Gatwick Airport facts for kids
Gatwick Airport, also known as London Gatwick Airport, is one of the main international airports serving London, Sussex, and Surrey. It's located near Crawley in West Sussex, about 30 miles south of central London. In 2024, Gatwick was the second busiest airport in the UK for passenger traffic, right after Heathrow Airport. It was also one of the busiest airports in Europe. The airport covers a large area of about 674 hectares (that's like 1,665 football fields!).
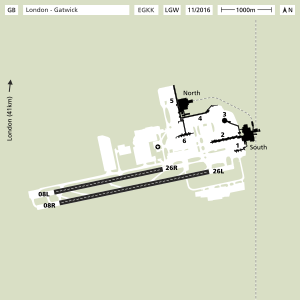
Gatwick started as an airfield in the late 1920s and has been used for commercial flights since 1933. The airport has two main terminals, the North Terminal and the South Terminal. It mostly uses one main runway, which is very long (about 3,316 meters or 10,880 feet). There's a second runway, but it's too close to the main one to be used at the same time. In 2018, over 46 million passengers traveled through Gatwick. It's a major base for airlines like British Airways and the biggest base for easyJet, a popular low-cost airline.
Quick facts for kids
London Gatwick Airport
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Gatwick Airport Limited | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Greater London, West Sussex and Surrey | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Crawley, West Sussex, England | ||||||||||||||
| Opened | 30 May 1958 | ||||||||||||||
| Hub for | British Airways | ||||||||||||||
| Built | November 1928 | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 203 ft / 62 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 51°08′53″N 0°11′25″W / 51.14806°N 0.19028°W | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
| Runway | |||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2023) | |||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Sources: UK AIP at NATS. Statistics from CAA.
|
|||||||||||||||
Contents
History of Gatwick Airport
How Gatwick Started

The land where Gatwick Airport is today was first used as an airfield in the late 1920s. In 1933, the government allowed commercial flights from the site. The first terminal, called "The Beehive," was built in 1935. Regular flights from this new terminal began the next year.
During World War II, the military took over the airport, and it was known as RAF Gatwick. After the war, it went back to being a civilian airport. The modern airport was built in the mid-1950s and opened in 1956.
Airlines and Growth
In the 1960s, British United Airways (BUA) and Dan-Air were two of the biggest independent airlines at Gatwick. BUA became the main airline for regular flights, while Dan-Air was known for holiday charter flights. The government even encouraged airlines to move their charter flights from Heathrow to Gatwick to help it grow.
Later, British Caledonian (BCal) became the main airline at Gatwick in the 1970s and 1980s. When British Airways (BA) took over BCal, BA started to make Gatwick a second major hub, like a smaller version of its main base at Heathrow. However, BA later decided to focus less on Gatwick, which allowed easyJet to grow and become the airport's biggest airline.
Flights to the United States
For many years, from 1978 to 2008, many flights between the UK and the United States used Gatwick. This was because of special rules that limited how many flights could go to Heathrow. When these rules changed in 2008, many airlines moved their US flights to Heathrow.
In 2013, US Airways stopped its flights from Gatwick, meaning there were no scheduled US airlines at the airport for the first time in 35 years. However, in 2021, JetBlue became the first US airline to return to Gatwick, with flights to New York and Boston.
Recent Developments
In 2008, the company that owned Gatwick, BAA, announced it would sell the airport. This happened because a report said BAA had too much control over airports in London. In 2009, a group of investors led by Global Infrastructure Partners (GIP) bought Gatwick for £1.51 billion.
In 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, Gatwick Airport announced plans to reduce its staff. This was due to a big drop in travel. The airport's workforce was cut significantly. In 2021, it was reported that Gatwick was talking with lenders after losing a lot of money.
In 2018, Vinci, a French company, announced it would buy a majority share (50.01%) of Gatwick Airport. This sale was completed in mid-2019.
