Radio facts for kids
Radio is a super cool way to send invisible waves called radio waves over long distances. These waves carry information from one place to another. A machine that sends out these radio waves is called a transmitter. A machine that "catches" or picks up these waves is called a receiver. If a machine can both send and receive, it's called a "transceiver". When radio waves are sent out to many receivers at the same time, it's called a broadcast.
Television also uses radio waves to send pictures and sound to your TV screen. Radio waves can even make things move, like opening gates from far away (this is called radio control). They can also lock and unlock your car doors without a key!
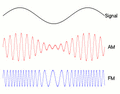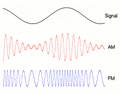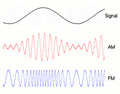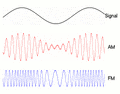
You might know radio best for sending sound, like when you listen to music or talk shows. This often happens using two main types of signals: Frequency Modulation (FM) or Amplitude Modulation (AM).
Contents
How Radio Began
Many clever people helped make radio possible. First, a scientist named James Clerk Maxwell thought about these invisible waves. Then, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz in Germany proved that radio waves really exist.
Later, Guglielmo Marconi from Italy found a way to use radio waves for sending messages without wires, especially for ships at sea. Some people say he invented radio. After that, other inventors learned how to send voices, which led to radio stations broadcasting news, music, and fun shows.
What Radio is Used For Today
Radio started as a way to send messages between two people without wires. Soon, two-way radios allowed people to talk to each other, leading to things like walkie-talkies and even mobile phones.
Today, a big use for radio is broadcasting music, news, and entertainers, including "talk radio" shows. Before TV was common, radio shows were very popular. In the 1930s, the US President even used radio to talk to the American people every week.
Companies that create and send radio programs are called radio stations. Some are run by governments, while others are private companies that earn money by playing advertisements. Other stations are supported by local communities. In the early days, companies would pay to broadcast full stories or plays on the radio. Because companies that made soap often paid for these shows, they were called "soap operas"!
Radio waves are still used for talking between people. This is different from listening to "talk radio." Citizens band radio (CB radio) and amateur radio (ham radio) use special radios for people to chat back and forth. Policemen, firemen, and other emergency helpers use radio to talk to each other during emergencies. It's like a mobile phone (which also uses radio waves), but these radios usually work over shorter distances, and everyone needs to use the same type of radio.
Most radio broadcasting for sound uses lower frequencies and longer waves than TV broadcasting. Microwaves have much higher frequencies and shorter waves. They are also used to send TV and radio programs, and for other purposes. Communications satellites use microwaves to send signals around the world.
A radio receiver doesn't need to see the transmitter directly to get signals. Low frequency radio waves can bend around hills. Also, Shortwave radio signals can bounce off a special layer in the upper atmosphere called the Ionosphere. This means they can travel very far, sometimes even around the world!
Radio telescopes use radio waves from space to study distant objects like stars and galaxies.
Radio's Many Uses
Here are some of the most important ways radio is used:
Broadcasting to Everyone
Broadcasting means sending information one way from a radio transmitter to many people's receivers. Because radio waves get weaker over distance, a broadcasting station can only be heard within a certain range. However, systems that broadcast from satellites can send signals across an entire country or continent!
Old radio and TV stations were paid for by commercial advertising or governments. In newer systems like satellite television and satellite radio, you pay a monthly fee. In these systems, the radio signal is scrambled (encrypted) and can only be unscrambled by your receiver, which the company controls.
Broadcasting uses different parts of the radio spectrum. Long and medium waves can cover areas hundreds of kilometers wide and are good for sound (speech and music). Shortwave radio bands can reach even farther, but they can sometimes have more interference.
For higher frequencies, like those above 30 megahertz, the Earth's atmosphere affects the signals less. These higher frequencies allow for the large amount of data needed for TV broadcasting. They also allow for high-quality sound using frequency modulation.
Audio Broadcasting
The first type of radio broadcast was analog audio. AM broadcasting started in the early 1900s. FM broadcasting came later, in the late 1930s, offering much better sound quality.
Digital audio broadcasting (DAB) began in some countries in 1998. It sends audio as a digital signal instead of an analog one. DAB can offer higher quality sound, is less affected by radio noise, uses radio space more efficiently, and has cool features like electronic program guides. The downside is that you need a new DAB radio to listen.
Television Broadcasting
Television broadcasting sends moving pictures by radio. These are like many still pictures shown quickly on a screen, along with sound. TV signals need more space (bandwidth) than regular radio signals.
Older analog television needed 6 MHz of space. The current TV standard, HDTV, sends much clearer pictures. Digital television (DTV) systems, which replaced analog TV, use clever ways to send HDTV video in less space. This means each old 6 MHz channel can now carry up to 7 DTV channels!
