Macon, Georgia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Macon
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Consolidated city-county
|
||
| Macon–Bibb County | ||
|
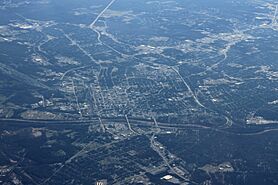
Aerial photograph of Macon
Bibb County Courthouse
|
||
|
||
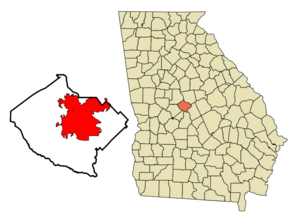
Location within Bibb County
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | Georgia | |
| County | Bibb | |
| Settled around Fort Benjamin Hawkins | 1809 | |
| Named for | Nathaniel Macon | |
| Area | ||
| • Consolidated city-county | 254.90 sq mi (660.19 km2) | |
| • Land | 249.38 sq mi (645.89 km2) | |
| • Water | 5.52 sq mi (14.30 km2) | |
| Elevation | 381 ft (116 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Consolidated city-county | 157,346 | |
| • Rank | ||
| • Density | 630.95/sq mi (243.61/km2) | |
| • Metro | 233,802 (197th) | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | |
| ZIP Codes |
31200–31299
|
|
| Area code(s) | 478 | |
| FIPS code | 13-49000 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 0332301 | |
| Website | maconbibb.us | |
Macon (pronounced MAY-kən), officially called Macon–Bibb County, is a city in Georgia, United States. It's a special kind of city called a consolidated city-county, meaning the city and county governments have joined together.
Macon is located near the Ocmulgee River, about 85 miles (137 km) southeast of Atlanta. It's also close to the center of Georgia, which is why it's nicknamed "The Heart of Georgia."
In 2020, Macon had a population of 157,346 people. It's the main city in the Macon metropolitan area, which had about 234,802 people in 2020.
In 2012, people in Macon and Bibb County voted to combine their governments. This merger became official on January 1, 2014. After this, Macon became the fourth-largest city in Georgia.
Macon is served by three major highways: I-16 (which goes to Savannah), I-75 (which connects to Atlanta), and I-475 (a bypass around the city). The area also has two smaller airports. For bigger flights, people usually use the airport in Atlanta, which is about 80 miles (129 km) away.
The city is home to several colleges and universities, as well as many museums and places to visit.
Contents
History of Macon
Macon was built on a historic site called the Ocmulgee Old Fields. This was once home to the Creek Indians in the 1700s. Even before them, the Mississippian culture lived here from about 950 to 1100 AD. They were known for building large earthwork mounds for ceremonies, religious events, and burials. People have lived along the rivers in this part of the Southeast for 13,000 years!
Early Beginnings and Fort Hawkins
Macon started near Fort Benjamin Hawkins, which was built in 1809. President Thomas Jefferson ordered it built after the Creek people gave up their lands east of the Ocmulgee River. The fort was named after Benjamin Hawkins, who worked with Native American groups for over 20 years. He even lived among the Creek people.
Fort Hawkins was important because it was a trading post with Native Americans. It was also at the "fall line" of the Ocmulgee River, which was the furthest point boats could travel from the coast. The fort also protected a major Native American trail called the Lower Creek Pathway. This trail later became the Federal Road, connecting Washington, D.C., to cities like Mobile, Alabama and New Orleans, Louisiana.
The fort was a key military spot during the War of 1812 and the Creek War of 1813. It was used for trading and had soldiers stationed there until 1821. The fort was later taken out of service and burned down. Today, a copy of one of its buildings stands on a hill in east Macon. Archeologists are still finding parts of the old fort, showing how important it was.
Growth and Development
As more settlers arrived, Fort Hawkins was renamed "Newtown." In 1823, the city was officially named Macon, honoring Nathaniel Macon, a statesman from North Carolina. Early city planners wanted Macon to be "a city within a park." They set aside over 250 acres (1 sq km) for Central City Park. They also made rules for residents to plant shade trees in their front yards.