How Gatwick Works
Airport Facilities
Gatwick has special lounges for travelers, including one for Virgin Holidays. There's also a pay-for-access lounge in the South Terminal. The airport has a conference center and several hotels nearby.
The airport also has chaplains from different churches and multi-faith prayer rooms in each terminal. This means people of all faiths can find a quiet place to pray or reflect.
Before it was sold, the previous owners planned to invest £874 million in Gatwick. This included making both terminals bigger, improving transport, and adding a new baggage system for the South Terminal.
In 2013, Gatwick started "Gatwick Connect," a free service to help passengers who are changing flights at Gatwick, especially if their airlines don't offer a full connection service. This service was renamed "GatwickConnects" in 2015.
Flight Operations
Gatwick has two runways, but it usually operates as a single-runway airport. The northern runway can only be used if the main runway is closed. The main runway is 3,316 meters long, and the northern runway is 2,565 meters long. They are too close together (about 200 meters apart) to be used at the same time for takeoffs and landings. When not in use for flights, the northern runway acts as a taxiway for planes.
In 2018, the airport started looking into using its standby runway more often. One idea is to use the northern runway only for smaller planes taking off, while the main runway would handle all landings and takeoffs for larger planes. In 2023, plans were announced to expand the second runway for regular use.
Planes arriving at Gatwick use special systems to land safely, even in bad weather. They also use a "continuous descent approach" to reduce noise and pollution, especially at night.
Night flights have rules to reduce noise. Between 11 pm and 7 am, noisier planes are not allowed to operate. There are also limits on the total number of flights and noise levels during the night.
Airport Security
The Gatwick District of Sussex Police patrols the airport. This includes armed and unarmed officers. They are responsible for the entire airport area and even planes in flight in some situations. They also check vehicles around the airport.
Access to areas where planes are parked or moving is controlled by the airport's security team. This is regulated by the Civil Aviation Authority. There's also an immigration removal center near the airport called Brook House.
Major Airlines at Gatwick
Gatwick is a base for several airlines, including British Airways (BA), easyJet, Wizz Air, and holiday charter airlines like TUI Airways. Gatwick is special because it hosts all three main types of airlines: full-service, low-cost, and charter.
By late 2015, easyJet flew over 100 routes from Gatwick and had more than 60 planes based there. It's their largest base, and easyJet passengers made up 45% of Gatwick's total passengers in 2013.
easyJet, BA, and Norwegian Air Shuttle were Gatwick's three biggest airlines. However, Norwegian closed its base at Gatwick in late 2020. These three airlines together accounted for a large share of Gatwick's passenger traffic.
In 2008, easyJet bought another airline, GB Airways, which increased its share of flights at Gatwick. By 2009, BA's share of flights had dropped significantly from its peak in 2001. By mid-2012, easyJet had a large share of Gatwick's busy early-morning flights.
Many full-service airlines have started or restarted flights at Gatwick, including Air China, Cathay Pacific, Delta Air Lines, JetBlue, Qatar Airways, Singapore Airlines, and Turkish Airlines. This helps Gatwick attract more business travelers and use its capacity better throughout the year.
In May 2020, Virgin Atlantic announced it would stop flights from Gatwick due to the COVID-19 pandemic. In August 2020, Wizz Air opened a new base at Gatwick. In September 2021, British Airways announced it would stop most of its short and medium-haul flights from Gatwick. However, British Airways has since resumed these flights under a new subsidiary called "BA EuroFlyer."
Terminals
Gatwick Airport has two terminals, the South Terminal and the North Terminal. Together, they have 65 gates. Both terminals have shops and restaurants before and after security. All areas are easy to access for passengers with disabilities. There are also places for baby changing and feeding. Business travelers can use special lounges. The North and South Terminals are connected by a 0.75-mile (1.2 km) elevated shuttle train that runs outside of security. They are not connected once you pass through security.
