Williamson County, Illinois facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Williamson County
|
|
|---|---|

Williamson County Courthouse in Marion
|
|
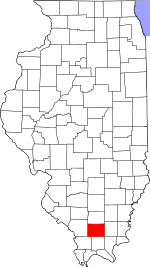
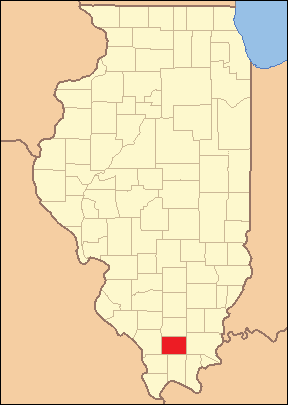
Location within the U.S. state of Illinois
|
|
 Illinois's location within the U.S. |
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | February 28, 1839 |
| Named for | Williamson County, Tennessee |
| Seat | Marion |
| Largest city | Marion |
| Area | |
| • Total | 444 sq mi (1,150 km2) |
| • Land | 420 sq mi (1,100 km2) |
| • Water | 24 sq mi (60 km2) 5.4% |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 67,153 |
| • Density | 150/sq mi (60/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 12th |
Williamson County is a county located in Southern Illinois. In 2020, about 67,153 people lived there. The biggest city and the main government center, called the county seat, is Marion.
Williamson County is part of the Carbondale-Marion area, which is a larger group of cities. This part of Southern Illinois is often called "Little Egypt" by local people.
The county is also in the Metro Lakeland area. It is about 88 miles (142 km) southeast of St. Louis, Missouri. Important roads like Interstates 57 and 24, and Illinois Route 13, help connect the county to nearby cities. These cities include Murphysboro, Carbondale, Carterville, Herrin, Marion, and Harrisburg.
The Metro Lakeland area, which includes Jackson and Williamson counties, has about 120,000 residents. Carbondale, Herrin, and Marion are the main urban areas. Together, they have a population of over 65,000 people. More than 235,000 people live within 35 miles (56 km) of the county.
Contents
History of Williamson County
Williamson County was created on February 28, 1839. It was formed from parts of Franklin County. The county was named after Williamson County, Tennessee. Many of the first people to settle here came from Tennessee and Virginia. They often traveled along the Ohio River.
The county became an important place for coal mining. Many immigrants from Europe moved here in the late 1800s and early 1900s to work in the mines. Sometimes, there were disagreements between workers and mine owners. Workers wanted better pay and safer conditions. These disagreements sometimes led to serious events.
Williamson County is sometimes called "Bloody Williamson." This is because of several times in history when there was violence. These events include:
- The Bloody Vendetta (1876): A conflict between families.
- The Carterville Massacre (1899): A mining dispute.
- A Coal Strike (1906): Another labor conflict.
- The Herrin Massacre (1922): A major event during a coal strike.
- The Klan War (1924–1926): A period of conflict involving the Ku Klux Klan.
- The Birger/Shelton Gang War (1926): A conflict between criminal gangs.
Williamson County can also experience strong weather. In 1925, the northwest part of the county was badly damaged by the Tri-State Tornado. On May 29, 1982, two tornadoes hit the county. These storms caused 10 deaths in the Marion, Illinois tornado outbreak. On May 8, 2009, the cities of Carterville, Herrin, and Marion were heavily damaged by a powerful storm called the May 2009 Southern Midwest derecho.
Geography and Location
The United States Census Bureau says that Williamson County covers a total area of 444 square miles (1,150 km²). About 420 square miles (1,088 km²) of this is land. The remaining 24 square miles (62 km²), or 5.4%, is water.
Neighboring Counties
Williamson County shares its borders with several other counties:
- Franklin County (to the north)
- Saline County (to the east)
- Pope County (to the southeast)
- Johnson County (to the south)
- Union County (to the southwest)
- Jackson County (to the west)
Protected Natural Areas
Part of the Crab Orchard National Wildlife Refuge is located in Williamson County. This refuge helps protect wildlife and their habitats.
Main Roads and Transportation
 Interstate 24
Interstate 24 Interstate 57
Interstate 57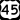 U.S. Highway 45
U.S. Highway 45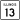 Illinois Route 13
Illinois Route 13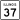 Illinois Route 37
Illinois Route 37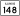 Illinois Route 148
Illinois Route 148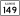 Illinois Route 149
Illinois Route 149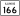 Illinois Route 166
Illinois Route 166
The Williamson County Regional Airport serves as the local airport for the area.
Climate and Weather Patterns
| Weather chart for Marion, Illinois | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3.3
38
19
|
3.2
44
23
|
4.5
55
33
|
4.5
66
42
|
4.9
75
52
|
4.3
83
61
|
3.9
87
65
|
3.7
86
63
|
3.1
79
55
|
3.1
68
43
|
4.8
55
34
|
3.7
43
24
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: The Weather Channel |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Williamson County is in a unique climate zone. It is on the edge of two types of climates: humid continental climate (Dfa) and humid subtropical climate (Cfa). This means it gets both cold air from the Arctic and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico. Because of this, the county can have some of the biggest temperature changes in the world.