Macon's early economy relied on cotton, thanks to the rich local soil and the use of enslaved labor. The city's location on the Ocmulgee River helped it grow by allowing goods to be shipped to new markets. Cotton steamboats and the arrival of the railroad in 1843 further boosted Macon's economy.
In 1836, Wesleyan College was founded in Macon. It was the first college in the United States to grant degrees to women.
Macon During the Civil War
During the American Civil War, Macon was an important place for the Confederacy. It was where many weapons parts, like percussion caps and bullets, were made. A prison camp called Camp Oglethorpe was also set up here for captured Union soldiers.
Macon City Hall was used as Georgia's temporary state capital in 1864. It also became a hospital for wounded Confederate soldiers. Union General William Tecumseh Sherman famously marched through Georgia but did not attack Macon. His troops went around the city, even though Macon residents were ready for a fight.
The Macon Telegraph newspaper reported that Macon sent 23 companies of men to fight for the Confederacy. However, many were lost, and by the end of the war, only enough men for five companies remained. Union forces took control of Macon on April 20, 1865.
Modern Macon
Because of its central location, Macon became a major transportation center in Georgia. In 1895, the New York Times called Macon "The Central City" because it was a hub for railroads and textile factories. Terminal Station was built in 1916. Macon continued to grow and thrive in the 20th century.
Macon has also faced natural disasters. In 1994, Tropical Storm Alberto caused major flooding in Macon, with 24 inches (61 cm) of rain falling. In 2008, an EF2 tornado hit Macon, causing significant damage to businesses and Macon State College.
City and County Join Forces
On July 31, 2012, voters in Macon and Bibb County approved a plan to merge their city and county governments. This was not the first time this idea was proposed; four earlier attempts to combine the governments had failed.
As a result of the vote, the city and county governments were replaced by a single mayor and a nine-member county commission. Robert Reichert was elected as the first mayor of the new Macon-Bibb government in 2013.
Geography of Macon
The Ocmulgee River flows through Macon. Macon is one of Georgia's three main "Fall Line Cities," along with Augusta and Columbus. The Fall Line is where the hilly Piedmont region meets the flat coastal plain. This means Macon has rolling hills in the north and flat areas in the south. The drop in elevation at the fall line makes rivers flow quickly, which was once used to power textile mills.
Macon is about 330 feet (100 meters) above sea level. The city covers a total area of about 56.3 square miles (145.8 sq km). Most of this is land, with a small amount of water.
Macon's Climate
Macon has a humid subtropical climate, which means it has hot, humid summers and mild winters. The average temperature in January is about 47.6°F (8.7°C), and in July, it's about 82.5°F (28.1°C).
On average, Macon sees about 46.9 inches (119 cm) of rain each year. The wettest day on record was July 5, 1994, when over 10 inches (25 cm) of rain fell! Snow is rare, with most winters getting very little or no snowfall.
| Climate data for Macon, Georgia (Middle Georgia Regional Airport), 1991−2020 normals, extremes 1892−present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 84 (29) |
85 (29) |
92 (33) |
96 (36) |
100 (38) |
108 (42) |
108 (42) |
105 (41) |
105 (41) |
103 (39) |
88 (31) |
83 (28) |
108 (42) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 73.9 (23.3) |
76.8 (24.9) |
83.9 (28.8) |
88.0 (31.1) |
93.6 (34.2) |
97.5 (36.4) |
99.1 (37.3) |
98.7 (37.1) |
95.1 (35.1) |
88.9 (31.6) |
81.8 (27.7) |