South Terminal
The South Terminal has 32 gates with jetbridges (the walkways that connect the terminal to the plane) and 7 remote gates (where you take a bus to the plane). The central part of the South Terminal opened in 1958. Gatwick was one of the first airports in the world to have a terminal with enclosed walkways, allowing passengers to walk to their planes under cover. The terminal was also designed to be expanded easily.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the South Terminal was temporarily closed from June 2020. All airlines moved to the North Terminal because there were so few passengers. It fully reopened in March 2022.
North Terminal
The North Terminal has 31 gates with jetbridges, including three that can handle very large planes like the Airbus A380. Building the North Terminal was a huge project in the 1980s, costing £200 million. In 1991, another pier (a section with gates) was added. In 2005, a new Pier 6 opened, adding 11 more gates. This pier is connected to the main North Terminal building by one of the largest air passenger bridges in the world. This bridge goes over a taxiway, giving passengers great views of the airport.
A big expansion to the North Terminal was opened in November 2011 by former Prime Minister John Major.
Terminal Changes for Airlines
Gatwick and easyJet made a deal to move airlines around the terminals. This meant easyJet would have all its flights in the North Terminal, while British Airways and Virgin Atlantic would switch terminals. This was done to make the airport run more smoothly, especially during busy times.
It was confirmed in January 2015 that British Airways would move all its flights to the South Terminal, and all easyJet flights would be in the North Terminal. This change happened on January 25, 2017.
Airlines and Destinations
As of 2015, many airlines fly to and from Gatwick Airport. Here are some of the destinations:
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aegean Airlines | Seasonal: Athens |
| Air Arabia | Tangier |
| Air China | Beijing–Capital, Shanghai–Pudong |
| Air Europa | Madrid |
| Air India | Ahmedabad (ends 31 July 2025) |
| Air Mauritius | Mauritius |
| Air Peace | Abuja (begins 28 October 2025), Lagos |
| Air Sierra Leone | Freetown |
| Air Transat | Toronto–Pearson Seasonal: Montréal–Trudeau |
| airBaltic | Riga, Tallinn |
| Atlantic Airways | Seasonal: Vágar |
| Aurigny | Guernsey |
| Azerbaijan Airlines | Baku |
| British Airways | Accra, Agadir, Algiers, Alicante, Antigua, Bordeaux, Cancún, Dubrovnik, Faro, Funchal, Georgetown–Cheddi Jagan, Glasgow, Gran Canaria, Graz (begins 21 November 2025), Grenada, Islamabad, Jersey, Kingston–Norman Manley, Lanzarote, Larnaca, Málaga, Malta, Marrakesh, Mauritius, Nice, Orlando, Palma de Mallorca, Porto, Port of Spain, Punta Cana, Rabat (begins 5 November 2025), Salzburg, Seville, St. Kitts, St. Lucia–Hewanorra, Tampa, Tenerife–South, Tobago, Turin, Verona Seasonal: Antalya, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Bari, Cagliari, Cape Town, Catania, Chambéry, Corfu, Dalaman, Fuerteventura, Geneva, Grenoble, Heraklion, Ibiza, Innsbruck, Ivalo, Kos, Las Vegas, Lyon, Menorca, Montpellier, New York–JFK, Paphos, Rhodes, Salerno, San José (CR), Sharm El Sheikh, Thessaloniki, Vancouver |
| China Eastern Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong |
| China Southern Airlines | Guangzhou, Zhengzhou |
