Cold War facts for kids
The Cold War was a long period of tension and rivalry between the United States and its friends, and the Soviet Union (also known as the USSR) and its friends. It lasted from the end of World War II until the Soviet Union broke apart. It was called "Cold" because the US and the USSR never fought each other directly. Instead, they supported different sides in smaller wars around the world, called proxy wars.
Contents
Two Sides: East and West
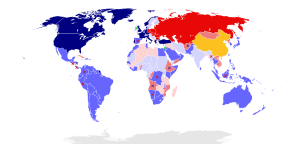
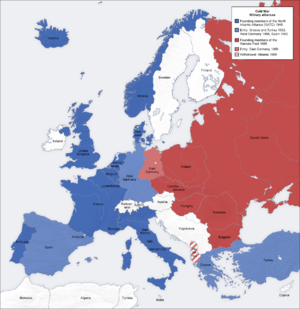
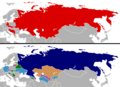
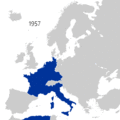
During the Cold War, the world was largely divided into two main groups. On one side was the Western Bloc, led by the United States. This group believed in capitalism and democracy. Many of these countries joined an alliance called NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) in 1949. Important members included the US, United Kingdom, France, West Germany, and Canada. Other friends of the Western Bloc were Japan, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand.
On the other side was the Eastern Bloc, led by the Soviet Union (USSR). This group believed in communism. Many of these countries formed an alliance called the Warsaw Pact in 1955. Key members included the USSR, East Germany, Poland, and Hungary. Other allies of the Eastern Bloc included Cuba, North Korea, and Vietnam.
How the Cold War Started
The roots of the Cold War go back to the early 1900s in Russia. In 1917, the old Russian king, Tsar Nicholas II, was overthrown. Later that year, a communist group called the Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, took control. They created a new communist government.
Not everyone agreed with the communists. A civil war broke out in Russia. Other countries, like the United States and the United Kingdom, even sent troops to support the groups fighting against the communists. However, the communists won the war in 1922 and formed the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), or Soviet Union.
After World War II, the United States and the Soviet Union were the two strongest powers. They had different ideas about how countries should be run. The Western allies worried that the Soviet Union wanted to spread communism by force. They were also concerned when the Soviet Union developed its own atomic bomb after the war. This made the tension much worse.
Germany Divided
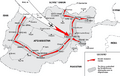
After World War II, Germany was in ruins. The winning countries, including the US, UK, France, and the USSR, divided Germany into four parts. Each country occupied one part. The city of Berlin, which was deep inside the Soviet-controlled part, was also divided among the four countries.
In 1949, the Western parts of Germany became a capitalist democracy called West Germany. West Berlin was part of it. The Soviet part became a communist country called East Germany.
From 1948 to 1949, the Soviets tried to block all roads and railways into West Berlin. This was called the Berlin Blockade. The United States and its allies supplied the city by air, flying in food and supplies. This was known as the Berlin Airlift.
Many people in East Germany wanted to move to West Germany because life there was better and they had more freedom. So, in 1961, the East German government built the Berlin Wall. This wall divided the city and was heavily guarded to stop people from escaping to the West. The Berlin Wall became a strong symbol of the Cold War and the "Iron Curtain" that split Europe.
The 1950s: Spies and Space
Spying was a big part of the Cold War. The USSR had its spy agency, the KGB. The US had the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) for spying abroad and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) for catching spies at home.
In the Soviet Union, the leader Joseph Stalin died in 1953. Nikita Khrushchev eventually took his place. Khrushchev tried to change some of Stalin's harsh policies.
In the United States, there was a "Red Scare." People worried about communists in America, especially after the USSR got its own atomic bomb. Some famous Americans were even accused of being communists, which ruined their careers.
The 1950s also saw the start of the Space Race between the US and the USSR. In 1957, the USSR launched Sputnik 1, the first satellite to orbit Earth. This shocked the US, which then created NASA. The Soviet Union also sent the first man, Yuri Gagarin, into space. They used this to show that communism was better.
Both sides built up their nuclear weapons. The US developed a policy called "New Look," which meant relying more on nuclear weapons to stop the Soviet Union from attacking. This led to a dangerous situation called mutual assured destruction, where both sides knew that a nuclear war would destroy everyone.
In 1956, the Soviet Union sent troops to stop an anti-communist uprising in Hungary. The Western allies did not step in. This showed that each side mostly stuck to its own area of influence.
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
This was the most dangerous moment of the Cold War. After the US tried and failed to invade Cuba (the Bay of Pigs incident), the Soviet Union tried to send nuclear missiles to Cuba. These missiles would have been very close to the United States.
