List of regions of Canada facts for kids
Canada is a huge country, and to make it easier to understand, people often divide it into different areas called regions. These regions can be based on geography, how people speak, or even for government purposes. Think of it like dividing your school into different sections for sports, clubs, or classes.
Contents
How Canada is Divided: National Regions
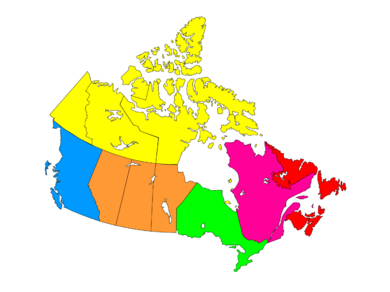
Canada's ten provinces and three territories are often grouped together into larger regions. These groupings help us understand different parts of the country. For example, the Senate, which is part of Canada's Parliament, divides the country into four main regions to make sure all areas are fairly represented. These are the West, Ontario, Quebec, and the Maritimes. Newfoundland and Labrador, and the three territories, have special status.
Other groups, like Statistics Canada, use slightly different ways to divide the country. Statistics Canada uses six regions: British Columbia, the Prairies, Ontario, Quebec, Atlantic Canada, and the Territories. Even though there are different ways to group them, these regions help us talk about Canada's geography and people.
| Provinces and Territories | Senate Regions | Six-Region Model (Statistics Canada) |
|---|---|---|
| British Columbia | Western Canada | British Columbia |
| Alberta | Canadian Prairies | |
| Saskatchewan | ||
| Manitoba | ||
| Ontario | Ontario | Ontario |
| Quebec | Quebec | Quebec |
| New Brunswick | The Maritimes | Atlantic |
| Prince Edward Island | ||
| Nova Scotia | ||
| Newfoundland and Labrador | Newfoundland and Labrador | |
| Yukon | The North | Territories (Northern Canada) |
| Northwest Territories | ||
| Nunavut |
Regions Across Provinces
Some regions in Canada aren't just inside one province. They stretch across several provinces or territories because they share similar features, like language or geography.
Language Regions
- French Canada: This region is mostly in Quebec, but you can also find French-speaking communities in other provinces like Ontario and Manitoba.
- Bilingual Belt: This is an area where both English and French are commonly spoken. It includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, and New Brunswick.
- English Canada: This term often refers to the parts of Canada where English is the main language, usually excluding Quebec.
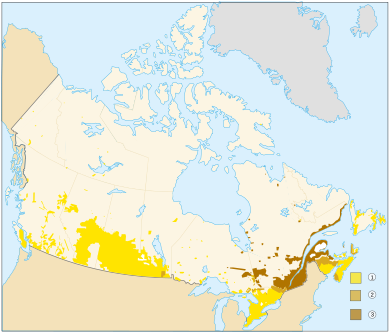
- Inuit Nunangat: This is a large area in northern Canada where most people are Inuit. Many Inuit people speak their own languages, not English or French, as their first language.
Geographic Regions
Canada has many different landscapes, which create unique geographic regions.
- Arctic Archipelago: This is a huge group of islands in the Arctic Ocean, located in Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and a small part of Yukon.
- Canadian Cordillera: This region includes most of British Columbia and Yukon, known for its mountains and plateaus.
- Interior Plains: These flatlands stretch across western Canada, from the Arctic Ocean to the US border. They include the Prairies, which are famous for farming.
- Canadian Shield: This is a massive rocky area around Hudson Bay. It covers parts of almost every province and territory, except British Columbia and the Maritimes.
- Hudson Bay Lowland: A large wetland area that stretches from Manitoba through northern Ontario into Quebec.
- Quebec City–Windsor Corridor: This busy area connects southern Ontario with southern Quebec, where many Canadians live.
- Appalachian Mountains: These old mountain ranges extend into southeastern Canada from the United States, covering parts of the Maritimes and eastern Quebec.
Administrative Regions
- National Capital Region: This special federal region includes Canada's capital city, Ottawa, in Ontario, and Gatineau in Quebec. It's where many government offices are located.
Regions Within Provinces
Each province and territory also has its own smaller regions. These can be geographic areas, or they can be administrative regions used by the local government.