The region experiences four clear seasons. Spring is usually the wettest time of year. It can bring strong weather like tornadoes and winter storms. Summers are hot and humid. The humidity often makes it feel much hotter than 100°F (38°C).
Fall is mild with less humidity. It can have periods of heavy rain. The first snow flurries usually happen in late November. Winters are cold, with temperatures often below freezing. However, warmer periods are common. Winter storms can bring days of freezing rain, ice pellets, and snowfall.
In July, the average high temperature is 90°F (32°C). In January, the average low is 19°F (−6°C). Temperatures of 100°F (38°C) or 0°F (−18°C) can happen a few days each year. The lowest temperature ever recorded was -25°F (-32°C) in January 1977. The highest was 113°F (45°C) in August 1977.
Williamson County has thunderstorms about 50 days a year. These storms bring more than half of the county's yearly rain. Especially in spring, these storms can be very strong. They can have high winds, large hail, and tornadoes. Sometimes, late autumns have warm weather known as Indian summer. Roses can even bloom as late as early December in some years.
People and Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 4,457 | — | |
| 1850 | 7,216 | 61.9% | |
| 1860 | 12,205 | 69.1% | |
| 1870 | 17,329 | 42.0% | |
| 1880 | 19,324 | 11.5% | |
| 1890 | 22,226 | 15.0% | |
| 1900 | 27,796 | 25.1% | |
| 1910 | 45,098 | 62.2% | |
| 1920 | 61,092 | 35.5% | |
| 1930 | 53,880 | −11.8% | |
| 1940 | 51,424 | −4.6% | |
| 1950 | 48,621 | −5.5% | |
| 1960 | 46,117 | −5.2% | |
| 1970 | 49,021 | 6.3% | |
| 1980 | 56,538 | 15.3% | |
| 1990 | 57,733 | 2.1% | |
| 2000 | 61,296 | 6.2% | |
| 2010 | 66,357 | 8.3% | |
| 2020 | 67,153 | 1.2% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 66,706 | 0.5% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1960 1900-1990 1990-2000 2010-2013 |
|||
In 2010, there were 66,357 people living in Williamson County. There were 27,421 households and 17,999 families. The county had about 157.9 people per square mile. There were 30,359 housing units, with about 72.3 units per square mile.
Most people in the county were white (92.7%). Other groups included black or African American (3.8%), Asian (0.8%), and Native American (0.4%). About 2.0% of the population was of Hispanic or Latino origin.
Many residents have European backgrounds. For example, 23.6% had German ancestry, 17.3% had Irish ancestry, and 16.0% had English ancestry.
About 30.2% of households had children under 18 living with them. About 49.4% were married couples. The average household had 2.35 people, and the average family had 2.88 people. The average age of people in the county was 40.1 years.
The average income for a household in the county was $40,579. For a family, it was $50,929. About 16.7% of the population lived below the poverty line. This included 24.3% of those under 18 and 9.9% of those aged 65 or older.
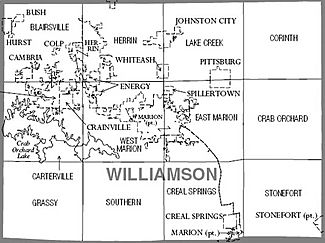
Cities and Towns
Williamson County has several cities and villages.
Cities in Williamson County
Villages in Williamson County
Other Communities
Some areas are called Census-designated places (CDPs). These are like towns but not officially incorporated as cities or villages.
There are also other smaller communities that are not incorporated:
- Corinth
- Crenshaw
- Dewmaine
- Dykersburg
- Lake of Egypt
- No. 9
- Paulton
- Pulleys Mill
Some communities that once existed are now considered "ghost towns":
Precincts
These precincts are areas used for local government, not for voting. Most have several voting areas within them.
- Blairsville
- Carterville
- Corinth
- Crab Orchard
- Creal Springs
- East Marion
- Grassy
- Herrin
- Lake Creek
- Southern
- Stonefort
- West Marion
Education
Williamson County has several school districts. These districts manage schools for students from kindergarten through 12th grade, or just for high school or elementary school.
Schools for All Grades (K-12)
- Carrier Mills-Stonefort Community Unit School District
- Carterville Community Unit School District 5
- Crab Orchard Community Unit School District 3
- Frankfort Community Unit School District 168
- Galatia Community Unit School District 1
- Herrin Community Unit School District 4
- Johnston City Community Unit School District 1
- Marion Community Unit School District 2
- Zeigler-Royalton Community Unit School District 188
High Schools (Secondary)
- Carbondale Community High School District 165
- Vienna High School District 133
Elementary Schools
- Giant City Community Consolidated School District 130
- New Simpson Hill Consolidated District 32
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Williamson (Illinois) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Williamson (Illinois) para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |