Alexandria, Virginia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Alexandria
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

|
|||
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| State | Virginia | ||
| County | None (Independent city) | ||
| Founded | 1749 | ||
| Incorporated (town) | 1779 | ||
| Incorporated (city) | 1852 | ||
| Incorporated (Independent city) | 1870 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Council-manager | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 15.35 sq mi (39.75 km2) | ||
| • Land | 14.93 sq mi (38.68 km2) | ||
| • Water | 0.41 sq mi (1.07 km2) | ||
| Highest elevation | 287 ft (87 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 0 ft (0 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 159,467 |
||
| • Rank | 169th in United States 6th in Virginia |
||
| • Density | 10,680.97/sq mi (4,122.72/km2) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Alexandrian | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| ZIP Codes |
20598, 22301-22315, 22320, 22331-22334, 22350
|
||
| Area codes | 703 and 571 | ||
| FIPS code | 51-01000 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 1492456 | ||
| Primary Airports | Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport Dulles International Airport |
||
| Commuter rail | Virginia Railway Express | ||
Alexandria is an independent city in the northern part of Virginia, United States. It's located on the western side of the Potomac River, about 7 miles (11 km) south of downtown Washington, D.C.. Alexandria is a big part of the Washington metropolitan area. In 2022, about 159,467 people lived there, making it the sixth-largest city in Virginia.
Because it's so close to the U.S. capital, many people in Alexandria work for the federal government, the U.S. military, or for companies that work with the government. The city's biggest employers include the U.S. Department of Defense. Alexandria is known for having a high average income among independent cities in Virginia.
The oldest part of Alexandria is called Old Town Alexandria, or just "Old Town." It's a popular spot with lots of unique shops, restaurants, and theaters. Many neighborhoods in Alexandria are easy to walk around. Sometimes, people get confused because a large area of nearby Fairfax County also uses Alexandria mailing addresses, even though it's a separate government area. That's why the city is sometimes called the "City of Alexandria" to avoid mix-ups.
Contents
- Exploring Alexandria's Past
- Where is Alexandria?
- Who Lives in Alexandria?
- What Does Alexandria Do for Work?
- What's Fun to Do in Alexandria?
- News and Media
- Sports Fun
- Parks and Outdoor Adventures
- Learning in Alexandria
- Getting Around Alexandria
- Famous People from Alexandria
- Friendship Cities
- See also
Exploring Alexandria's Past
How Alexandria Began
The first European settlement in this area started in 1695. In 1730, a law in Virginia said that all tobacco grown in the colony had to be inspected at special warehouses. One of these warehouses was set up near Hunting Creek on the Potomac River.
Later, in 1748, people living in Fairfax County asked the government to create a town at this warehouse site. George Washington, who was a young surveyor at the time, even drew a map to show why it was a good spot for a trading port.
The land belonged to Captain Philip Alexander II. To get him to agree, the petitioners offered to name the new town "Alexandria" after his family. Philip and his cousin, Captain John Alexander, gave land to help the town grow. On May 2, 1749, the plan was approved, and an auction for town lots was held in July.
For a short time, the town was called "Belhaven," but the name "Alexandria" stuck. The town officially became a city in 1779.
Alexandria in the Early 1800s
During the War of 1812, in 1814, a British fleet attacked Alexandria. The city surrendered without a fight, and the British took goods like flour and tobacco from stores and warehouses.
From 1828 to 1836, Alexandria was home to the Franklin & Armfield Slave Market, one of the biggest companies involved in the slave trade in the country. They sent many enslaved people from Alexandria to other states.
In 1791, Alexandria was chosen by George Washington to be part of the new District of Columbia. However, the city's economy struggled compared to other ports, and people in Alexandria wanted to be part of Virginia again. They also worried about the idea of ending slavery in the capital, which would hurt their economy. After a vote, the area was returned to Virginia in 1846. The City of Alexandria became independent from the surrounding county in 1870.
Alexandria During the Civil War
The American Civil War brought major changes to Alexandria. On May 24, 1861, Union troops took control of the city. A famous event happened when Colonel Elmer E. Ellsworth tried to remove a large Confederate flag from a hotel roof and was killed by the hotel owner. Ellsworth became a hero in the North.
