ALBA facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America – Peoples' Trade Treaty
Alianza Bolivariana para los Pueblos de Nuestra América – Tratado de Comercio de los Pueblos (Spanish)
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Headquarters | Caracas |
| Official languages |
|
| Member states |
Pending full membership Observers Former members |
| Leaders | |
|
• Secretary General
|
|
| Establishment | |
|
• Cuba–Venezuela Agreement
|
14 December 2004 |
|
• People's Trade Agreement
|
29 April 2006 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
2,513,337 km2 (970,405 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2008 estimate
|
69,513,221 |
|
• Density
|
27.65/km2 (71.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$636.481 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$9,156 |
| Currency | |
| Time zone | UTC-4 to -6 |
| Internet TLD | |
ALBA or ALBA–TCP is a group of countries in Latin America and the Caribbean. Its full name is the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America – Peoples' Trade Treaty. It's an organization that helps these countries work together politically and economically.
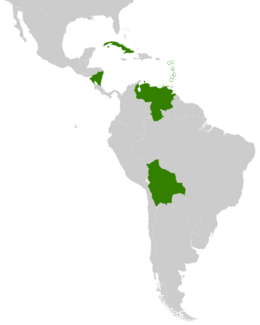
ALBA was started in 2004 by Cuba and Venezuela. It focuses on helping countries grow together, sharing resources, and supporting each other. This is different from traditional trade agreements. The group aims for social well-being and mutual aid. Today, ten countries are full members of ALBA. These include Antigua and Barbuda, Bolivia, Cuba, Dominica, Grenada, Nicaragua, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Venezuela. Suriname joined as a guest country in 2012.
History of ALBA

The idea for ALBA came from the government of Venezuela, led by Hugo Chávez. He wanted to create an alternative to a large trade agreement proposed by the United States. This agreement was called the Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA). The FTAA never actually happened.
How ALBA Started
ALBA officially began on December 14, 2004. Presidents Chávez of Venezuela and Fidel Castro of Cuba signed an agreement. This agreement focused on exchanging important resources. Venezuela, which has a lot of oil, agreed to send oil to Cuba at good prices. In return, Cuba sent many doctors and teachers to help people in Venezuela. This also allowed Venezuelans to get special medical care in Cuba for free.
When it first started, ALBA only had two members: Venezuela and Cuba. Over time, more countries joined this "Peoples' Trade Agreement." This agreement helps put ALBA's ideas into action.
Countries Joining and Leaving
- Bolivia joined ALBA in 2006.
- Nicaragua became a member in 2007.
- Ecuador joined in 2009 but left in August 2018.
- Honduras joined in 2008 but left in 2010 after a political change.
- Several Caribbean nations also joined, including Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Saint Lucia.
- In December 2014, Grenada and Saint Kitts and Nevis became full members.
- Bolivia's government left ALBA in November 2019 during a political crisis. However, a new government in Bolivia rejoined the alliance in 2020.
In 2023, ALBA invited Russia to take part in the ALBA Games. This happened while Russia was facing international challenges.
Virtual Currency: The SUCRE
In October 2009, ALBA leaders decided to create a special virtual currency called the SUCRE. The goal was to have an independent money system for trade between member countries. By 2015, the SUCRE was being used for trade between Bolivia, Cuba, Nicaragua, Ecuador, and Venezuela.
Important Meetings: Summits
ALBA leaders meet regularly at summits to discuss plans and make decisions. Here are some key meetings:
- The first summit was in Havana, Cuba, on December 14, 2004. This is when ALBA was founded.
- In April 2006, Bolivia joined the group at a summit in Havana.
- Nicaragua joined in January 2007 at a meeting in Managua.
- Dominica became a member in January 2008 at a summit in Caracas.
- Honduras joined in August 2008 in Tegucigalpa.
- Antigua and Barbuda, Ecuador, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines joined in June 2009.
- The SUCRE virtual currency was adopted in October 2009 in Cochabamba, Bolivia.
- Saint Lucia joined in July 2013 in Guayaquil, Ecuador.
- Grenada and Saint Kitts and Nevis joined in December 2014 in Havana.
- The 20th summit was held in December 2021 in Havana.
- The 24th summit is planned for December 2024 in Caracas to celebrate ALBA's 20th anniversary.
ALBA Member Countries
ALBA has full members, observer members, and some countries that were members in the past.
