Timeline of Cheshire history facts for kids
The timeline of Cheshire history tells the story of important events that happened in the English county of Cheshire. It covers many centuries, from Roman times to today, showing how the area grew and changed.
Contents
Early History: Roman Times to the 9th Century
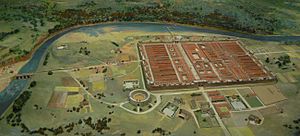
The story of Cheshire begins a very long time ago. Around 70 AD, the Romans built a strong fortress and town called Deva Victrix. This place is now known as Chester. A Roman army group, the Legio XX Valeria Victrix, arrived in Chester around 90 AD.
The Romans left Britain in 410 AD. Later, in 429 AD, a battle near Mold helped set up a Christian kingdom called Powys. This kingdom included parts of what is now Cheshire.
Cheshire in the 7th Century
In 616 AD, a big battle happened near Chester. King Æthelfrith of Northumbria defeated a Welsh army there. Later, in 689 AD, the Church of St John the Baptist was started outside Chester's city walls.
Cheshire in the 9th Century
Around 830 AD, the area of Cheshire became part of the kingdom of Mercia. In 874 or 875 AD, the remains of St Werburgh were brought to Chester. This was done to keep them safe from Danish invaders.
Chester started making its own coins around 890 AD. Also, in 893 AD, people first wrote about Scandinavian settlers living in Chester. A Danish army stayed in Chester for a winter in 893–894 AD. But King Alfred drove them out in 894–895 AD.
Medieval Cheshire: 10th to 15th Centuries
Building and Battles in the 10th Century
In 907 AD, Chester was rebuilt as a protected town called a burh by Æthelflæd and King Edward the Elder. They also started to build new defenses. The church dedicated to St Werburgh, which later became Chester Cathedral, was also founded around this time.
Æthelflæd also strengthened an old Iron Age hill fort at Eddisbury in 914 AD. She built another burh at Runcorn in 915 AD. The defenses of Chester were likely finished between 915–920 AD.
In 923–924 AD, Chester rebelled against the rule from Wessex but was brought back under control. King Edward the Elder died near Farndon in 924 AD. In 937 AD, King Æthelstan won a big battle near Bromborough. Around 980 AD, Vikings raided Chester. This century also saw the first mention of the "shire" or county of Chester.
Norman Influence in the 11th Century
In 1069–1071 AD, William I led the Norman Conquest into Cheshire. He took control of Chester. In 1070 AD, Hugh d'Avranches became the first Earl of Chester. This was a very important title.
Also in 1070 AD, Chester Castle was built. A monastery was founded on the site of the current Chester Cathedral in 1092 AD.
Growth and Changes in the 12th Century

Many important buildings were founded in the 12th century. Norton Priory was started in 1115 AD, and Combermere Abbey in 1133 AD. Chester faced serious fires in 1140 AD and again in 1180 AD.
In 1182 AD, the land in Cheshire north of the River Mersey became part of the new county of Lancashire. Around 1195 AD, the oldest surviving piece of writing about Cheshire, Liber de Luciani laude Cestrie, was created.
Castles and Markets in the 13th Century
King John visited Chester Castle in 1211 AD. In the 1220s, the impressive Beeston Castle was built.
A big change happened in 1237 AD. The 7th Earl of Chester, John, died without a son. So, King Henry IV gave the title to his son, Prince Edward. Prince Edward later became King Edward I.
New markets were created in different towns: Aldford and Alderley in 1253 AD, Macclesfield in 1261 AD, and Congleton in 1272 AD. In 1277 AD, King Edward I laid the first stone for Vale Royal Abbey. Chester suffered another serious fire in 1278 AD, burning most of the city.
Black Death and Royal Visits in the 14th Century
A serious fire hit Northwich in 1306 AD. Between 1322–25 AD, the Water Tower was built in Chester.
A terrible disease, the black death, arrived in Cheshire in 1349 AD. This caused a lot of illness and death.
Richard II visited Chester with many important people in 1394 AD. In 1397 AD, lands from Wales were added to Cheshire, and it was given the special rank of a "principality." In 1399 AD, Henry IV took control of Chester Castle. He brought Richard II there, and Richard gave up his crown, making Henry king.
Challenges and Culture in the 15th Century
In 1400 AD, supporters of the old King Richard II tried to attack Chester Castle but failed. In 1403 AD, many important people from Cheshire supported an uprising against King Henry IV, but it was unsuccessful.
The first mention of the Chester Mystery Plays was in 1422 AD. These were religious plays performed in the city. Famine led to food shortages in Chester in 1433 AD. Henry VI visited Chester in 1444 AD.
Chester faced financial problems because the River Dee was silting up, making it harder for ships to reach the city. The rent paid to the Crown was cut in half in 1445 AD.
The Wars of the Roses affected Cheshire. In 1459 AD, many Cheshire people were killed fighting on both sides at the Battle of Blore Heath. Later, Edward IV visited Chester in 1470 AD. Richard III visited in 1484 AD, and Henry VII visited in 1486 AD.
Stockport Grammar School was founded in 1488 AD. Fires also hit Chester's streets in 1492 AD and 1494 AD.
