Duchy of Brabant facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Duchy of Brabant
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1183/1190–1406/1797 | |||||||||||||||
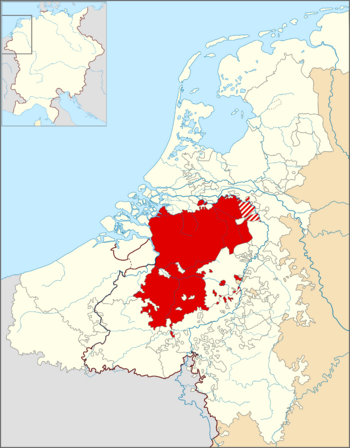
The Duchy of Brabant within the Seventeen Provinces of the Low Countries and the borders of the Holy Roman Empire (thick line)
|
|||||||||||||||
| Status |
|
||||||||||||||
| Capital | Brussels | ||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Feudal Duchy | ||||||||||||||
| Duke of Brabant | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1183/1184–1235
|
Henry I (first) | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1792–1797
|
Francis I (last) | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1183 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Inherited by Duchy of Burgundy
|
1430 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Inherited by House of Habsburg
|
1482 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Inherited by Habsburg Spain
|
1556 | ||||||||||||||
| 30 January 1648 | |||||||||||||||
| 7 March 1714 | |||||||||||||||
|
• Battle of Sprimont
|
18 September 1794 | ||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Today part of | Belgium Netherlands |
||||||||||||||
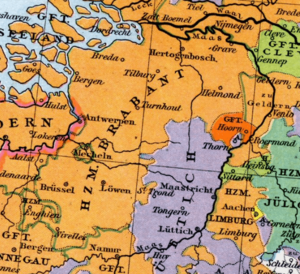
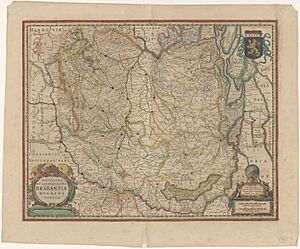
The Duchy of Brabant was an important state in the Holy Roman Empire. It was created in 1183. This duchy grew from an older area called the Landgraviate of Brabant. It was a central part of the historic Low Countries, which are now Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
From 1430, the Duchy of Brabant became part of the Burgundian Netherlands. Later, from 1482, it was part of the Habsburg Netherlands. The duchy was divided after the Dutch revolt (1566–1648).
In 1648, a peace treaty gave the northern part of Brabant (today's North Brabant) to the Dutch Republic. The rest of the duchy stayed with the Habsburg Netherlands. French forces took over this southern part in 1794. Today, most of the old Duchy of Brabant is in Belgium, except for the Dutch province of North Brabant.
Contents
Geography of Brabant
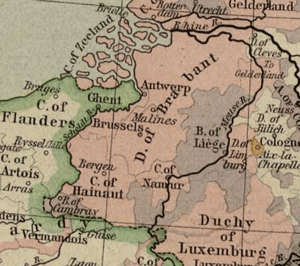
The Duchy of Brabant was split into four main areas. Each area had its own capital city. These capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp, and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenbosch was founded, Tienen was the fourth capital.
The land of the duchy mostly covered parts of modern-day Belgium. These include the provinces of Flemish Brabant, Walloon Brabant, and Antwerp. It also included the Brussels-Capital Region. A large part of the present-day Dutch province of North Brabant was also part of it.
The Brabantian Lion

The modern flag of Belgium uses colors from Brabant's old coat of arms. This coat of arms showed a gold lion on a black background. The lion had red claws and a red tongue.
This lion symbol was likely first used by Count Lambert I around the year 1000. You can see the Brabantian lion on the coats of arms of Flemish Brabant, Walloon Brabant, and the Dutch province of North Brabant even today.
History of Brabant
| History of the Low Countries | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frisii | Belgae | |||||||
| Cana- nefates |
Chamavi, Tubantes |
Gallia Belgica (55 BC – 5th c. AD) Germania Inferior (83 – 5th c.) |
||||||
| Salian Franks | Batavi | |||||||
| unpopulated (4th–5th c.) |
Saxons | Salian Franks (4th–5th c.) |
||||||
| Frisian Kingdom (6th c.–734) |
Frankish Kingdom (481–843)—Carolingian Empire (800–843) | |||||||
| Austrasia (511–687) | ||||||||
| Middle Francia (843–855) | West Francia (843–) |
|||||||
| Kingdom of Lotharingia (855– 959) Duchy of Lower Lorraine (959–) |
||||||||
| Frisia | ||||||||
Frisian Freedom (11–16th century) |
County of Holland (880–1432) |
Bishopric of Utrecht (695–1456) |
Duchy of Brabant (1183–1430) Duchy of Guelders (1046–1543) |
County of Flanders (862–1384) |
County of Hainaut (1071–1432) County of Namur (981–1421) |
P.-Bish. of Liège (980–1794) |
Duchy of Luxem- bourg (1059–1443) |
|
Burgundian Netherlands (1384–1482) |
||||||||
Habsburg Netherlands (1482–1795) (Seventeen Provinces after 1543) |
||||||||
Dutch Republic (1581–1795) |
Spanish Netherlands (1556–1714) |
|||||||
Austrian Netherlands (1714–1795) |
||||||||
United States of Belgium (1790) |
R. Liège (1789–'91) |
|||||||
Batavian Republic (1795–1806) Kingdom of Holland (1806–1810) |
associated with French First Republic (1795–1804) part of First French Empire (1804–1815) |
|||||||
Princip. of the Netherlands (1813–1815) |
||||||||
| United Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1830) | Gr D. L. (1815–) |
|||||||
Kingdom of the Netherlands (1839–) |
Kingdom of Belgium (1830–) |
|||||||
| Gr D. of Luxem- bourg (1890–) |
||||||||
The name "Brabant" comes from "Bracbatensis," which means "marshy region." This area was between the rivers Scheldt and Dijle. In 843, it became part of Lotharingia. Later, in 880, it was given to East Francia.