Terrestrial television (or over-the-air TV) is the oldest way to watch TV. Signals are sent from land-based television stations to TVs in homes. These signals travel in a straight line, so reception is usually limited to about 30-40 miles. Most people use a simple antenna, but those farther away might need an outdoor antenna on their roof.
Satellite television uses a special box that receives TV shows from a direct broadcast satellite orbiting 22,200 miles above Earth. This satellite sends many channels (sometimes up to 900!) to a satellite dish antenna on your roof. You pay a monthly fee for this service.
Time and Frequency Signals
Governments use radio to send very accurate time signals. These signals come from atomic clocks and help other clocks stay perfectly on time. You might have a radio clock or watch that uses these signals to set itself automatically.
Two-Way Voice Communication
A two-way radio is a device that can both send and receive sound, letting people talk to each other. This is sometimes called radiotelephony.
- Cell phones are portable phones that connect to the phone network using radio signals from local antennas called cellular base stations (or cell towers). The area a phone company covers is split into small "cells," each with its own antenna. All cell phones in a cell talk to this antenna.
* Cell phones use low-power transmitters so their signals don't travel far, allowing the same frequencies to be used in other cells far away. When you move from one cell to another, your phone automatically switches to the new antenna. * Modern phones, called smartphones, do much more than just make calls. They have other radio transmitters and receivers for things like WiFi, Bluetooth, and GPS. * 5G cellular networks are the newest generation, launched in 2019. They offer much faster internet speeds. To do this, they use higher frequency radio waves that have a shorter range. So, 5G networks will have many small antennas on poles and buildings instead of large cell towers.
- Satellite phones (satphones) are like cell phones but connect to orbiting communications satellites instead of cell towers. They are more expensive but can be used almost anywhere on Earth, even in remote areas.
- Cordless phones are home phones where the handset is portable and talks to the main phone base using a short-range radio link, so you don't need a cord.
- Land mobile radio systems are short-range radios often used in vehicles or as portable units. They are used by first responders like police and firemen, and also by businesses like taxi services.
* Walkie-talkies are battery-powered, handheld two-way radios used in these systems.
- Airband is a radio system used by aircraft pilots to talk to other planes and air traffic controllers on the ground. This is super important for air traffic safety.
- Marine radio is used on ships for talking between ships, to planes, and to shore stations.
- Amateur radio (ham radio) is a hobby where people use two-way radios for fun, to talk to other amateurs, help with emergency communication during disasters, and experiment. People who do this need a special license.
One-Way Voice Communication
One-way radio transmission is called simplex.
- Baby monitors are devices that send a baby's sounds to a receiver carried by a parent, so they can hear the baby from another room.
- Wireless microphones are microphones with a small transmitter that send sound by radio to a nearby receiver. This lets speakers and performers move freely without cords.
Data Communication
Wireless networking uses radio waves to send digital information between computers and other devices, connecting them in a computer network. These networks can send all kinds of data, like emails, web pages, phone calls, music, and videos. Security is important, so wireless networks often scramble their signals.

- Wireless LAN (or WiFi) is the most common type of computer network. It lets you connect computers, laptops, phones, game consoles, and smart TVs to the Internet without cables, usually through a wireless router. WiFi uses channels in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Wireless WAN (WWAN) provides wireless internet over a larger area, like a whole city. Cell phone modems and satellite internet are common types of WWAN.
- Bluetooth is a very short-range wireless connection used to exchange files between portable devices or connect phones to wireless headphones. It works over about 10 meters (30 feet).
- Packet radio is a way to send data packets between computers over long distances, often used by amateur radio enthusiasts.
- Text messaging (texting) lets you type short messages on your cell phone and send them to another phone. It uses a small part of the radio channel that cell phones use for background tasks.
- Microwave relay is a long-distance way to send digital data using a beam of microwaves between two dish antennas. Since the antennas need to "see" each other, distances are limited to about 30-40 miles.
- Telemetry is when measurements and data are sent automatically from a remote device to a receiver for monitoring. It's used for things like tracking missiles, drones, and satellites.
* Automated meter reading allows electric, water, and gas meters to send their readings by radio to a utility vehicle, so no one needs to come to your house to read them. * Electronic toll collection lets you pay tolls on roads without stopping. A device in your car sends a signal to a roadside receiver.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses small radio tags attached to items. When a reader sends out radio waves, the tag sends back an ID number, which helps keep track of goods. Passive tags are powered by the radio energy from the reader and can be tiny. They are used in products, clothes, and even implanted in pets (microchip implant).
- Submarine communication is tricky because seawater blocks most radio waves. But very low frequency radio waves can get through. Navies use huge transmitters on shore to send encrypted messages to their submarines.