| Corendon Airlines | Seasonal: Antalya, Heraklion |
| Croatia Airlines | Seasonal: Split |
| Delta Air Lines | Seasonal: New York–JFK |
| Eastern Airways | Newquay |
| easyJet | Aberdeen, Agadir, Alicante, Almería, Amsterdam, Antalya, Athens, Barcelona, Bari, Basel/Mulhouse, Belfast–City, Belfast–International, Berlin, Bordeaux, Budapest, Catania, Copenhagen, Dalaman, Düsseldorf, Edinburgh, Enfidha, Faro, Fuerteventura, Funchal, Geneva, Gibraltar, Glasgow, Gran Canaria, Hamburg, Hurghada, Innsbruck, Inverness, Isle of Man, Jersey, Kraków, Lanzarote, Larnaca, Lisbon, Ljubljana, Lyon, Madrid, Málaga, Malta, Marrakesh, Marseille, Menorca, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Montpellier, Munich, Murcia, Nantes, Naples, Nice, Olbia, Palma de Mallorca, Paphos, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Pisa, Porto, Prague, Rennes, Rome–Fiumicino, Sal, Seville, Sharm El Sheikh, Strasbourg, Tenerife–South, Thessaloniki, Toulouse (resumes 26 October 2025), Turin, Valencia, Venice, Verona, Zurich Seasonal: Akureyri, Bastia, Biarritz, Bodrum, Brest, Brindisi, Burgas, Chania, Corfu, Dubrovnik, Figari, Friedrichshafen, Grenoble, Heraklion, Ibiza, İzmir, Kalamata, Kefalonia, Kittilä, Kos, La Rochelle, Luxor, Mykonos, Palermo, Preveza/Lefkada, Pula, Reykjavík–Keflavík, Rhodes, Rimini, Rovaniemi, Sälen-Trysil (begins 6 December 2025), Salerno, Salzburg, Santorini, Skiathos, Sofia, Split, Tivat, Tromsø, Zadar, Vienna (begins 4 December 2025), Zakynthos |
| Emirates | Dubai–International |
| Ethiopian Airlines | Addis Ababa |
| FlyErbil | Erbil |
| Gulf Air | Bahrain |
| Iberia | Madrid |
| Icelandair | Reykjavik–Keflavik |
| ITA Airways | Seasonal: Rome-Fiumicino |
| JetBlue | Seasonal: Boston |
| Kenya Airways | Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta |
| KM Malta Airlines | Malta |
| Mavi Gök Airlines | Seasonal: Antalya |
| Norse Atlantic Airways | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi (begins 26 October 2025), Los Angeles, Miami, New York–JFK, Orlando Seasonal: Cape Town |
| Norwegian Air Shuttle | Bergen, Billund, Copenhagen, Helsinki, Oslo, Stavanger, Stockholm–Arlanda, Trondheim Seasonal: Ålesund, Gothenburg, Riga, Rovaniemi, Tromsø |
| Nouvelair | Tunis |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca Seasonal: Tangier |
| Royal Brunei Airlines | Seasonal: Bandar Seri Begawan (begins 22 July 2025) |
| Ryanair | Alicante, Cork, Dublin, Shannon |
| Saudia | Jeddah, Neom Bay |
| Singapore Airlines | Singapore |
| Sky Alps | Bolzano |
| Sky Express | Athens |
| SunExpress | Antalya Seasonal: Bodrum (begins 4 May 2026), Dalaman, İzmir |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Zurich Seasonal: Geneva |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon, Porto |
| TUI Airways | Agadir, Boa Vista, Cancún, Enfidha, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Hurghada, Lanzarote, La Palma, Marrakesh, Montego Bay, Punta Cana, Sal, Sharm El Sheikh, Tenerife–South Seasonal: Alicante, Antalya, Banjul, Barbados, Bodrum, Budapest, Burgas, Chambéry, Chania, Corfu, Dakar–Diass, Dalaman, Dubrovnik, Faro, Geneva (resumes 20 December 2025), Girona, Goa–Mopa, Heraklion, Ibiza, Innsbruck, Ivalo, Jerez de la Frontera, Kavala, Kefalonia, Kittilä, Kos, Kuusamo, Lamezia Terme, Larnaca, La Romana, Luxor, Málaga, Marsa Alam, Melbourne/Orlando, Menorca, Naples, Ohrid (resumes 27 May 2026), Olbia, Oslo, Palma de Mallorca, Paphos, Phuket, Preveza/Lefkada, Pula, Reus, Reykjavík–Keflavík, Rhodes, Rovaniemi, Sälen-Trysil (begins 21 December 2025), Salzburg, Samos, Skiathos, Sofia, Split, Thessaloniki, Toulouse, Turin, Verona, Zakynthos Seasonal charter: Mauritius |