Long before, during Roman times, a tribe called the Nervii lived here. They were part of the Roman province of Belgica. Later, Germanic Franks conquered the region.
Early Rulers
In 959, King Otto I made Count Godfrey a duke. His land was called Duchy of Lower Lorraine. This duchy became part of the Holy Roman Empire in 962.
The counts of Leuven became powerful in this area. Around 1000, Count Lambert I married Gerberga. She was the daughter of Duke Charles. This marriage helped Lambert gain control of the County of Brussels.
In 1085, Emperor Henry IV gave the land between the Dender and Zenne rivers to Count Henry III of Leuven. This land was called the Landgraviate of Brabant.
About 100 years later, in 1183 or 1184, Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa officially created the Duchy of Brabant. He made Henry I the first Duke of Brabant. Henry I was the son of Count Godfrey III.
Even though the original duchy was small, its name soon covered all the lands ruled by the dukes. After Godfrey III died in 1190, Henry I also became Duke of Lower Lotharingia. From then on, all the rulers were called Dukes of Brabant and Lower Lotharingia.
In 1288, after the Battle of Worringen, the dukes of Brabant also gained the Duchy of Limburg. In 1354, Duke John III gave the people of Brabant a special charter called the "Joyous Entry." This charter gave them more rights and freedoms.
Under Burgundy and Habsburgs
In 1430, the Duchies of Brabant and Limburg were passed to Philip the Good of Burgundy. They became part of the larger Burgundian Netherlands.
In 1477, the Duchy of Brabant became part of the House of Habsburg. This happened when Mary of Burgundy married into the Habsburg family. At this time, the duchy stretched from Luttre to 's Hertogenbosch. Leuven was its capital city. The history of Brabant then became part of the history of the Habsburg Seventeen Provinces.
The Eighty Years' War and Division
The Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) was a long conflict. During this war, the northern parts of Brabant came under the control of the northern rebels. After the war ended with the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, the northern part of Brabant was officially given to the United Provinces. This area was called Staats-Brabant.
The southern part of Brabant remained under Spanish Habsburg rule. It was later transferred to the Austrian branch of the Habsburg monarchy in 1714.
During the French Revolution in 1794, French forces took over the area. In 1795, France officially took control. The Duchy of Brabant was then dissolved. Its territory was divided into new areas called "départements."
After Napoleon's defeat in 1815, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands was formed. The old provinces of Brabant were restored as North Brabant, Antwerp, and South Brabant. When modern Belgium was created in 1830, Antwerp and South Brabant became part of it. South Brabant is now simply called Brabant province.
Cities of Brabant
Brabant had both fortified cities with walls and unwalled cities. Walled cities could build walls, which often led to more trade and larger populations. Unwalled cities could hold markets, which helped them grow. However, unwalled cities often suffered more damage during wars.
Cities in the Leuven Area
- Leuven: The original capital city of Brabant. It has been a university town since 1425.
- Tienen: East of Leuven, it was one of the larger cities.
- Zoutleeuw: A wealthy merchant town near the border.
- Aarschot: Known for its beautiful architecture made from local red stone.
- Diest: One of Brabant's biggest cities, famous for its breweries and historical monuments.
Cities in the Brussels Area
- Brussels: The capital city of this part of Brabant. It was also the capital of the Seventeen Provinces and is now the capital of Belgium.
- Vilvoorde: Home to the first modern prison in the Austrian Netherlands.
- Nivelles: Known for its church and as the birthplace of Saint Gertrude of Nivelles.
- Braine-l'Alleud: The famous Battle of Waterloo took place near this small city.
Cities in the Antwerp Area
- Antwerp: The capital of this quarter. It was an important business and trade city with many grand merchant buildings.
- Lier: Known as the wedding site of the parents of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor.
- Breda: An important fortified city and military center.
Cities in the 's-Hertogenbosch Area
- 's-Hertogenbosch: The regional capital and an important religious center.
- Heusden: Known as an "untakeable city" in a military sense.
- Helmond: Has a large historic water fortress.
- Eindhoven: One of Europe's first "planned" new cities, founded in 1232. Its walls were destroyed during the Eighty Years War.
See also
- Duke of Brabant (with genealogies)
- Lohengrin (opera)
- War of Devolution (1667–1668)