75.9 (24.4) |
100.3 (37.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 59.3 (15.2) |
63.4 (17.4) |
70.6 (21.4) |
77.9 (25.5) |
85.8 (29.9) |
90.9 (32.7) |
93.5 (34.2) |
92.2 (33.4) |
87.6 (30.9) |
78.9 (26.1) |
69.1 (20.6) |
61.3 (16.3) |
77.5 (25.3) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 47.6 (8.7) |
51.2 (10.7) |
57.7 (14.3) |
64.5 (18.1) |
72.9 (22.7) |
79.5 (26.4) |
82.5 (28.1) |
81.4 (27.4) |
76.2 (24.6) |
66.0 (18.9) |
55.8 (13.2) |
49.5 (9.7) |
65.4 (18.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 35.9 (2.2) |
39.1 (3.9) |
44.9 (7.2) |
51.0 (10.6) |
60.0 (15.6) |
68.1 (20.1) |
71.5 (21.9) |
70.7 (21.5) |
64.8 (18.2) |
53.2 (11.8) |
42.5 (5.8) |
37.8 (3.2) |
53.3 (11.8) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 19.0 (−7.2) |
22.4 (−5.3) |
27.2 (−2.7) |
34.8 (1.6) |
45.0 (7.2) |
58.3 (14.6) |
64.8 (18.2) |
62.1 (16.7) |
51.1 (10.6) |
35.6 (2.0) |
26.5 (−3.1) |
22.8 (−5.1) |
17.0 (−8.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −6 (−21) |
8 (−13) |
14 (−10) |
28 (−2) |
40 (4) |
46 (8) |
54 (12) |
55 (13) |
35 (2) |
26 (−3) |
10 (−12) |
5 (−15) |
−6 (−21) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 4.32 (110) |
4.17 (106) |
4.31 (109) |
3.62 (92) |
2.65 (67) |
4.44 (113) |
4.79 (122) |
4.38 (111) |
3.66 (93) |
2.63 (67) |
3.37 (86) |
4.57 (116) |
46.91 (1,192) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0.4 (1.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.7 (1.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.2 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 8.2 | 7.5 | 11.2 | 11.3 | 10.2 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 9.4 | 107.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70.2 | 67.2 | 66.6 | 64.8 | 68.5 | 70.7 | 74.2 | 76.1 | 76.4 | 71.2 | 71.1 | 70.9 | 70.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 179.5 | 192.2 | 250.8 | 283.2 | 315.3 | 300.0 | 293.9 | 288.0 | 247.4 | 253.7 | 200.2 | 182.2 | 2,986.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 56 | 62 | 67 | 73 | 73 | 70 | 67 | 70 | 67 | 72 | 64 | 59 | 67 |
| Source: NOAA (snow 1981–2010, relative humidity and sun 1961−1990) | |||||||||||||
Nearby Cities and Towns
People and Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 3,297 | — | |
| 1850 | 5,720 | 73.5% | |
| 1860 | 8,247 | 44.2% | |
| 1870 | 10,810 | 31.1% | |
| 1880 | 12,749 | 17.9% | |
| 1890 | 22,746 | 78.4% | |
| 1900 | 23,272 | 2.3% | |
| 1910 | 40,665 | 74.7% | |
| 1920 | 52,995 | 30.3% | |
| 1930 | 53,829 | 1.6% | |
| 1940 | 57,865 | 7.5% | |
| 1950 | 70,252 | 21.4% | |
| 1960 | 69,764 | −0.7% | |
| 1970 | 122,423 | 75.5% | |
| 1980 | 116,896 | −4.5% | |
| 1990 | 106,612 | −8.8% | |
| 2000 | 97,255 | −8.8% | |
| 2010 | 91,351 | −6.1% | |
| 2020 | 157,346 | 72.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1850-1870 1870-1880 1890-1910 1920-1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 |
|||
Macon is the largest city in a larger area called the Macon-Warner Robins-Fort Valley Combined Statistical Area. This area includes several counties and had a population of 411,898 people in 2010.
In 2020, Macon's population was 157,346. The city is home to people from many different backgrounds. In 2020, about 54% of the population was Black or African American, and about 36% was White. Other groups, including Asian, Native American, and people of mixed races, also live in Macon. About 4% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
The average household in Macon had about 2.44 people, and the average family had about 3.08 people. About 26.9% of the population was under 18 years old.
Macon's Economy
Macon-Bibb County's economy is driven by several important industries. These include aerospace, advanced manufacturing, food processing, healthcare, and logistics (warehousing and distribution).