| Tunisair | Tunis |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul |
| Turkmenistan Airlines | Ashgabat |
| Uganda Airlines | Entebbe |
| Uzbekistan Airways | Tashkent |
| Volotea | Brest |
| Vueling | A Coruña, Asturias, Barcelona, Bilbao, Florence, Málaga, Paris–Orly, Rome–Fiumicino, Santiago de Compostela, Seville, Valencia Seasonal: Alicante |
| WestJet | Seasonal: Halifax, St. John's |
| Wizz Air | Antalya, Athens, Budapest, Istanbul, Jeddah, Kraków, Larnaca, Málaga, Medina (begins 1 August 2025), Milan–Malpensa, Prague, Rome–Fiumicino, Varna, Venice, Vienna, Warsaw–Chopin (begins 2 August 2025), Wrocław Seasonal: Agadir, Catania, Dalaman, Faro, Grenoble, Hurghada, Lyon, Marrakesh, Podgorica, Sharm El Sheikh |
Airport Statistics
Passenger Traffic Overview
In 2015, Gatwick became the first airport with a single runway to handle over 40 million passengers in a year. By 2016, easyJet carried over 40% of all passengers at Gatwick. Gatwick is known as the world's leading airport for low-cost airlines. Until March 2017, it had the busiest single-use runway in the world, with up to 55 plane movements per hour.
In 2018, 46.1 million passengers used Gatwick, which was a small increase from the year before. Flights to North America and other long-haul destinations saw big increases in passengers. However, flights within the UK and Europe saw slight decreases. The total number of aircraft movements (takeoffs and landings) went down slightly.
In the first three months of 2019, passenger numbers increased by 4% compared to the same period in 2018. Long-haul flights continued to grow, and the GatwickConnects service became more popular, helping passengers connect flights from places like Edinburgh, Jersey, and Belfast.
Busiest Routes
Here are some of the busiest international and domestic routes from Gatwick Airport in 2024:
| Rank | Destination | Passengers | Change 2023 / 24 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,350,954 | ||
| 2 | 1,197,738 | ||
| 3 | 1,053,277 | ||
| 4 | 927,798 | ||
| 5 | 925,000 | ||
| 6 | 853,429 | ||
| 7 | 787,710 | ||
| 8 | 778,472 | ||
| 9 | 764,195 | ||
| 10 | 739,804 | ||
| 11 | 729,229 | ||
| 12 | 729,018 | ||
| 13 | 725,857 | ||
| 14 | 636,616 | ||
| 15 | 605,656 | ||
| 16 | 593,613 | ||
| 17 | 586,369 | ||
| 18 | 526,369 | ||
| 19 | 520,953 | ||
| 20 | 503,953 | ||
| Source: CAA Statistics | |||
| Rank | Destination | Passengers | Change 2023 / 24 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 476,152 | ||
| 2 | 455,095 | ||
| 3 | 444,142 | ||
| 4 | 381,611 | ||
| 5 | 277,800 | ||
| 6 | 254,601 | ||
| 7 | 222,417 | ||
| 8 | 196,469 | ||
| 9 | 165,643 | ||
| 10 | 83,252 | ||
| Source: CAA Statistics | |||
Passenger Numbers Over Time
After its reconstruction in 1956–58, Gatwick handled 186,172 passengers in its first seven months. By 1962–63, passenger numbers reached one million for the first time. This number kept growing, reaching 5 million by the early 1970s, 10 million a decade later, and over 20 million by the late 1980s. By the year 2000, Gatwick was handling more than 30 million passengers annually.