Alberta
Alberta has both natural geographic regions and regions based on population or administration.
- Northern Alberta: Mostly forests, including the Peace River Country.
- Southern Alberta: Includes the Aspen Parkland and the Prairie grasslands.
- Calgary–Edmonton Corridor: A busy area between Alberta's two largest cities.
- Alberta's Rockies: The mountainous western part of the province.
British Columbia
British Columbia is very mountainous, so it has many unique local regions.
- British Columbia Interior: The large area east of the coastal mountains. It includes places like the Kootenays, Okanagan (famous for fruit and wine), and the Cariboo.
- Lower Mainland: The most populated area, including Greater Vancouver and the Fraser Valley.
- British Columbia Coast: The long coastline with many islands and inlets.
- Vancouver Island: A large island off the coast, home to the capital city, Victoria.
- Gulf Islands: Smaller islands between Vancouver Island and the mainland.
Manitoba
Manitoba's regions include:
- Northern Manitoba: Forests and parts of the Hudson Bay Lowlands.
- Central Manitoba: Includes the Interlake area.
- Southern Manitoba: The most populated part, including the Winnipeg Capital Region.
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is smaller, so its regions are mostly local geographic areas.
- Acadian Peninsula: An area with a strong Acadian (French-speaking) culture.
- Miramichi Valley: Known for its rivers and forests.
- Greater Moncton, Greater Saint John, and Greater Fredericton: The areas around the province's largest cities.
Newfoundland and Labrador
This province is made up of two main landmasses, each with its own regions.
- Labrador: The mainland part, including the Labrador West mining area and Nunatsiavut, an Inuit self-governing region.
- Newfoundland: The island part, with distinct peninsulas like the Avalon Peninsula (where the capital St. John's is) and the Great Northern Peninsula.
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories has large geographic regions and administrative regions.
- Arctic Archipelago: The northern islands.
- N.W.T. Mainland: Includes the Mackenzie Mountains and vast plains.
- Administrative regions: Such as the Inuvik Region and North Slave Region.
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is divided into mainland and island regions.
- Mainland Nova Scotia: Includes the South Shore, Annapolis Valley (known for farming), and the Eastern Shore.
- Cape Breton Island: An island off the northeast coast, famous for its scenic highlands.
Nunavut is a vast territory in the Arctic, with large geographic and administrative regions.
- Arctic Archipelago: Most of Nunavut is made up of Arctic islands.
- Nunavut Mainland: The small mainland portion.
- Administrative regions: Like the Kitikmeot Region and Kivalliq Region.
Ontario
Ontario, being a large province, has many regions.
- Northern Ontario: A vast, mostly forested area north of the French River.
- Southern Ontario: The most populated part of the province.
- Central Ontario: Includes popular vacation areas like the Muskoka Lakes area.
- Eastern Ontario: Home to the National Capital Region.
- Golden Horseshoe: A densely populated area around the western end of Lake Ontario, including Toronto and Hamilton.
- Southwestern Ontario: The part of Ontario west of the Golden Horseshoe.
Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is very small and doesn't have widely recognized geographic sub-regions.
Quebec
Quebec has large northern and southern geographic regions, plus many administrative regions.
- Northern Quebec: A vast, sparsely populated area that includes parts of the Arctic Cordillera.
- Quebec Boreal Shield: A large forested region.
- Southern Quebec: The most populated part, including the St. Lawrence Lowlands.
- Administrative regions: Such as Montreal, Laval, and Capitale-Nationale (Quebec City area).
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan's regions are mainly geographic.
- Northern Saskatchewan: Mostly forests.
- Southern Saskatchewan: Includes the Aspen Parkland and the Prairie Grassland, important for agriculture.
Yukon
Yukon's regions are primarily geographic.
- Northern Yukon: Includes Arctic coastal plains.
- Southern Yukon: Features the Klondike region, famous for its gold rush history, and the scenic Southern Lakes.
Images for kids
See also
- Geography of Canada
- Census geographic units of Canada
- Numbered Treaties: These are historical agreements between the Crown (government) and First Nations in Canada. Large parts of Western and Northern Canada are described by these treaty numbers.