Some of the largest employers in Macon are Mercer University, GEICO's Southeast Headquarters, and YKK USA. The city also has a major railway yard operated by Norfolk Southern Railway.
In the past, Macon's economy faced challenges when the textile industry declined and large factories, like the Brown and Williamson plant, closed. However, Macon has worked to bring in new companies to create more diverse jobs. For example, Irving Consumer Products and Kuhmo Tire manufacturing plants have opened. The Middle Georgia Regional Airport has also attracted aerospace companies, like an Embraer aircraft maintenance facility.
Healthcare is the largest industry in Macon by number of employees. Hospitals like Atrium Health Navicent and Piedmont Healthcare Macon make Macon a major healthcare center for central and southern Georgia.
Shopping in Macon
Macon has several shopping centers. These include The Shoppes at River Crossing, Macon Mall, and Eisenhower Crossing. You can also find traditional shopping areas in downtown Macon and Ingleside Village.
Military Presence
Macon is home to the headquarters of the 48th Infantry Brigade Combat Team of the Georgia Army National Guard.
The largest industrial complex in Georgia, Robins Air Force Base, is located just 10 miles (16 km) south of Macon.
Arts and Culture
Macon's Musical Roots
Macon has a rich musical history and has been home to many famous musicians. These include The Allman Brothers Band, Otis Redding, and Little Richard. Other artists like Mike Mills and Bill Berry from R.E.M. also have ties to Macon.
In the late 1960s and 1970s, Capricorn Records, started by Macon natives Phil Walden, helped make the city a center for Southern rock music.
The Macon Symphony Orchestra, a youth symphony, and the Middle Georgia Concert Band perform at the Grand Opera House in downtown Macon.
Festivals and Celebrations
Macon hosts many fun festivals throughout the year:
- International Cherry Blossom Festival - A 10-day celebration held every March, celebrating the city's beautiful cherry blossoms.
- The Mulberry Street Festival - An arts and crafts festival held downtown in late March.
- The Juneteenth Freedom Festival - An annual celebration in June that honors the end of slavery in 1865 and celebrates Black freedom and heritage.
- Pan African Festival - An annual event in April celebrating African culture and its spread around the world.
- Ocmulgee Indigenous Celebration - Held every September at Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park. It celebrates the original Native American residents of the land. Groups like the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek, and Seminole nations share their stories, art, songs, and dances.
- Skydog - A music festival in November that celebrates the life and music of Duane Allman, nicknamed "Skydog."
- Bragg Jam - This festival includes an Art and Kids' Festival along the Ocmulgee Heritage Trail and a nighttime Pub Crawl.
- Macon Film Festival - An annual event in July that showcases independent films.
Places to Visit
Historical Sites
- Terminal Station - A historic railroad station built in 1916.
- Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park - Located near downtown Macon, this park protects some of Georgia's largest ancient earthwork mounds. These mounds were built by the Mississippian culture about 1,000 years ago. The park has a spiral mound, temple mounds, and a rebuilt earth lodge.
- Fort Benjamin Hawkins - A major military outpost from 1806 to 1821, used as a command center and trading post.
- Cannonball House - A historic home listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
- Luther Williams Field - A historic baseball stadium.
- Old City Cemetery - One of Macon's oldest cemeteries.
- Rose Hill Cemetery - Another historic cemetery, also on the National Register of Historic Places.
- Sidney Lanier Cottage - The historic home of the poet Sidney Lanier.
- Temple Beth Israel - A beautiful domed building built in 1902 for Macon's Jewish community.
- Wesleyan College - The first college in the world chartered to grant degrees to women.
Museums
- The Allman Brothers Band Museum - Located in the "Big House" where the Allman Brothers Band lived. It shows their history and artifacts.
- The Georgia Children's Museum - An interactive museum for kids, located in the downtown Museum District.
- Georgia Sports Hall of Fame - Celebrates famous athletes from Georgia.
- The Little Richard House and Museum - A museum dedicated to the history and artifacts of Little Richard.
- Museum of Arts and Sciences and Planetarium - Features art, science exhibits, and a planetarium.
