Orange Group facts for kids

Logo used since 2013
|
|||
|
Formerly
|
France Télécom S.A. (1988–2013) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Public | |||
| Traded as |
|
||
| Industry | Telecommunications | ||
| Predecessor | Postes et Télégraphes | ||
| Founded | 1 January 1988 | ||
| Headquarters | Issy-les-Moulineaux, France | ||
|
Area served
|
Worldwide | ||
|
Key people
|
|||
| Products | |||
| Revenue | |||
|
Operating income
|
|||
| Total assets | |||
| Total equity | |||
| Owners | French State (23%) | ||
|
Number of employees
|
132,002 (2021) | ||
| Subsidiaries |
|
||
|
|||
Orange S.A. is a big French company that provides telecommunications services. It was started in 1988 and has its main office near Paris.
The name "Orange" became the main brand for its mobile, landline, internet, and Internet Protocol television (IPTV) services in 2006. The company grew by taking over other businesses. For example, it bought a company called Microtel Communications in the United Kingdom in 2000. This helped the company become international. Since then, Orange has grown into many countries in Europe, Africa, and the French West Indies. In 2013, the company officially changed its name from France Télécom to Orange S.A. In 2019, Orange S.A. had almost 148,000 employees around the world.
Orange also sells things like music and movies, offers online shopping, and provides smart home solutions. In 2023, the company made over €43 billion in sales from all its services.
How Orange Started and Grew
Early Communication in France (1878–1980s)
Long ago, in 1792, France created a communication network. This network used optical telegraphy to send messages quickly. It was important for a country that was often at war.
Later, in 1878, after the invention of the electrical telegraph and the telephone, France created a special government department. This department managed posts and telegraphs. Telephone services were added in 1889. By 1923, it became known as PTT, which stood for Posts, Telegraphs, and Telephones.
In the 1970s, France worked hard to improve its communication systems. Engineers and researchers helped invent important technologies. These included digital switching, Minitel, and the GSM standard for mobile phones. In 1982, Minitel allowed customers to order things online.
Becoming France Télécom (1988–1997)
Before 1988, the company was a part of the government's Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications. In 1990, it became its own company, called France Télécom. This change happened because of a European rule that wanted more competition in public services.
France Télécom became a private company starting in 1998. The French government still owns a part of the company. In 1995, Michel Bon was chosen to lead the France Télécom Group.
Growth and Changes (1997–2000)
In 1997, France Télécom offered shares of its company to the public. This was a good time because the internet boom made stock markets strong. The company wanted to grow internationally, like its rivals.
Orange Joins the Family
The Orange brand started in the UK in 1994. A company called Hutchison Telecom launched it. Orange quickly became popular. In 1996, Orange shares were sold on the London Stock Exchange.
In 1999, a German company called Mannesmann bought Orange. But soon after, Vodafone bought Mannesmann. Vodafone then had to sell Orange because of rules that prevented one company from owning too many mobile networks.
In 2000, France Télécom bought Orange from Vodafone for a lot of money. This made France Télécom one of the biggest phone companies in the world. The mobile parts of Orange and France Télécom then joined to form the new Orange S.A. group.
In 2001, Orange S.A. shares were listed on the Euronext Paris stock exchange. This meant people could buy and sell shares of the company. In June 2001, France Télécom's mobile brands, like Itinéris, were all changed to the Orange brand.
In 2002, the company faced financial challenges. Thierry Breton became the CEO and worked to improve the company's finances. He helped the company get back on track. In 2005, Didier Lombard took over as CEO.
Becoming Orange (2006–Present)
Orange launched a plan to bring all its services under one name. From June 2006, Orange became the main brand for internet, TV, and mobile services in most countries where the company operated. Even business services were rebranded as Orange Business Services.
In 2008, Orange started its own TV channels, called Orange Cinema Series. They showed movies from big studios like Warner Bros. and HBO. Orange also got the rights to show some football matches.
In 2009, Orange and T-Mobile decided to combine their operations in the UK. This created the largest mobile operator there. Both brands, T-Mobile and Orange, continued to exist.
In 2010, Stéphane Richard became the new CEO of Orange. In 2013, the company officially changed its name from France Télécom to Orange S.A. This completed the rebranding process.