| Year | Number of passengers |
Percentage change |
Number of aircraft movements |
Freight (tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 32,068,540 | – | 260,859 | 318,905 |
| 2001 | 31,181,770 | 252,543 | 280,098 | |
| 2002 | 29,627,420 | 242,379 | 242,519 | |
| 2003 | 30,005,260 | 242,731 | 222,916 | |
| 2004 | 31,466,770 | 251,195 | 218,204 | |
| 2005 | 32,775,695 | 261,292 | 222,778 | |
| 2006 | 34,163,579 | 263,363 | 211,857 | |
| 2007 | 35,216,113 | 266,550 | 171,078 | |
| 2008 | 34,205,887 | 263,653 | 107,702 | |
| 2009 | 32,392,520 | 251,879 | 74,680 | |
| 2010 | 31,375,290 | 240,500 | 104,032 | |
| 2011 | 33,674,264 | 251,067 | 88,085 | |
| 2012 | 34,235,982 | 246,987 | 97,567 | |
| 2013 | 35,444,206 | 250,520 | 96,724 | |
| 2014 | 38,103,667 | 259,692 | 88,508 | |
| 2015 | 40,269,087 | 267,760 | 73,371 | |
| 2016 | 43,119,628 | 280,666 | 79,588 | |
| 2017 | 45,516,700 | 285,969 | 96,983 | |
| 2018 | 46,075,400 | 283,926 | 112,600 | |
| 2019 | 46,574,786 | 282,896 | 110,358 | |
| 2020 | 10,171,867 | 79,489 | 26,063 | |
| 2021 | 6,260,072 | 52,000 | 11,623 | |
| 2022 | 32,800,000 | 217,524 | 36,407 | |
| 2023 | 40,894,242 | 253,047 | 61,123 | |
| 2024 | 43,242,000 | 265,358 | 103,961 | |
| Source 2000–2016: UK Civil Aviation Authority Source 2017: Gatwick Airport Limited |
||||
Getting To and From Gatwick
By Road
Gatwick Airport is easy to reach by car. It has a special road that connects directly to the M23 motorway. The M23 then connects to the M25, which is a big ring road around London. This makes it easy to get to the airport from many parts of London and the South East of England. You can also reach Gatwick from the A23 road, which goes to nearby towns like Crawley and Brighton. The airport has both long-stay and short-stay car parks.
Gatwick aims for a certain percentage of people to use public transport. The goal was 40% by 2015 and 45% by the time passenger numbers reach 45 million.
By Train
Gatwick Airport has its own railway station right next to the South Terminal, which opened in 1958. Trains from Southern, Thameslink, and Gatwick Express serve the station. Great Western Railway also offers a service every half hour.
You can take trains south to places like Brighton, Eastbourne, and Portsmouth. Northbound trains go to London Bridge and London Victoria. Thameslink trains continue further north to St Pancras International, Bedford, Peterborough, and Cambridge. Great Western Railway trains go to Reading.
You can even reach Heathrow Airport and Luton Airport from Gatwick with just one train change. For Heathrow, you change to the Elizabeth line at Farringdon. For Luton, you change to the Luton DART at Luton Airport Parkway. You can use London Oyster Cards and contactless payment cards for all train journeys from Gatwick into London.
By Bus
National Express Coaches run services from Gatwick to Heathrow Airport, London Stansted Airport, and many other cities and towns across the UK. Oxford Bus Company has direct services to Oxford, and EasyBus runs mini-coaches from both terminals to Earls Court and West Brompton in London.
Local buses connect the North and South Terminals to nearby towns like Crawley, Horley, and Redhill. Metrobus operates these services, including their Fastway system, which is a special bus rapid transit system.
Moving Between Terminals
The North and South Terminals are connected by a 0.75-mile (1.2 km) elevated shuttle train. This shuttle runs automatically and has two trains, each with three cars. Even though some people call it a "monorail," it actually runs on two concrete tracks with rubber tires. The shuttle is outside of security and connects both terminals to the airport railway station.