In response, the US sent many ships to blockade Cuba, stopping the Soviet ships. The world held its breath, fearing a nuclear war. Finally, the US and the Soviet Union reached an agreement. The Soviets would remove their missiles from Cuba, and the US promised not to invade Cuba again. This crisis showed how close the world came to a massive war.
Détente: A Period of Calm
After the Cuban Missile Crisis, relations between the US and the USSR became a bit calmer. This period was called "Détente," which means a relaxing of tension. During this time, both sides signed treaties to reduce the number of nuclear weapons.
The US also started building a better relationship with China, which had been an ally of the Soviet Union. This was a big change in global politics.
The End of the Cold War
In the 1980s, US President Ronald Reagan took a strong stance against the Soviet Union. He increased military spending and supported anti-communist groups around the world.
The Soviet Union's economy was struggling, partly because it tried to keep up with the US in military spending. The USSR also faced a difficult war in Afghanistan starting in 1979, fighting against resistance groups that were supported by the US.
In the late 1980s, a new Soviet leader, Mikhail Gorbachev, came to power. He wanted to fix the Soviet Union's problems and improve relations with the US. He tried to make changes within the Soviet Union, but this led to political disagreements.
The biggest symbol of the Cold War, the Berlin Wall, fell in 1989. This was a huge moment, showing that communist rule was weakening. Without the Communist Party holding everything together, the Soviet Union began to break apart. In December 1991, the USSR officially ended, splitting into many smaller countries like Russia, Ukraine, and Georgia. The countries of Eastern Europe also became capitalist democracies again. This marked the end of the Cold War.
Some historians believe the Cold War ended when the Berlin Wall fell in 1989. Others think it ended when the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991.
Images for kids
-
Allied troops in Vladivostok, August 1918, during the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War
-
The "Big Three" at the Yalta Conference: Winston Churchill, Franklin D. Roosevelt and Joseph Stalin, 1945
-
Clement Attlee, Harry S. Truman and Joseph Stalin at the Potsdam Conference, 1945
-
Remains of the "Iron Curtain" in the Czech Republic
-
President Truman signs the North Atlantic Treaty with guests in the Oval Office.
-
US Marines engaged in street fighting during the liberation of Seoul, September 1950
-
From left to right: Soviet head of state Kliment Voroshilov, Soviet premier Nikita Khrushchev and Finnish president Urho Kekkonen at Moscow in 1960.
-
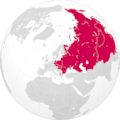
The maximum territorial extent of Soviet influence, after the Cuban Revolution of 1959 and before the official Sino-Soviet split of 1961
-
The United States reached the Moon in 1969.
-
Che Guevara (left) and Fidel Castro (right) in 1961
-
Soviet and American tanks face each other at Checkpoint Charlie during the Berlin Crisis of 1961.
-
Aerial photograph of a Soviet missile site in Cuba, taken by a US spy aircraft, 1 November 1962
-
US combat operations during the Battle of Ia Drang, South Vietnam, November 1965
-
A manifestation of the Finlandization period: in April 1970, a Finnish stamp was issued in honor of the 100th anniversary of Vladimir Lenin's birth and the Lenin Symposium held in Tampere. The stamp was the first Finnish stamp issued about a foreign person.
-
The invasion of Czechoslovakia by the Soviet Union in 1968 was one of the biggest military operations on European soil since World War II.
-
Suharto of Indonesia attending funeral of five generals slain in 30 September Movement, 2 October 1965
-
Egyptian leader Anwar Sadat with Henry Kissinger in 1975
-
Chilean leader Augusto Pinochet shaking hands with Henry Kissinger in 1976
-
Mao Zedong and US President Richard Nixon, during his visit in China
-
Leonid Brezhnev and Jimmy Carter sign the SALT II treaty, 18 June 1979, in Vienna
-
Iranian people protesting against the Iranian Revolution
-
President Reagan with Prime Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher during a working luncheon at Camp David, December 1984
-
Delta 183 launch vehicle lifts off, carrying the Strategic Defense Initiative sensor experiment "Delta Star".
-
After ten-year-old American Samantha Smith wrote a letter to Yuri Andropov expressing her fear of nuclear war, Andropov invited Smith to the Soviet Union.
-
Otto von Habsburg, who played a leading role in opening the Iron Curtain.
-
Erich Honecker lost control in August 1989.
-
August Coup in Moscow, 1991
-
The human chain in Lithuania during the Baltic Way, 23 August 1989
-
Since the end of the Cold War, the EU has expanded eastwards into the former Warsaw Pact and parts of the former Soviet Union.
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra Fría para niños
In Spanish: Guerra Fría para niños