Major League Baseball facts for kids
 |
|
| Sport | Baseball |
|---|---|
| Founded | National League (NL), 1876 American League (AL), 1901 National Agreement signed, 1903 Merged into one organization, 2000 |
| Commissioner | Rob Manfred |
| No. of teams | 30 |
| Countries |
|
| Headquarters | 1271 Avenue of the Americas New York, New York 10020 U.S. |
| Confederation | WBSC Americas |
| Most recent champion(s) |
Los Angeles Dodgers (8th title) |
| Most titles | New York Yankees (27 titles) |
| TV partner(s) |
|
| Streaming partner(s) |
|
Major League Baseball (MLB) is the top professional baseball league in North America. It has 30 teams, with 29 in the United States and one in Canada. The teams are split into two groups: the National League (NL) and the American League (AL).
MLB is the highest level of professional baseball in the world. Each team plays 162 games during the regular season, which starts in late March. After the season, the best teams from each league compete in a tournament called the postseason.
The postseason ends with the World Series. This is a championship series between the AL and NL champions. The first team to win four games becomes the World Series champion. The Los Angeles Dodgers are the most recent champions, having won in 2024.
Contents
History of MLB
How MLB Started
Baseball became a popular game across the country after the Civil War. The first all-professional team, the Cincinnati Red Stockings, was formed in 1869. This led to the creation of a professional league in 1871.
In 1876, the National League (NL) was founded. It focused on making the sport more organized and fair. The NL stopped players from switching teams whenever they wanted and made sure teams played all their scheduled games.
Another league, the American League (AL), was formed in 1901. The AL and NL were rivals at first, but in 1903 they signed an agreement to work together. This agreement created Major League Baseball and started the first World Series.
The Dead-Ball Era
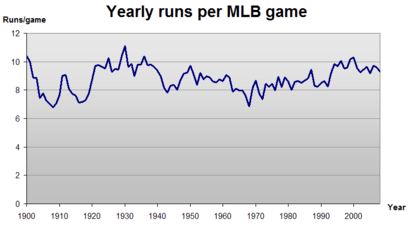
The period from about 1900 to 1919 is called the "dead-ball era." During this time, it was very hard to hit a home run. The baseballs used were not wound as tightly as modern balls, so they didn't travel as far.
Games were low-scoring and pitchers like Walter Johnson and Cy Young were the biggest stars. Teams focused on "small ball" tactics like stealing bases and bunting to score runs.
This era ended after a major event in 1919. Some players on the Chicago White Sox were accused of losing the 1919 World Series on purpose. This was known as the Black Sox Scandal. After this, MLB made big changes to how the sport was run.
Baseball Becomes More Popular

In the 1920s, baseball's popularity exploded, thanks to new rules and exciting players. One of the biggest stars was Babe Ruth of the New York Yankees. He amazed fans by hitting more home runs than entire teams. In 1927, he set a record with 60 home runs in one season.
Even during the tough times of the Great Depression and World War II, baseball remained popular. President Franklin D. Roosevelt said that keeping baseball going during the war was good for the country's spirit. Many MLB players, like Joe DiMaggio and Ted Williams, served in the military during the war.
Breaking the Color Barrier

For many years, Black players were not allowed to play in Major League Baseball. They played in their own leagues, known as the Negro Leagues. This changed in the mid-1940s.
Branch Rickey, the manager of the Brooklyn Dodgers, decided to sign a Black player. He chose Jackie Robinson, a star from the Negro Leagues. On April 15, 1947, Robinson played his first game for the Dodgers, breaking baseball's color barrier.
Robinson faced many challenges but played with great courage and skill. He became a hero and opened the door for other African-American players like Larry Doby, Roy Campanella, and Satchel Paige to join MLB.
Teams on the Move
From 1903 to 1952, all 16 MLB teams were located in the northeastern and midwestern United States. But in the 1950s, teams started moving to new cities. The Dodgers moved from Brooklyn to Los Angeles, and the New York Giants moved to San Francisco. This made MLB a truly nationwide league.
In the 1960s, MLB added eight new teams, called expansion teams. This included the New York Mets, the Houston Astros, and the first team in Canada, the Montreal Expos. More teams were added in later decades, bringing the total to 30.
Big Changes in the Game
In the late 1960s, pitchers became so dominant that it was hard to score runs. This was called "the year of the pitcher." To help hitters, MLB lowered the pitcher's mound and made the strike zone smaller.
In 1973, the American League introduced the designated hitter (DH) rule. This allowed a player to bat in place of the pitcher, who is often not a good hitter. This rule was added to the National League in 2022, making the rules the same for both leagues.
Many new stadiums were built with artificial turf in the 1970s and 1980s. This surface made the ball travel faster and bounce higher, changing how the game was played. Speed and defense became more important.
MLB Teams
There are 30 teams in MLB, divided into the American League and the National League. Each league has three divisions: East, Central, and West.
The MLB Season
The MLB year is divided into three main parts: spring training, the regular season, and the postseason.
Spring Training
Before the regular season begins, teams gather for spring training. They practice and play exhibition games in warm places like Florida and Arizona. This gives new players a chance to make the team and veteran players time to get ready for the season.
The teams in Florida play in the Grapefruit League, and the teams in Arizona play in the Cactus League. Spring training lasts for about two months, from February to late March.
Regular Season
Each team plays 162 games in the regular season. They play most of their games against teams in their own division. They also play games against every other team in both the American and National Leagues.
This part of the season runs from late March or early April until the end of September or early October. At the end of the regular season, the teams with the best records move on to the postseason.
All-Star Game

In the middle of the season, there is a break for the All-Star Game. This is an exhibition game between the best players from the American League and the National League.
Fans vote for their favorite players to be in the starting lineup. The game is a fun celebration of baseball's biggest stars. The first All-Star Game was held in 1933.
Postseason and World Series
The postseason is a tournament to decide the MLB champion. Twelve teams qualify for the playoffs: the six division winners and six "wild card" teams (the non-division winners with the best records).
There are four rounds:
- Wild Card Series: A best-of-three game series.
- Division Series: A best-of-five game series.
- League Championship Series: A best-of-seven game series. The winners are the AL and NL champions.
- World Series: A best-of-seven game series between the AL and NL champions.
The winner of the World Series is awarded the Commissioner's Trophy and is crowned the champion of Major League Baseball.
Images for kids
-
Mark McGwire was a famous home run hitter in the 1990s.
- Australian Baseball League
- Baseball Assistance Team (B.A.T.)
- Baseball in Canada
- Baseball in the United States
- Bob Feller Act of Valor Award
- Comparison of Major League Baseball and Nippon Professional Baseball
- List of all-time Major League Baseball win–loss records
- List of American and Canadian cities by number of major professional sports franchises
- List of current Major League Baseball stadiums
- List of former Major League Baseball stadiums
- List of Major League Baseball awards
- List of Major League Baseball managers
- List of Major League Baseball retired numbers
- List of Major League Baseball spring training ballparks
- List of professional sports leagues
- List of professional sports teams in the United States and Canada
- Major League Baseball attendance records
- Major League Baseball draft
- MLB Industry Growth Fund
- Reviving Baseball in Inner Cities
See also
 In Spanish: Grandes Ligas de Béisbol para niños
In Spanish: Grandes Ligas de Béisbol para niños