Modern Cheshire: 16th to 21st Centuries
Reformation and Rebuilding in the 16th Century
Macclesfield Grammar School was founded in 1502 AD. Between 1504-1508 AD, the earliest part of Little Moreton Hall was built near Congleton.
In 1506 AD, a special charter made Chester a county and set up its government. An outbreak of "sweating sickness" hit Chester in 1507 AD.
The Dissolution of the Monasteries by King Henry VIII greatly changed Cheshire. Norton Priory was dissolved in 1536 AD, followed by Vale Royal Abbey and Combermere Abbey in 1538 AD. Chester's three friaries were also dissolved in 1538 AD, and St Werburgh's Abbey in 1540 AD.
In 1541 AD, St Werburgh's Abbey became a cathedral for the Church of England, known as Chester Cathedral. Chester became a diocese, which is an area managed by a bishop. In 1543 AD, Cheshire sent its first members to sit in Parliament. The Chester Mystery Plays were banned in 1575 AD.
A large fire destroyed much of Nantwich in 1583 AD. However, Churche's Mansion, built in 1577 AD, survived the fire. Elizabeth I helped raise money to rebuild Nantwich in 1584 AD.
Civil War and Industry in the 17th Century
A new outbreak of the plague killed about 500 people in Nantwich in 1604 AD. Crewe Hall was finished in 1636 AD.
The English Civil War had a big impact on Cheshire. An attempt to keep Cheshire neutral failed in 1642 AD. Charles I visited Chester in 1642 AD. There were battles in Middlewich in 1643 AD and Nantwich in 1644 AD. Chester itself was under siege from 1644–1645 AD. The Battle of Rowton Heath took place near Chester in 1645 AD. Finally, Chester surrendered to the Parliamentary forces in 1646 AD.
Salt mining restarted in Northwich in 1670 AD. A stagecoach service between London and Chester began in 1657 AD.
Canals and New Industries in the 18th Century
Salt springs were found in Winsford in 1700 AD. To help ships, a new channel was dug along the River Dee from Chester to Connah's Quay between 1735–36 AD.
In 1744 AD, Charles Roe built a watermill in Macclesfield, which started the important silk industry there.
Many canals were built, making transport easier. The Bridgewater Canal was completed to Runcorn in 1776 AD. The Trent and Mersey Canal was finished in 1777 AD. The Chester Canal opened between Chester and Nantwich in 1779 AD. This canal was later extended to Ellesmere Port in 1795 AD.
Chester's main gates were rebuilt: Eastgate in 1780 AD, Northgate in 1781 AD, and Watergate in 1788 AD.
Railways and Growth in the 19th Century
More canals opened, like the Runcorn to Latchford Canal in 1804 AD and the Middlewich Branch in 1806 AD.
In 1832 AD, the future Queen Victoria opened the Grosvenor Bridge in Chester. This was a very grand event.
The railway era began in Cheshire. Crewe railway station was built in 1837 AD. The railway line connecting Crewe, Chester, and Birkenhead opened in 1840 AD. Crewe Railway Works, a major train factory, opened in 1843 AD.
A sad event happened in 1847 AD: five people were killed in the Dee bridge disaster when a railway bridge over the River Dee broke. Chester railway station opened in 1848 AD.
The Cheshire Constabulary, the local police force, was founded in 1857 AD. A terrible cattle disease, rinderpest, caused big problems for the county's economy between 1865–66 AD.
The Runcorn Railway Bridge opened in 1868 AD. In 1874 AD, John Brunner and Ludwig Mond started the company Brunner Mond near Northwich, making important chemicals. The Anderton Boat Lift, a unique way to move boats between different water levels, opened in 1875 AD.
The Cheshire County Council was founded in 1889 AD. The Manchester Ship Canal, a huge project allowing ships to reach Manchester, officially opened in 1894 AD. The famous Eastgate Clock in Chester was officially opened in 1899 AD.
Major Changes in the 20th Century
Widnes-Runcorn Transporter Bridge opened in 1905 AD. Cheshire School of Agriculture opened in 1921 AD.
Chester Zoo opened in 1931 AD, becoming a popular attraction. A new gate, Newgate, opened in Chester in 1938 AD. The Chester Mystery Plays were brought back to life in 1951 AD.
The Runcorn-Widnes road bridge, later called the Silver Jubilee Bridge, opened in 1961 AD. In 1964 AD, Runcorn was named a "New Town" to help with housing and development.
In 1974 AD, Cheshire's boundaries changed. Runcorn and Widnes joined to form the Borough of Halton. The Anderton Boat Lift closed in 1983 AD.
Sadly, in 1993 AD, there were bomb attacks by the IRA in Warrington. These attacks killed two children and injured many people. In 1998 AD, Halton and Warrington became separate "unitary authorities," meaning they managed their own local government.
Cheshire in the 21st Century
The Anderton Boat Lift reopened in 2002 AD, after being restored. In 2007 AD, the Cheshire Regiment, a local army group, merged into the Mercian Regiment.
A big change in local government happened in 2009 AD. The old Cheshire County Council was replaced by two new unitary authorities: Cheshire West and Chester and Cheshire East. This means these areas now manage their own services directly.
In 2017 AD, the Mersey Gateway Bridge, a new six-lane road bridge, opened across the River Mersey between Runcorn and Widnes.
See also










