Connecting to Other Waters
In the mid-1900s, the Saint Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway were built. These allowed large ships to travel from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes. However, many modern ocean-going ships are too wide for the locks on these routes. Special "lake freighters" are used for shipping on the lakes. During winter, large parts of the Great Lakes can freeze, which stops most shipping.
Lake Michigan is also connected to the Gulf of Mexico through the Illinois Waterway, which links to the Illinois River and the Mississippi River. This route is busy with barges carrying goods. Smaller boats can also travel between the Great Lakes and the Atlantic Ocean using the Erie Canal in New York.
Water Levels: Highs and Lows
The water level in Lake Michigan changes throughout the year. It's usually highest in the summer and lowest in the winter. For example, in October 1986, the lake reached a very high level. In January 2013, the water level dropped to an all-time low since records began in 1918. This was due to less snow in the winter and very hot, dry weather in the summer of 2012. Since then, water levels have risen significantly, reaching historical record highs.
Drinking Water and Protecting the Lake
Lake Michigan provides drinking water for millions of people living nearby. The Great Lakes are managed by a group called the Conference of Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Governors and Premiers. This group includes leaders from U.S. states and Canadian provinces that border the lakes. They work together to protect this important resource.
However, environmental challenges still exist. Some industries near the lake have faced concerns about pollution. For example, an oil refinery in Whiting, Indiana, was reported to have released waste into the lake, and in March 2014, it was responsible for an oil spill. Protecting the lake from pollution is a continuous effort.
Along the Shores: Beaches, Cities, and Parks
Sandy Beaches and Towering Dunes
Lake Michigan is famous for its many beautiful beaches. People sometimes call this area the "Third Coast" of the United States. The sand is often soft and light-colored, and it can even make a squeaking sound when you walk on it, which is why it's called "singing sands."
The eastern shore of Lake Michigan has the largest freshwater sand dune system in the world! These dunes can rise hundreds of feet above the lake. You can see amazing dune formations at places like Indiana Dunes National Park and Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore. On the western shore, you can find smaller dunes at places like Illinois Beach State Park. The water is usually clear and cool, even in late summer.
Cities by the Lake
About twelve million people live along the shores of Lake Michigan. Many live in the large metropolitan areas of Chicago and Milwaukee. In northern Michigan and Door County, Wisconsin, tourism is a big part of the economy. Many people have summer homes along the waterfront. The southern end of the lake, near Gary, Indiana, is a busy industrial area.
Here are some of the cities you can find on Lake Michigan's shores: Illinois
Indiana
Michigan
Wisconsin
Parks for Fun and Nature
Many parks protect the natural beauty of Lake Michigan's shoreline. The National Park Service manages the Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore and Indiana Dunes National Park. Parts of the shoreline are also within national forests like the Hiawatha National Forest.
There are also many state and local parks where you can enjoy the lake:
- Chicago Park District Beaches
- Grand Haven State Park
- Holland State Park
- Hoffmaster State Park
- Illinois Beach State Park
- Indiana Dunes State Park
- Kohler-Andrae State Park
- Ludington State Park
- Muskegon State Park
- Peninsula State Park
- Saugatuck Dunes State Park
- Silver Lake State Park
- Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore
- Traverse City State Park
- Van Buren State Park
- Warren Dunes State Park
- Whitefish Dunes State Park
- Wilderness State Park
Fun and Work on Lake Michigan
Fishing in the Lake
Lake Michigan is home to many kinds of fish. Originally, it had fish like lake whitefish, lake trout, and yellow perch. Over time, some invasive species, like sea lampreys and alewife, entered the lake and caused problems for native fish.
To help balance the ecosystem, different types of salmon and trout, such as coho and chinook salmon, were introduced. These fish became very popular for sport fishing! Today, Lake Michigan is stocked every year with these fish, and some have even started to reproduce naturally in the rivers that flow into the lake. Commercial fishing also takes place, mainly for lake whitefish.
Shipping Goods
Like all the Great Lakes, Lake Michigan is used for shipping large amounts of goods. Ships carry things like iron ore, grain, and coal. These materials are often used in industries like steelmaking. While some liquid and containerized cargo is shipped, many modern container ships are too wide to pass through the locks that connect the Great Lakes to the ocean.
Lake Ferries
Two passenger and vehicle ferries cross Lake Michigan, connecting Wisconsin and Michigan. The historic steamship, SS Badger, travels daily between Manitowoc, Wisconsin, and Ludington, Michigan, from May to October. The Lake Express, which started in 2004, is a faster ferry that carries people and cars between Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and Muskegon, Michigan.
Tourism and Recreation
Tourism and recreation are huge industries around the Great Lakes. People enjoy many water sports on Lake Michigan, including yachting, kayaking, and even lake surfing! Small cruise ships also operate on the lake.
The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a special scenic road system that goes around all the Great Lakes. In winter, if you visit the lake, you might even see amazing "ice volcanoes" forming along the shore!
Images for kids
-
The Milwaukee lakefront
-
Chicago's Oak Street Beach
-
Lake Michigan beach at Holland State Park in Park Township, Michigan
-
Chicago's North Avenue Beach, Lincoln Park
-
Big Sable Point, Michigan in Ludington State Park
-
Lake view from the Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore, with people climbing uphill
-
Sleeping Bear Dunes from the Empire Bluffs Trail near Empire, Michigan
-
Eichelman Park in Kenosha, Wisconsin, with Lake Michigan in the background
-
Lake Michigan and the Chicago skyline from Portage, Indiana
See also
 In Spanish: Lago Míchigan para niños
In Spanish: Lago Míchigan para niños
- Breakwater Chicago
- Jardine Water Purification Plant
- Lake Michigan Shore AVA
- List of lighthouses in the United States
- Leelanau Peninsula
- Little Traverse Bay
- Port of Milwaukee
- Great Lakes offshore wind power potential
- United Air Lines Flight 389, a plane that crashed into the lake in 1965.