Subtropics facts for kids
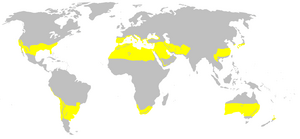
The subtropics are areas on Earth found just outside the tropics. The tropics are located between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S). Subtropical zones are usually found between 20 and 40 degrees of latitude in both the northern and southern parts of the world. These regions have a special kind of climate.
Contents
What Makes Subtropical Climates Special?
In subtropical climates, winters are quite warm. They are not as hot as the summer season. These areas rarely get frost or snow. Because of this, many plants like palm trees, citrus trees, and evergreen trees grow well here. This is different from colder places where deciduous trees (which lose their leaves) and conifer trees (like pines) are more common.
As you move closer to the tropics, the cool winter season almost disappears. But if you move closer to the poles, the winters become much cooler.
Rainfall in subtropical areas can be very different. Some parts are hot deserts, while others have savannas (grasslands with scattered trees). You can also find monsoon forests (which get a lot of rain in one season) and humid forests. The warmer parts of the Mediterranean climate zone are also subtropical.
Where Are Subtropical Areas Found?
Subtropical regions are found all over the world. Here are some examples:
In Africa
- North Africa: Cities like Algiers in Algeria, Alexandria in Egypt, Casablanca in Morocco, Tripoli in Libya, and Tunis in Tunisia.
- Southern Africa: Cities such as Cape Town, Durban, and East London in South Africa. Also, Maseru in Lesotho.
- Atlantic Islands: Islands like Las Palmas in Spain (Canary Islands) and Funchal in Portugal (Madeira).
In The Americas
- United States: Many cities in the southern USA, including Atlanta, Austin, Houston, Jacksonville, Florida, Los Angeles, New Orleans, Phoenix, San Diego, and Tampa.
- Mexico: Cities like Monterrey, Hermosillo, and Tijuana.
- Brazil: States such as São Paulo, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul.
- Latin America: Cities like Buenos Aires in Argentina, Montevideo in Uruguay, Santiago, Chile, and Lima in Peru.
In Eurasia
- Mainland China: Major cities like Shanghai, Guangzhou, Hong Kong, and Macau.
- Taiwan: Cities like Taipei and Kaohsiung.
- Japan: Islands like Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa.
- European Union: Many areas around the Mediterranean Sea, including parts of Spain, Italy, and the Balkans. Major cities include Lisbon, Barcelona, Madrid, Rome, and Athens. Also, Malta and Gibraltar.
- India: Cities like Amritsar and New Delhi.
- Pakistan: Cities like Islamabad and Peshawar.
- Russia: Cities on the Black Sea coast like Sochi.
- Philippines: Areas like Baguio and Batanes.
- Middle East: Parts of Iran, Iraq (like Baghdad), Israel, northern Saudi Arabia, Beirut in Lebanon, and Latakia in Syria.
- Vietnam: Cities like Hanoi and Hai Phong.
In Oceania
- Australia: Many parts of New South Wales, Queensland, Western Australia, South Australia, and north-eastern Victoria (Australia).
- New Zealand: Regions like Auckland, Northland, and Coromandel.
Subtropical Plants
Many unique plants thrive in subtropical climates. These include various types of palm trees, citrus trees (like oranges and lemons), and a wide range of evergreen plants that keep their leaves all year.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Clima subtropical para niños
In Spanish: Clima subtropical para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |