Tropics facts for kids
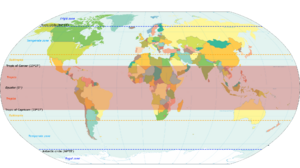
The tropics are special areas on Earth that are found around the Equator. They are located between two important imaginary lines: the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere (at about 23.5° N) and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere (at about 23.5° S). These areas are also known as the tropical zone or the torrid zone.
In terms of weather, the tropics get more direct sunlight than other parts of Earth. This usually makes them hotter and wetter, and they don't experience big changes in seasons like other regions do. Sometimes, when people say "tropical," they are talking about this kind of warm, wet weather, not just the geographical area. However, the tropical zone also includes places like deserts and mountains with snow, which don't have a typical "tropical" climate. The tropics are different from the middle latitudes and the polar regions, which are found further away from the Equator.
The tropics cover almost 40% of Earth's surface and about 36% of its land. In 2014, about 40% of the world's people lived here, and experts think this number could reach 50% by 2050. Because of global warming, the weather in the tropics is changing. Areas near the tropics, called the subtropics, are seeing more extreme weather events, like very hot days and stronger storms. These changes might make some parts of the tropics difficult to live in.
Contents
What Does "Tropic" Mean?
The word "tropic" comes from an old Greek word, tropē, which means "to turn" or "change direction."
How Astronomers Define the Tropics
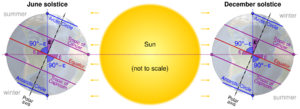
The tropics are defined by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere. These lines are at about 23.5 degrees north and south of the Equator. This specific angle matches the way Earth is tilted on its axis.
The Tropic of Cancer is the northernmost point where the Sun can be seen directly overhead (at its highest point in the sky) during the June solstice. The Tropic of Capricorn is the southernmost point where the Sun can be directly overhead during the December solstice. This means that any place within the tropical zone will have the Sun directly overhead at least once during the year. The maximum latitudes of the tropics are equally far from the Equator on both sides. While Earth's tilt changes very slightly, the tropical lines are set by agreement, and their small changes don't affect the definition much.
Seasons and Weather in the Tropics
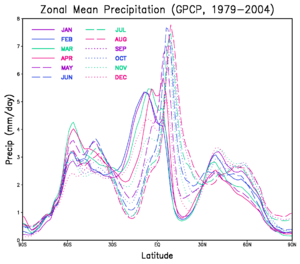
Many tropical areas have two main seasons: a dry season and a wet season. The wet season, also called the rainy season or green season, is when most of the year's rainfall happens. This can last for one or more months. Wet seasons are common in parts of the tropics and subtropics, and even in some temperate regions.
In tropical climates, a wet-season month is defined as having at least 60 millimeters (about 2.4 inches) of rain. Some areas with strong rainy seasons might have a short break in rainfall during the middle of the season. This happens when the intertropical convergence zone (a band of low pressure where winds meet) or monsoon trough moves away from their location. Plants in these areas can range from moist seasonal tropical forests to savannahs (grasslands with scattered trees).
When the wet season happens during the warmer months, rain usually falls in the late afternoon and early evening. The wet season brings many good things: air quality often gets better, freshwater becomes more plentiful, and plants grow a lot. This leads to good crop yields later in the season. However, heavy rains can cause rivers to overflow, leading to flooding, and some animals move to higher ground. Soil nutrients can also be washed away, and erosion increases. In places where the rainy season is also hot, there can be more cases of malaria. Animals in these regions have special ways to adapt and survive the wetter conditions. The dry season before the wet season can cause food shortages until new crops grow.
It's important to remember that not all places within the geographical tropics have a "tropical" climate. For example, large parts of the tropics are actually very dry, like the Sahara Desert, the Atacama Desert, and the Australian Outback. There are also high mountains with alpine tundra and snow-capped peaks, such as Mauna Kea, Mount Kilimanjaro, Puncak Jaya, and parts of the Andes mountains in South America.
How Climate Change Affects the Tropics
The climate in the tropics is changing, just like everywhere else in the world. The effects of increasing greenhouse gases might be harder to notice for people living in the tropics because there are also natural changes in the weather. Much of this natural change is caused by the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO). The tropics have warmed by about 0.7-0.8°C (1.3-1.4°F) over the last century, which is similar to the global average. A strong El Niño event made 1998 the warmest year in most tropical areas, and there hasn't been much warming since then. However, climate models predict that the tropics will warm another 1-2°C (1.8-3.6°F) by 2050 and 1-4°C (1.8-7.2°F) by 2100.
Tropical Ecosystems

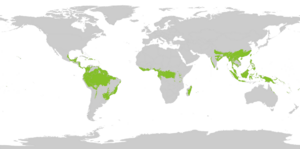
Tropical plants and animals are species that naturally live in the tropics. Tropical ecosystems can include many different types of habitats, such as tropical rainforests, seasonal tropical forests, dry forests (where trees often lose their leaves), spiny forests, deserts, savannahs, and grasslands. These areas often have a huge variety of living things (biodiversity) and many species that are found nowhere else (endemism), especially in rainforests and seasonal forests.
Some examples of important places with high biodiversity and unique species include El Yunque National Forest in Puerto Rico, the rainforests of Costa Rica and Nicaragua, parts of the Amazon rainforest in several South American countries, the dry forests of Madagascar, the Waterberg Biosphere in South Africa, and the eastern rainforests of Madagascar. The soils in tropical forests are often low in nutrients. This makes them very sensitive to farming methods like slash-and-burn (cutting and burning trees to clear land), which is sometimes part of shifting cultivation farming systems.
In the study of where living things are found (biogeography), the tropics are divided into two main parts: the Paleotropics (which includes Africa, Asia, and Australia) and the Neotropics (which includes the Caribbean, Central America, and South America). Sometimes, both are called the Pantropic.
Tropical Plants (Flora)
Flora refers to all the plants found in a specific region at a certain time. Here are some well-known plants that are found only in, originally came from, or are often linked with the tropics:
- Stone fruits like mangos, avocado, and sapote.

- Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and mandarins.
- Banana trees.
- Bird of paradise flower.
- Palm trees.
- Ferns.
- Orchids.
- Papaya trees.
- Dragon fruit.
- Bamboo.
- Jackfruit.
- Giant Water Lily.
- Rubber Tree.
- Cacao (where chocolate comes from!).
- Coffee.
See also
 In Spanish: Zona intertropical para niños
In Spanish: Zona intertropical para niños
- Hardiness zone
- Tropical ecology
- Tropical marine climate
- Tropical year