Blue jay facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Blue jay |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| In Algonquin Provincial Park (Canada), the large subspecies C. c. bromia occurs | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Cyanocitta
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cyanocitta cristata Linnaeus, 1758
|
|
 |
|
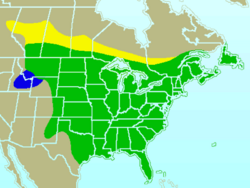
| Global range: yellow: breeding only; green: resident all year blue: wintering only | |
The blue jay (Cyanocitta cristata) is a beautiful passerine bird. It lives in North America. These birds are very good at adapting to different places. They are also known for being quite bold and eating many kinds of food.
Contents
What Does a Blue Jay Look Like?
Blue jays are about 22–30 cm (9–12 inches) long. This is from their beak to their tail. They weigh 70–100 grams (2.47–3.53 oz). Their wings can spread out to 34–43 cm (13–17 inches).
Their Special Crest
Blue jays have a special crown of feathers on their head. This is called a crest. They can raise or lower this crest. It shows how the bird is feeling.
- If a blue jay is excited or bold, its crest stands up tall.
- If it is scared, the crest spreads out like a brush.
- When the bird is eating or resting, the crest lies flat on its head.
Colors and Features
The feathers on their crest, back, wings, and tail are a lovely lavender-blue to mid-blue color. Their face is white. Their belly is off-white. A thin black stripe goes around their neck and along the sides of their head. The main feathers on their wings and tail are deep black, sky-blue, and white. Their beak, legs, and eyes are all black. Male and female blue jays look almost the same. Males are usually just a little bit bigger.
Blue jays have strong black beaks. They use them to crack open nuts and acorns. They also eat corn, grains, and seeds. Besides plants, they enjoy eating insects. These include beetles, grasshoppers, and caterpillars.
How Do Blue Jays Communicate?
Blue jays can make many different sounds. Each sound can also change a little bit. They are very good at copying other sounds.
Mimicking Sounds
Blue jays can even learn to mimic human speech! They are also amazing at copying the calls of local hawks. Sometimes, it's hard to tell if it's a hawk or a blue jay calling.
Common Calls
Their voice is very varied, like most jays. The most common sound is their "alarm call." This is a loud, almost gull-like scream. They also have a high-pitched "jayer-jayer" call. This call gets faster as the bird gets more excited. This call can sound a lot like a chickadee's song.
Blue jays use these calls to work together. They will "mob" predators like hawks. This means they gather together and chase the predator away from their nests.
Blue Jay Behavior
Blue jays are not very fast fliers. They fly about 32–40 km/h (20-25 mi/h) when they are not being chased. This makes them easy prey for hawks and owls in open areas. They fly with their body and tail held flat, using slow wing beats.
Interactions with Other Birds
Blue jays can sometimes be bold towards other birds. They might chase birds away from bird feeders. However, this doesn't happen as often as people think. This behavior can actually help other birds. Blue jays will chase away predatory birds like hawks and owls. These predators sometimes hunt jays. If a blue jay sees a predator in its area, it will scream loudly.
Smaller birds often understand this "alarm call." They will hide themselves when they hear it. Blue jays can also be aggressive towards humans who get too close to their nests. If an owl rests near a blue jay's nest during the day, the jays will mob it until it leaves.
What Do Blue Jays Eat?
Blue jays find their food both on the ground and in trees. They eat almost every type of plant and animal food. This includes acorns and beech nuts, weed seeds, grain, fruits, and other berries. They also like peanuts, bread, and meat. They eat small invertebrates like insects. In towns, they might eat scraps of food. They also visit bird feeders. Sometimes, they even eat eggs and baby birds from other nests, but this is rare. Blue jays will sometimes hide food for later. How much they do this depends on each bird.
How Do Blue Jays Raise Their Young?

The mating season for blue jays starts in mid-March and lasts until July. They can build a nest in any nice tree or large shrub. They often prefer evergreen trees. The nest is usually built about 3 to 10 meters high.
Building a Nest
The nest is shaped like a cup. It is made of twigs, small roots, strips of bark, moss, and other plant materials. They also use cloth, paper, and feathers. Sometimes, they add mud to the nest cup to make it stronger.
Raising a Family
Blue jays usually stay with the same partner for life. This is called being monogamous. Both the male and female help build the nest. They also both take care of the young birds. However, only the female sits on the eggs to keep them warm. While she is doing this, the male brings her food.
Female blue jays usually lay 4–5 eggs. They sit on the eggs for 16–18 days. This is called incubation. The young birds usually leave the nest when they are 17–21 days old.
How Smart Are Blue Jays?
Jays are known to be some of the smarter birds. They will watch a person put food down. As soon as the person walks away, the jays will fly down from their hiding spot and take the food. Like crows, jays will also watch people planting seeds. After the person leaves, the jays might dig up and eat the seeds.
Blue jays are very territorial birds. They will chase other birds away from a feeder to get an easier meal. Blue jays have a bad reputation for raiding other birds' nests. People think they often take eggs, baby birds, and even nests. However, this might not happen as much as people believe.
Images for kids
-
John James Audubon drawing circa 1830s
-
Merlin chasing a blue jay
-
Cyanocitta cristata cristata in Johnston County, North Carolina
-
C. c. bromia, Northern blue jay, juvenile, in Ontario, Canada
See also
 In Spanish: Chara azul para niños
In Spanish: Chara azul para niños