Alexandria remained under Union control for the rest of the war. The Union army built forts, like Fort Ward, to protect Washington, D.C.. During this time, many escaped African American slaves came to Alexandria, seeking safety and work behind Union lines. They were called "contrabands" and helped the Union army. By 1863, Alexandria's population had grown a lot.
After the war, in 1870, African Americans in Alexandria County gained the right to vote. This helped elect the first black Alexandrians to the City Council and the Virginia Legislature.
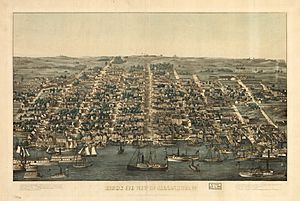
Alexandria in the 20th Century

At the start of the 1900s, Alexandria was known for making glass, fertilizer, beer, and leather. Many businesses were small, with the owner living above their shop. In 1916, a law called Prohibition stopped the making and selling of alcohol, which closed the big Portner Brewing Company.
Important events in the 20th century include:
- In 1930, Alexandria grew by adding the town of Potomac.
- In 1939, Samuel Wilbert Tucker organized a sit-in at the segregated public library to protest unfair rules.
- In the 1950s, famous musicians like Jim Morrison of The Doors and Cass Elliot of The Mamas & The Papas attended George Washington High School.
- In 1961, the Woodrow Wilson Bridge opened, connecting Virginia and Maryland.
- In 1965, Alexandria's schools became integrated, meaning students of all races could attend the same schools.
- In 1971, all high school students in the city began attending T. C. Williams High School. That same year, Coach Herman Boone led the football team to an amazing season, which inspired the movie Remember the Titans.
- In 1974, the Torpedo Factory Art Center opened, turning an old torpedo factory into a place for artists.
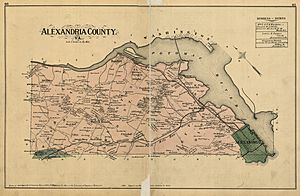
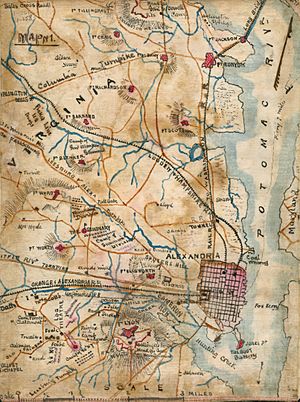
Where is Alexandria?
Alexandria covers about 15.35 square miles (39.75 km2). Most of this is land, with a small part being water. The city is bordered by the Potomac River to the east, Arlington County to the north, and Fairfax County to the south and west.
The way addresses are numbered in Alexandria can be a bit tricky because the city grew by adding several smaller communities. For example, in Old Town, numbers go north and south from King Street. In other areas, they might go east and west from Commonwealth Avenue.
The ZIP codes for Alexandria all start with 223. However, some areas in Fairfax County also use Alexandria ZIP codes.
Nearby Areas
- Arlington County, Virginia – to the north
- Fairfax County, Virginia – to the west and south
- District of Columbia – to the northeast
- Prince George's County, Maryland – to the east
Who Lives in Alexandria?
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 2,748 | — | |
| 1800 | 4,971 | 80.9% | |
| 1810 | 7,227 | 45.4% | |
| 1820 | 8,218 | 13.7% | |
| 1830 | 8,241 | 0.3% | |
| 1840 | 8,459 | 2.6% | |
| 1850 | 8,734 | 3.3% | |
| 1860 | 12,652 | 44.9% | |
| 1870 | 13,570 | 7.3% | |
| 1880 | 13,659 | 0.7% | |
| 1890 | 14,339 | 5.0% | |
| 1900 | 14,528 | 1.3% | |
| 1910 | 15,329 | 5.5% | |
| 1920 | 18,060 | 17.8% | |
| 1930 | 24,149 | 33.7% | |
| 1940 | 33,523 | 38.8% | |
| 1950 | 61,787 | 84.3% | |
| 1960 | 91,023 | 47.3% | |
| 1970 | 110,927 | 21.9% | |
| 1980 | 103,217 | −7.0% | |
| 1990 | 111,183 | 7.7% | |
| 2000 | 128,283 | 15.4% | |
| 2010 | 139,966 | 9.1% | |
| 2020 | 159,467 | 13.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010-2020 2010 2020 |
|||
Alexandria's Population in 2020
| Race / Ethnicity | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 74,878 | 78,519 | 53.50% | 49.24% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 29,778 | 31,314 | 21.28% | 19.64% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 327 | 217 | 0.23% | 0.14% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 8,351 | 11,205 | 5.97% | 7.03% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 109 | 77 | 0.08% | 0.05% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 485 | 1,026 | 0.35% | 0.64% |
| Mixed Race/Multi-Racial (NH) | 3,514 | 7,737 | 2.51% | 4.85% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 22,524 | 29,372 | 16.09% | 18.42% |
| Total | 139,966 | 159,467 | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Note: the US Census treats Hispanic/Latino as an ethnic category. This table excludes Latinos from the racial categories and assigns them to a separate category. Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race.
In 2010, there were about 140,000 people living in Alexandria. The city is very diverse, with people from many different backgrounds.
- About 60.9% of the people were White.
- 21.8% were African American.
- 6.0% were Asian.
- 16.1% of the population were Hispanic or Latino, with many from El Salvador, Mexico, and Honduras.
The median age in Alexandria in 2000 was 34 years old. This means half the people were younger than 34 and half were older.
Most adults in Alexandria have a college degree or higher. About 65.9% of residents have a bachelor's degree or more, which is much higher than the state average for Virginia.
What Does Alexandria Do for Work?
Many companies and organizations have their main offices in Alexandria. Some well-known ones include Five Guys (a burger chain), The Motley Fool (a financial advice company), and Pentagon Federal Credit Union (PenFed).
Several U.S. government agencies are also located here. These include the United States Patent and Trademark Office, where new inventions are registered, and the National Science Foundation, which supports scientific research.
Alexandria is also home to many charities and non-profit groups. These include Catholic Charities, United Way, and Volunteers of America, which help people in need.
The main types of jobs in Alexandria are in management consulting, business and finance, and computer-related fields. Many jobs are found near the city's Metrorail stations, like in Old Town and near the Eisenhower Avenue station.
Most people who work in Alexandria actually live outside the city and travel in. About 87% of workers commute from other areas, with many coming from Fairfax County. Also, many Alexandria residents travel to work in Washington, D.C. or Fairfax County.
| # | Employer | # of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States Department of Defense - Mark Center | 8,000 |
| 2 | United States Department of Commerce (includes Patent and Trademark Office) | 5,500 |
| 3 | City of Alexandria | 2,700 |
| 4 | Alexandria City Public Schools | 2,500 |
| 5 | Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority | 1,200 |
| 6 | United States Department of Agriculture | 800 |
| 7 | United States General Services Administration | 600 |
| # | Employer | # of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inova Health System | 1,700 |
| 2 | Institute for Defense Analyses | 750 |
| 3 | Systems Planning & Analysis Inc | 700 |
| 4 | Goodwin House | 700 |
| 5 | Kearney & Company | 600 |
| 6 | CRS Facility Service | 400 |
| 7 | United Parcel Service (UPS) | 350 |
What's Fun to Do in Alexandria?

Fun Events and Festivals
Alexandria hosts many fun events throughout the year. A popular one around Christmas is the Scottish Christmas Walk. This event, started in 1969, includes a parade through Old Town and celebrates the city's Scottish heritage. It also helps raise money for local charities.
Other parades celebrate Saint Patrick's Day and George Washington's birthday. There's also the Red Cross Waterfront Festival in June, the city's birthday celebration with fireworks in July, and "First Night Alexandria" on New Year's Eve. These events are often led by Alexandria's town crier, who wears a special traditional outfit.
Famous Places to Visit
Alexandria has many interesting landmarks. You can visit the George Washington Masonic National Memorial, which is a beautiful building with an observation deck. Other historic places include Christ Church, where George Washington and Robert E. Lee once went, and Gadsby's Tavern, an old inn.
The Torpedo Factory Art Center is a cool place on the Old Town waterfront. It used to be a factory that made torpedoes, but now it's full of art studios and exhibits. The Athenaeum is another art center. If you like theater, check out the Little Theatre of Alexandria.
Near Old Town, you can find the United States Patent and Trademark Office, which has the National Inventors Hall of Fame Museum. This museum celebrates amazing inventors. For music lovers, The Birchmere is a concert hall that hosts many different performers.
Just outside the city, but with Alexandria addresses, are places like Mount Vernon, George Washington's historic estate, and his Grist Mill.