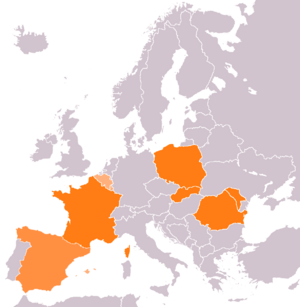
In 2014, Orange bought a Spanish company called Jazztel. In 2018, Orange teamed up with Google to build a new undersea cable called Dunant. This cable helps send data faster between the United States and France. It started working in 2020. In July 2020, Orange also launched a home internet service using satellites.
In November 2024, Orange announced a partnership with OpenAI. This partnership will give Orange access to new AI models. Orange also signed an agreement with Meta and OpenAI to help translate African languages for its telecom groups.
Who Owns Orange
The main owners of Orange are the French government, through different agencies. They own about 23% of the company. Orange employees also own a small part of the company, about 4.81%.
What Orange Does
Mobile Services
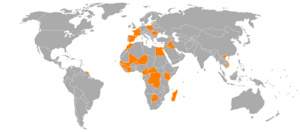
Orange is the only brand used for the company's mobile phone services. Older brands like Itineris were changed to Orange in 2001. As of 2010, Orange had 150 million mobile customers worldwide. Orange France is the biggest mobile operator in France.
Here are some countries where Orange operates mobile networks:
| Country | Operator | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange (Group Sonatel) | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange (Group Sonatel) | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange (Group Sonatel) | ||
| Orange (Group Sonatel) | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange | ||
| Orange |
The Orange brand was also used by other companies that Orange S.A. did not own. Here are some examples:
| Country | Former operator | Rebranding/ License cancellation | Present operator | Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA Orange | 2006 | TrueMove H | ||
| Orange | January 2006 | Vodafone Idea | ||
| Orange | February 2015 | EE | ||
| Orange | April 2015 | Salt | ||
| Orange | April 2015 | Salt | ||
| Orange | December 2015 | Ucom | ||
| Orange | February 2016 | Partner | ||
| Orange | November 2017 | My.T | ||
| Orange | November 2017 | Altice | ||
| Orange | October 2018 | GETESA |
Landline and Internet Services
Orange also provides landline phone and internet services. It took over these businesses from France Telecom and Wanadoo in 2006. The company's internet services often come with a special device called the Livebox. As of 2010, Orange had 13.7 million internet customers worldwide.
The Livebox is an ADSL modem that Orange gives to its internet customers. It connects your home network to the internet. The Livebox has changed over time with new versions.
TV and Entertainment
Orange has focused on providing TV shows, movies, and other content since 2003. They created a TV service called MaLigne.tv, which later became Orange TV. They also offer video-on-demand services, where you can watch shows whenever you want.
OCS (Orange Cinema Series)
OCS launched in November 2008. It has five channels dedicated to movies. These channels mainly show films from Warner Bros. and HBO. OCS also offers video-on-demand, so viewers can watch programs from the past 30 days.
Orange Sport
Orange Sport also launched in November 2008. It showed football matches and other sports. This created competition with other sports channels.
Online Entertainment
In 1997, France Telecom created Goa, a company for online entertainment. It started as a platform for online games. Later, Goa focused more on general online entertainment. In 2010, goa.com became the Orange Jeux portal.
Music Services
Orange created Liveradio in 2008. This is a free service that streams live and on-demand radio. Users can listen to over 10,000 radio stations and 11,000 podcasts from many countries.
In 2010, Orange bought a part of Deezer, a music streaming site. This allowed Orange to offer its customers a special "Deezer Premium" service with no ads and millions of songs.
Other Orange Companies
Orange offers many types of communication services. These include:
- Landline phones, mostly in France and Poland.
- Broadband internet access.
- Mobile phone services.
- IPTV (TV over the internet), known as Orange TV in some countries.
All these services now operate under the Orange brand.
Orange Business
Orange Business is the part of Orange that provides services to other businesses. Orange also has research and development labs in places like Boston and San Francisco.
Orange has a large network called OpenTransit. This network connects Europe, the United States, Japan, and Hong Kong.
EE (in the UK)
Orange and Deutsche Telekom combined their UK businesses in 2010. They formed a joint company called EE. In 2015, BT Group bought EE. Orange S.A. then became a small owner in BT Group.
Globecast
Globecast helps media companies send TV channels and other content. They distribute TV channels using satellites and the internet. They also help with live events and preparing content for broadcast.
Viaccess Orca
Viaccess Orca provides platforms and security for TV services over the internet. They also help track content online to prevent piracy.
Orange Labs (Research and Development)
Orange Labs is the part of Orange that focuses on research and development. It started from older research groups. Orange Labs helps create new technologies and standards for communication. For example, they helped develop the MPEG audio standard.
In 2010, Orange spent a lot of money on research and development. They have many patents for their inventions. Orange Labs works with universities and other companies to develop new ideas.
Orange Labs has research centers and "technocentres" around the world. Technocentres bring together researchers, engineers, and marketing people to develop new innovations.
| Type | City | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Technocentre | Chatillon | France |
| Technocentre | London | United Kingdom |
| Technocentre | Warsaw | Poland |
| Technocentre | Amman | Jordan |
| R&D | - | Spain |
| R&D | San Francisco | United States |
| R&D | Beijing | China |
| R&D | Cairo | Egypt |
| R&D | Tokyo | Japan |
| R&D | Issy les Moulineaux | France |
| R&D | Caen | France |
| R&D | Grenoble | France |
| R&D | Rennes | France |
| R&D | Lannion | France |
| R&D | Sophia Antipolis | France |
| R&D | La Turbie | France |
| R&D | Belfort | France |
Dailymotion
In 2011, Orange bought a part of Dailymotion, a French online video platform. This helped Orange offer more video content to its customers.
Studio 37
Orange Studio was created in 2007. It helps produce and buy films. They work with big studios like Warner Bros. and HBO to get movies for Orange's TV channels. In 2011, Orange Studio helped produce the film The Artist, which won many awards.
Cloudwatt
Cloudwatt was a company that provided cloud services. Orange bought all of Cloudwatt's shares in 2015 to improve its services for businesses.
SecureData and SecureLink
Orange bought two cybersecurity companies, SecureData (in 2019) and SecureLink (in 2019). These purchases helped Orange strengthen its cybersecurity services.
Telekom Romania
In 2020, Orange agreed to buy Telekom Romania. This deal helped Orange expand its services in Romania.
Future4care
In 2021, Orange partnered with other companies to launch Future4care. This is a special program that helps new companies focused on digital health.
How Orange is Managed
Orange is managed by a board of directors and an executive committee. These groups help guide the company's plans and make sure it meets its goals.
Leaders of Orange
- Chairmen:
* Didier Lombard (2005) * Stéphane Richard (2010-2021)
- Chief Executive Officers: The company is led by either the chairman or another person chosen by the board.
Board of Directors
The board of directors has between 12 and 22 members. Some are chosen by the French government, some by employees, and others by shareholders. They serve for four years.
Head Office
Since 2012, Orange's main office is in Paris. Before that, it was in a different building in Paris from 1998 to 2012.
Orange Foundation
In 1987, the company started the France Télécom Foundation, which later became the Orange Foundation in 2007. This foundation helps with projects related to health, especially autism. It also supports education, like schooling for girls in developing countries, and culture, such as group singing. The Foundation works with other organizations to help with these projects.
Orange Sponsorships
Orange has sponsored many events and teams:
- From 2000 to 2002, Orange sponsored the British Formula One team Arrows.
- Orange was a sponsor for the UEFA Euro 2012 and UEFA Euro 2016 football tournaments.
- The company sponsored the national basketball teams of the Central African Republic and Senegal in 2015.
- Orange was the jersey sponsor for the French football club Olympique de Marseille for the 2017/18 and 2018/19 seasons.
- In 2018, Orange became a sponsor of the esports team Team Vitality.
Awards and Recognition
In 2021, the "My Orange" app for customers won the "Janus of the digital experience" award. It also won the "Red Dot" award in the same year. In 2023, the "Orange Design System" demo app also won a "Red Dot" award.
Images for kids