- Tubman Museum of African American Art, History, and Culture - The largest African American museum in the Southeast.
Community and Entertainment
- City Hall - This building served as Georgia's capital for part of the Civil War.
- Douglass Theatre - Named after its founder, Charles Henry Douglass, an important Black entrepreneur. This theater hosts many events.
- The Grand Opera House - Where the Macon Symphony Orchestra performs.
- Hay House - Also known as the "Palace of the South," it's a grand historic home.
- City Auditorium - Features the world's largest true copper dome.
- Macon Coliseum - A large arena for sports and concerts.
- Macon Little Theatre - Established in 1934, it's the oldest community theater in the area, putting on many plays and musicals each season.
- Waddell Barnes Botanical Gardens - Beautiful gardens to explore.
- Theatre Macon - Located in the old Ritz Theatre, they perform about nine shows a year.
Sports in Macon
Macon is home to the Mercer Bears, who have NCAA Division I teams in many sports like soccer, football, baseball, and basketball. Central Georgia Technical College also has men's and women's basketball teams. Wesleyan College, a women's school, has teams in basketball, soccer, cross country, and more.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macon Bacon | Baseball | Coastal Plain League | Luther Williams Field |
| Macon Mayhem | Ice hockey | SPHL | Macon Coliseum |
Past Sports Teams
Macon has been home to many sports teams over the years, especially in baseball and ice hockey.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue | Active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macon State College Blue Storm | Various | NCCAA | Various | 2009–2013 |
| Macon Central City/Hornets | Baseball | Southern League | Central City Park | 1892–1894 |
| Macon Highlanders/Brigands/Peaches/Tigers | Baseball | South Atlantic League | Central City Park and Luther Williams Field | 1904–1917, 1923–1930 |
| Macon Peaches/Dodgers/Redbirds/Pirates | Baseball | Southeastern League (1932), South Atlantic League (1936–42, 1946–60, 1962–63, 1980–87), Southern Association (1961), Southern League (1964, 1966–67) | Luther Williams Field | 1932, 1936–1942, 1946–1960, 1961–1964, 1966–1967, 1980–1982 |
| Macon Braves | Baseball | South Atlantic League | Luther Williams Field | 1991–2002 |
| Macon Peaches | Baseball | Southeastern League | Luther Williams Field | 2003 |
| Macon Music | Baseball | South Coast League | Luther Williams Field | 2007 |
| Macon Pinetoppers | Baseball | Peach State League | Luther Williams Field | 2010 |
| Macon Blaze | Basketball | World Basketball Association | Macon Coliseum | 2005 |
| Macon Whoopees | Ice hockey | Southern Hockey League | Macon Coliseum | 1974 |
| Macon Whoopee | Ice hockey | Central Hockey League (1996–2001), ECHL (2001–02) | Macon Coliseum | 1996–2002 |
| Macon Trax | Ice hockey | Atlantic Coast Hockey League (2002–03), World Hockey Association 2 (2003–04), Southern Professional Hockey League (2004–05) | Macon Coliseum | 2002–2005 |
| Macon Knights | Arena football | af2 | Macon Coliseum | 2001–2006 |
| Macon Steel | Indoor football | American Indoor Football | Macon Coliseum | 2012 |
| Georgia Doom | Indoor football | American Arena League | Macon Coliseum | 2018–2019 |
| Middle Georgia United | Soccer | UPSL | Cavalier Fields | 2021-2021 |
Parks and Recreation
Macon has many parks and community centers for everyone to enjoy.
- Ocmulgee Heritage Trail - A green pathway with parks and landmarks along the Ocmulgee River in downtown Macon.
- Bloomfield Park
- East Macon Park
- Frank Johnson Recreation Center
- Freedom Park
- L.H. Williams Community School Center
- Memorial Park
- North Macon Park
- Rosa Jackson
- Senior Center
- John Drew Smith Tennis Center
- Tattnall Square Tennis Center
- Charles H. Jones Gateway Park
- Carolyn Crayton Park (formerly Central City Park)
- Central City Skatepark
Education in Macon
About 30,000 college students live in the greater Macon area.