Full Members
These are the main countries that are part of ALBA:
| Country |
Join date |
Capital City |
|---|---|---|
| 24 June 2009 | St. John's | |
| 29 April 2006 | Sucre | |
| 14 December 2004 | Havana | |
| 20 January 2008 | Roseau | |
| 14 December 2014 | St. George's | |
| 11 January 2007 | Managua | |
| 14 December 2014 | Basseterre | |
| 20 July 2013 | Castries | |
| 24 June 2009 | Kingstown | |
| 14 December 2004 | Caracas |
Observer Members
These countries attend ALBA meetings and participate in some activities, but are not full members:
| Country | Capital City |
|---|---|
| Port-au-Prince | |
| Tehran |
Former Members
These countries were once part of ALBA but have since left:
| Country | Joined | Left | Capital City |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 2010 | Tegucigalpa | |
| 2009 | 2018 | Quito |
Other ALBA Projects
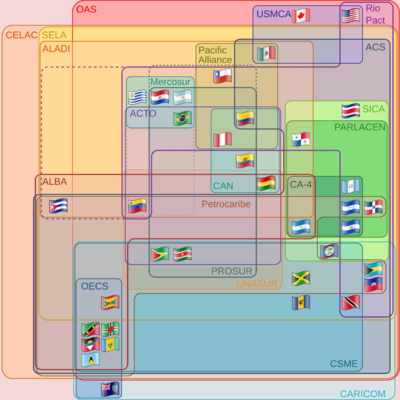
ALBA also supports other projects to help its member countries.
PetroCaribe
PetroCaribe was started in 2005. It helps Caribbean countries get oil from Venezuela at special, affordable prices. Many of these countries do not have their own oil. In return, they provide services or goods to Venezuela. For example, Cuba receives oil in exchange for sending medical doctors to Venezuela.
Other Energy Efforts
Cuba has worked with ALBA countries to improve energy use. Cuban social workers have traveled to many countries. They help develop projects that make energy use more efficient.
TeleSUR News Network
Launched in 2005, TeleSUR is a news network for the ALBA countries. It provides news and current events. It has an online TV channel and is a team effort by the governments of Venezuela, Cuba, and Nicaragua.
PETROSUR Energy Alliance
PETROSUR is an energy partnership between oil companies from Venezuela, Argentina, and Brazil. Its goal is to use money from oil to fund social programs in these countries.
ALBA and Climate Change
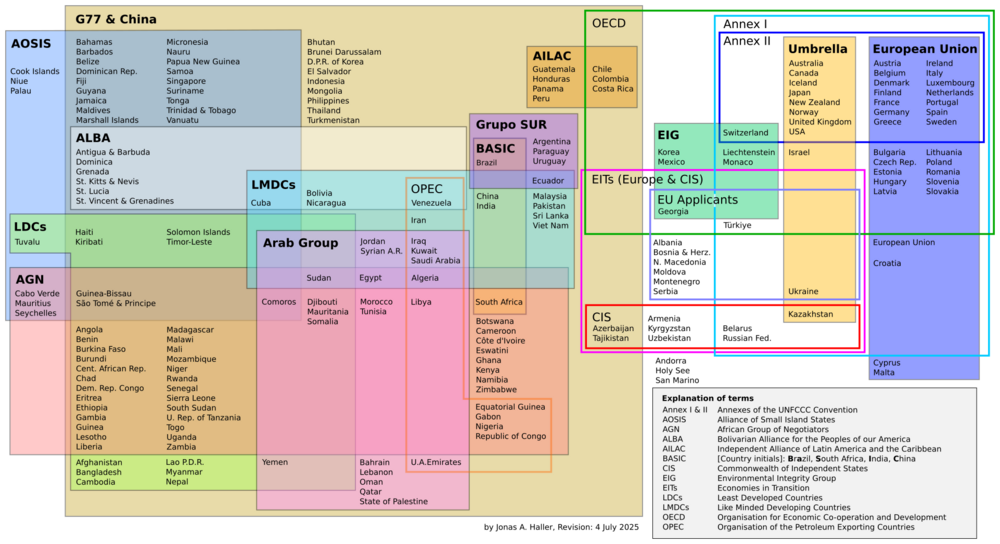
ALBA also represents its member countries at international meetings about climate change. This happens when the countries agree on a common position. These meetings are part of the UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change).
See also
- Andean Community of Nations
- Association of Caribbean States
- Axis of Resistance
- Belt and Road Initiative
- CARIFORUM
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
- Copenhagen Accord
- CSTO
- Eurasian Economic Union
- Foro de São Paulo
- International trade
- Latin American integration
- Lima Group
- Mercosur
- Non Aligned Movement
- Pacific Alliance
- PetroCaribe
- Pink tide
- Social security
- SUCRE
- Trade bloc
- Union of South American Nations
- Warsaw Pact
- Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA or ALCA)
- Latin American Free Trade Agreement
- North American Free Trade Agreement