The Skinny House
A unique spot in Alexandria is the Hollensbury Spite House. In 1830, John Hollensbury built this very narrow house, only 7 feet (2.1 meters) wide, to stop people from using the alleyway next to his home. It's still standing today!
News and Media
Alexandria has two local weekly newspapers: the Alexandria Gazette Packet and the Alexandria Times.
Sports Fun
The city is home to the Alexandria Aces, a baseball team in the Cal Ripken Sr. Collegiate Baseball League. They play their games at Frank Mann Field.
Parks and Outdoor Adventures
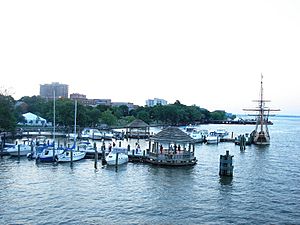
Alexandria has over 900 acres (3.6 km2) of green space, including 566 acres (2.29 km2) of city parks and 10 recreation centers. Chinquapin is one of the largest recreation centers, offering swimming, tennis, and racquetball. The city also organizes sports leagues for volleyball, softball, and basketball.
You can visit Cameron Run Regional Park, which has a water park, a miniature golf course, and batting cages. A part of the Mount Vernon Trail, a popular path for biking and jogging, runs through Old Town along the Potomac River. There are also many parks along the Alexandria waterfront.
Learning in Alexandria
Colleges and Universities
Alexandria has several places for higher education. Virginia Tech has a campus in Old Town called the Washington-Alexandria Architecture Center, where students can study architecture and urban planning. Virginia Commonwealth University and The George Washington University also have campuses here, offering various programs. The city is also home to a campus of the Northern Virginia Community College. The Virginia Theological Seminary, a large seminary for the Episcopal Church, is also located in Alexandria.
Schools for Kids
The Alexandria City Public Schools system serves the city's students. There are twelve elementary schools for grades Kindergarten through 5th grade, with some also offering Pre-K. Two schools, Patrick Henry and Jefferson-Houston, serve Pre-K through 8th grade.
The middle schools, George Washington and Francis C. Hammond, are for 6th through 8th graders. All 9th graders attend Minnie Howard Ninth Grade Center, and students in 10th through 12th grades go to Alexandria City High School.
Alexandria also has several private schools, such as St. Stephen's and St. Agnes School, Bishop Ireton High School, and Episcopal High School.
Getting Around Alexandria
Major highways like I-95 and I-495 (the Capital Beltway), which includes the Woodrow Wilson Bridge, run near Alexandria. Interstate 395 goes through the western part of the city. Other important roads include State Route 7 (King Street) and State Route 236 (Duke Street).
Alexandria has its own bus system called DASH, which is free to ride! DASH also has a "trolley" bus that runs along King Street. The Metrorail's Blue and Yellow Lines also have several stops in Alexandria, making it easy to travel to Washington, D.C. and other nearby areas.
The city's historic train station, Alexandria Union Station, offers Amtrak services for longer trips and the Virginia Railway Express (VRE) for regional travel. You can also rent bikes through Capital Bikeshare to explore the city.
Famous People from Alexandria
- Diedrich Bader, actor
- Stewart Copeland, drummer for The Police
- Elena Delle Donne, WNBA basketball star
- Stefon Diggs, NFL wide receiver
- Donna Dixon, former actress and model
- Gerald R. Ford, former President of the United States
- Rick Franklin, blues musician
- Dave Grohl, founder of Foo Fighters, drummer for Nirvana
- Moses Hepburn, first African American town councilor
- Thomas Kail, theater director
- Angus King, U.S. Senator
- Robert E. Lee, Civil War general
- George Washington, first U.S. President, lived and worked in Alexandria
- Jim Morrison of The Doors
- Dermot Mulroney, actor
- Richard M. Nixon, former President of the United States
- Willard Scott, national television personality
- Kali Uchis, singer
- Wernher von Braun, NASA rocket scientist
- Megan Young, Miss World 2013
Friendship Cities
Alexandria has special "sister city" relationships with four cities around the world:
 Gyumri, Armenia
Gyumri, Armenia Helsingborg, Sweden
Helsingborg, Sweden Dundee, Scotland
Dundee, Scotland Caen, France
Caen, France
Alexandria became friends with Gyumri to show support after a big earthquake in Armenia in 1988.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Alexandria (Virginia) para niños
In Spanish: Alexandria (Virginia) para niños