Public Schools
The Bibb County Public School District manages the public schools in Macon. Public high schools include:
- Central High School
- Howard High School
- Northeast Health Science Magnet High School
- Rutland High School
- Southwest Magnet High School and Law Academy
- Westside High School
The Georgia Academy for the Blind is a statewide school for blind students, run by the state of Georgia.
Other schools operated by Bibb County Public Schools:
- Elam Alexander Academy
- Northwoods Academy
Private High Schools
Macon has several private high schools:
- Covenant Academy
- First Presbyterian Day School
- Mount de Sales Academy
- Stratford Academy
- Tattnall Square Academy
- Windsor Academy
State Public Charter Schools
- The Academy for Classical Education
- Cirrus Academy Charter School
Colleges and Universities
- Central Georgia Technical College
- Mercer University
- Middle Georgia State University
- Miller-Motte Technical College - satellite campus
- Wesleyan College
Media
Macon has many local television and radio stations, as well as two local newspapers.
Newspapers and Magazines
- The 11th Hour
- Gateway Macon (web portal), a guide for things to do in Macon
- Macon Business Journal, a magazine about businesses in the Middle Georgia region
- Macon Community News, a monthly newspaper with positive news
- The Mercer Cluster
- The Telegraph, a daily newspaper published in Macon
Transportation and Infrastructure
Hospitals
- The Medical Center, Navicent Health (part of Atrium Health)
- Atrium Health Navicent Beverly Knight Olson Children's Hospital
- Piedmont Health Macon (formerly Coliseum Medical Centers)
- Piedmont Macon Medical Center
- Piedmont Macon North Hospital
- The American Red Cross of Central Georgia
- Central Georgia Rehabilitation Hospital
Airports
- Macon Downtown Airport is close to downtown and handles many corporate and private planes.
- Middle Georgia Regional Airport offers public flights to Macon and cargo services. It's about 9 miles (14 km) south of downtown.
Highways
Macon is connected by several major highways:
 Interstate 16
Interstate 16 Interstate 75
Interstate 75 Interstate 475
Interstate 475 Interstate 14 (proposed)
Interstate 14 (proposed)
U.S. Routes:
State Routes:
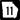 State Route 11
State Route 11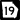 State Route 19
State Route 19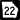 State Route 22
State Route 22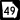 State Route 49
State Route 49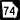 State Route 74
State Route 74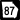 State Route 87
State Route 87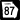 State Route 87 Connector
State Route 87 Connector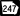 State Route 247
State Route 247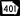 State Route 401 (unsigned designation for I-75)
State Route 401 (unsigned designation for I-75)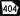 State Route 404 (unsigned designation for I-16)
State Route 404 (unsigned designation for I-16)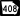 State Route 408 (unsigned designation for I-475)
State Route 408 (unsigned designation for I-475)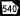 State Route 540 (Fall Line Freeway)
State Route 540 (Fall Line Freeway)
Public Transportation
The Macon Transit Authority (MTA) is Macon's public bus system. It operates 10 city bus routes throughout Macon-Bibb County, with the main hub at Terminal Station.
Bus and Train Travel
Greyhound Lines offers bus service to other cities. In 2019, Greyhound moved its station to the Terminal Station, making it easier to connect with local buses.
Macon became a major center for train travel after the Macon and Western Railroad opened in 1846. Famous train companies like the Central of Georgia Railway and the Southern Railway operated through the city. Passenger trains served Macon until 1971.
Since 2006, there have been plans to bring back inter-city train service to Macon as part of the Georgia Rail Passenger Program. In 2022, Amtrak announced plans to expand its services, which could include Macon in the future.
Walking and Biking Paths
- Heritage Trail
- Ocmulgee Heritage Trail
Famous People from Macon
Sister Cities
Macon has six sister cities around the world. These partnerships help promote cultural understanding and exchanges.
Images for kids
-
Child labor in Macon, 1909. Photo by Lewis Hine.
See also
 In Spanish: Macon (Georgia) para niños
In Spanish: Macon (Georgia) para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |