List of Spanish missions in California facts for kids
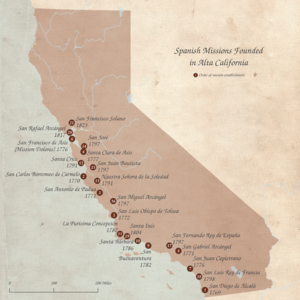
Between 1769 and 1833, Franciscan priests built 21 missions in a region then known as Alta California. They also built military forts nearby. Their main goals were to teach Christianity to the local Native American people. They also wanted to make sure Spain, and later Mexico, kept control of the land.
Contents
Exploring the California Missions Trail
To make travel easier, the missions were built about 30 miles (48 kilometers) apart. This was about a one-day trip on horseback or three days on foot. This long path eventually became a 600-mile (966-kilometer) trail called the "California Mission Trail."
A priest named Rev. Lasuén thought it was a good idea to add more stops along the trail. These extra spots would give travelers safe and comfortable places to rest. It's also a fun story that the priests sprinkled mustard seeds along the trail. This made bright yellow flowers grow, marking the way.
Today, many people enjoy walking parts of this mission trail. They call themselves California Mission Walkers. Walking the trail helps them feel connected to the history of the missions. For some, it's a special spiritual journey, like a pilgrimage.
The 21 California Missions
There were 21 main missions built in what is now California. There were also 8 smaller branch missions called asistencias and 5 large farms called estancias.
| Name | Image | Date | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mission San Francisco Solano | 1823 | Sonoma | This mission is now a museum. | |
| Mission San Rafael Arcángel | 1817 | San Rafael | The original mission is gone. A new building was made in 1949. It is now a church and museum. | |
| Mission San Francisco de Asís | 1776 | San Francisco | Also known as Mission Dolores. It is still a church today. | |
| Mission San José | 1797 | Fremont | This mission is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission Santa Clara de Asís | 1777 | Santa Clara | It is a church inside Santa Clara University. | |
| Mission Santa Cruz | 1791 | Santa Cruz | The original mission is gone. A new one was built in the 1930s. It is a church and museum. | |
| Mission San Juan Bautista | 1797 | San Juan Bautista | This mission is still a church. | |
| Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo | 1770 | Carmel | It is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission Nuestra Señora de la Soledad | 1791 | Soledad | The original mission is in ruins. A new part was built in 1955. It is a church and museum. | |
| Mission San Antonio de Padua | 1771 | near Jolon | This mission is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission San Miguel Arcángel | 1797 | San Miguel | It is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa | 1772 | San Luis Obispo | This mission is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission La Purísima Concepción | 1787 | Lompoc | This mission is now a museum. | |
| Mission Santa Inés | 1804 | Solvang | It is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission Santa Barbara | 1786 | Santa Barbara | This mission is a church and a home for priests. | |
| Mission San Buenaventura | 1782 | Ventura | It is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission San Fernando Rey de España | 1797 | Los Angeles | This mission is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission San Gabriel | 1771 | San Gabriel | The church building you see today was finished in 1805. It is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission San Juan Capistrano | 1776 | San Juan Capistrano | The Serra Chapel, built in 1782, is the oldest building still standing in California. It is a church and a museum. | |
| Mission San Luis Rey de Francia | 1798 | Oceanside | This mission is a church, a museum, and a place for religious retreats. | |
| Mission San Diego de Alcalá | 1769 | San Diego | It is a church and a museum. |
Two other Franciscan missions, Mission Puerto de Purísima Concepción and Mission San Pedro y San Pablo de Bicuñer, were also built in California. However, they were managed as part of the Spanish missions in a different region and are not counted among the 21 California missions.
What were Asistencias?
Asistencias were like smaller branch missions. They helped the priests reach more Native American people without costing too much money.
| Name | Image | Date | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Santa Eulalia Asistencia | 1824 | Cordelia | You can still see the ruins of this asistencia behind a business park. | |
| San Pedro y San Pablo Asistencia | 1786 | Pacifica | The original building is gone. It was the first branch mission of Mission San Francisco de Asís. | |
| Mission Dolores Asistencia | 1793-94 | San Mateo | The original buildings are gone. A granary (a building to store grain) was built in 1793-94. It was destroyed by an earthquake in 1808. A new one was built but was torn down in 1868. | |
| Santa Margarita de Cortona Asistencia | 1787 | Santa Margarita | This was a branch of Mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa. Its ruins are kept inside a barn on a private ranch. | |
| Santa Paula Asistencia | around 1800 | Santa Paula | The original building is gone. It was a branch of Mission San Buenaventura. Not much else is known about it. | |
| Nuestra Señora Reina de los Ángeles Asistencia | 1784 | Los Angeles | The original building is gone. This was a branch of Mission San Gabriel Arcángel. A church called La Iglesia de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles now stands on its site. | |
| Santa Ysabel Asistencia | 1818 | Santa Ysabel | The original building is gone. It was a branch of Mission San Diego de Alcalá. A new chapel was built in 1924. It is now a church and museum. | |
| San Antonio de Pala Asistencia | 1816 | Pala Indian Reservation | This was a branch of Mission San Luis Rey de Francia. Its chapel is now a church and museum. |
What were Estancias?
An estancia was a Spanish word for a large private farm or ranch. These farms helped their main missions by growing food or raising animals.
| Name | Image | Date | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Marcos Estancia | around 1800 | near Santa Ynez | The original building is gone. It was a farm for Mission Santa Barbara. Not much else is known. | |
| San Francisco Xavier Estancia | 1804 | Castaic Junction | The original building is gone. It was a farm for Mission San Fernando Rey de España. | |
| San Bernardino de Sena Estancia | 1819 | Redlands | This was a farm for Mission San Gabriel Arcángel. The rebuilt buildings are now a museum. | |
| Santa Ana Estancia | 1817 | Costa Mesa | Also known as the Costa Mesa Estancia. It was a farm for Mission San Juan Capistrano. The Diego Sepúlveda Adobe building is now a museum. | |
| Las Flores Estancia | 1823 | Camp Pendleton | This was a farm for Mission San Luis Rey de Francia. The building is now part of a Boy Scout camp. |
Military Forts (Presidios)
The Spanish also built military forts, called Presidios, to protect the missions and Spanish land claims. Here are the main ones:
- Presidio of San Diego, started July 16, 1769
- Presidio of Monterey, California, started June 3, 1770
- Presidio of San Francisco, started December 17, 1776
- Presidio of Santa Barbara, started April 12, 1782
- Sonoma Barracks, started 1810
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Misiones españolas en California para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Misiones españolas en California para niños
- Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail
- History of California through 1899
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
- Native Americans in the United States