The shuttle opened in 1987 with the North Terminal. It was upgraded in 2008, and new trains were installed. The system reopened in July 2010. Before this, in 1983, Gatwick had the UK's first automated people-moving system, which connected the main terminal (now the South Terminal) to a circular pier. That system has since been replaced by a moving walkway.
Future Plans for Gatwick
Gatwick has been part of many discussions about how to increase airport capacity in southeastern England. Ideas for expansion have included a third terminal and a second runway. An agreement not to build a second runway expired in 2019.
In July 2013, the airport proposed building a second runway south of the existing one. This idea was considered by the Airports Commission. Another idea was to extend the North Terminal with a passenger bridge. Gatwick's plan from 2011 suggested a new satellite building near the control tower, connecting to the North Terminal, as part of a larger airport with one runway and two terminals by 2030.
In late 2011, the government also looked into a high-speed rail link between Gatwick and Heathrow. The idea was to combine the airports into a "virtual hub" called "Heathwick." This train would travel very fast, covering 35 miles in 15 minutes. However, this idea was not very popular.
On July 1, 2015, the Airports Commission recommended expanding Heathrow Airport instead of Gatwick. They felt Heathrow's expansion would bring greater economic benefits. Gatwick disagreed with these findings.
On September 9, 2021, Gatwick Airport started a public discussion about major work to increase its capacity. The plan is to move the northern "emergency" runway slightly north so it can be used regularly alongside the main runway. This would allow the airport to handle more passengers, from 64 million to 75 million per year. The airport hopes to get approval in 2024. The main construction would take about 4 years, and the whole project would be fully complete in 13 years. This work would also include a new pier, hotels, terminal expansion, and road improvements. The planning request for the runway change was officially made in July 2023. This project is expected to cost around £2.2 billion and would be paid for by private investors.
On February 27, 2025, the Transport Secretary said she was likely to approve the plans, as long as noise issues were addressed. A final decision is expected in October 2025.
If Gatwick expands, it is expected to create about 14,000 new jobs and add £1 billion to the local economy each year. The airport hopes its new technology upgrades will help balance these economic benefits with any environmental impact.
Accidents and Incidents
- September 15, 1936 – A British Airways plane crashed during takeoff on a night mail flight, and three crew members died.
- November 1936 – A British Airways plane crashed in a wood near Gatwick while trying to land in bad weather, killing both pilots.
- February 17, 1959 – A Turkish Airlines plane crashed in heavy fog while approaching Gatwick after hitting trees. Some people died, but the Turkish Prime Minister survived.
- January 5, 1969 – An Ariana Afghan Airlines plane crashed into a house near Horley in low visibility. Many people on board and two people on the ground died.
- January 28, 1972 – A British Caledonian plane was badly damaged after a hard landing at Gatwick. No one was hurt, but the plane was too damaged to be repaired.
- July 20, 1975 – A British Island Airways plane was involved in a runway accident during takeoff. The plane lifted off, but then the back of the fuselage hit the runway. No one was hurt.
- December 29, 2014 – A Virgin Atlantic Boeing 747 plane had a problem with its hydraulic fluid while flying to Las Vegas. The crew had to return to Gatwick and landed safely with some landing gear issues.
- December 19–21, 2018 – There was a major disruption at the airport due to reports of drones flying near the runway. The runway was closed, and many flights were canceled, affecting thousands of passengers. The army was called in to help. Two people were arrested but later released.
- February 26, 2020 – A Titan Airways plane had engine problems shortly after takeoff. The aircraft landed safely at Gatwick 11 minutes later. An investigation found that fuel contamination caused the incident.
More to Explore
- Airports of London
- List of airports in the United Kingdom and the British Crown Dependencies
- List of busiest airports by passenger traffic
- List of the busiest airports in Europe
See also
 In Spanish: Aeropuerto de Londres-Gatwick para niños
In Spanish: Aeropuerto de Londres-Gatwick para niños