Space Communication
This is radio communication between a spacecraft and a ground station on Earth, or between two spacecraft. Sending signals to distant spacecraft, sometimes billions of kilometers away, requires very large dish antennas and super sensitive receivers on Earth. High-frequency microwaves are used because they can pass through the atmosphere easily.

- Communication satellites are artificial satellites that act as relays to send data between far-apart places on Earth. They are used because microwaves travel in straight lines and can't go around the curve of the Earth. Most are in a special orbit 22,200 miles above the equator where they appear to stay in the same spot in the sky.
- Direct broadcast satellites are communication satellites that send TV and radio programs directly to homes and vehicles. They use stronger transmitters so you can receive their signals with a smaller antenna.
Radar
Radar uses radio waves to find and track objects like aircraft, ships, and even to map weather. A radar set sends out a narrow beam of radio waves. When the beam hits an object, the waves bounce back to the receiver. By knowing the direction of the beam, you know where the object is. Since radio waves travel at a constant speed, measuring the time it takes for the "echo" to return tells you how far away the object is. Radar often shows targets on a screen like a map. Doppler radar can even tell you how fast an object is moving.
Radar mostly uses high-frequency microwaves because they create strong reflections from objects and can be focused into narrow beams with small antennas.
- Airport surveillance radar is the main tool for air traffic control. A rotating dish antenna sweeps microwaves around the airspace, showing aircraft as "blips" on a radar screen.
* Secondary surveillance radar works with special devices on aircraft called transponders. When the radar signal hits the plane, the transponder sends back a stronger signal, plus the plane's altitude and ID number, making it show up clearly on the radar screen.
- Electronic countermeasures (ECM) are military systems designed to mess with enemy radar, making it harder for them to find friendly forces.
- Radar altimeter is a radar on an aircraft that measures its height above the ground.
- Marine radar is used on ships to find other ships and obstacles like bridges.
- Weather radar uses radar to map weather systems and measure wind speeds by bouncing microwaves off raindrops.
- Phased-array radar uses a computer-controlled antenna that can quickly steer the radar beam without moving the antenna itself. This is useful for tracking fast-moving objects.
- Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is a special radar on aircraft or spacecraft that creates very detailed maps of the ground.
- Ground-penetrating radar sends radio waves into the ground to find objects hidden underground.
- Collision avoidance system is a radar system in cars that detects if the car is about to hit something and can apply the brakes.
- Radar speed gun is a handheld radar used by police to measure how fast vehicles are going.
Radiolocation is a general term for using radio waves to find the location of objects or for navigation.
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) or satnav systems use satellites to figure out your exact location on Earth (latitude, longitude, and height) very precisely.
* Global Positioning System (GPS) is the most widely used satnav system. It uses 31 satellites orbiting Earth. Each satellite sends a continuous radio signal with a precise time and its position. Your GPS receiver calculates its location by timing how long it takes to get signals from at least four satellites. GPS receivers are in almost all cell phones, cars, planes, and ships, and are used to guide drones and missiles.
- Radio beacons are fixed radio transmitters on land that send a continuous signal used by aircraft and ships for navigation.
* Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR) is a worldwide aircraft navigation system using ground radio beacons. An instrument on the aircraft shows the direction to a nearby VOR transmitter. * Non-directional beacon (NDB) are older radio beacons that send a simple signal in all directions for aircraft or ships to find their way.
- Emergency locator beacon is a portable, battery-powered radio transmitter used in emergencies to find airplanes, ships, or people who are lost or in trouble. When activated, it sends a continuous radio signal that search and rescue teams use to find them. The latest ones have a GPS receiver and broadcast their exact location.
* Cospas-Sarsat is an international group that helps with search and rescue. They use satellites to detect distress signals from emergency beacons anywhere on Earth and send the location to rescue teams.
- Radio direction finding (RDF) is a technique using special radio receivers with directional antennas to find the exact direction of a radio signal, which helps locate the transmitter. It's used by military forces to find enemy radios, by governments to find illegal transmitters, and by scientists to track wild animals.
Remote Control

Radio remote control means using electronic signals sent by radio waves from a transmitter to control a device far away. For example, unmanned spacecraft are controlled by commands sent from ground stations. Most handheld remote controls for TVs use infrared light, not radio waves.
- Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV, drone) – A drone is an aircraft without a pilot inside. It's flown by remote control from a pilot on the ground. Drones are used by the military for looking around and attacking, and by civilians for news and taking pictures from the air.
- Keyless entry systems are small handheld transmitters (like a key fob) that come with most modern cars. They can lock and unlock the car doors from a short distance away. When you press a button, it sends a coded radio signal to the car.
- Garage door openers are handheld transmitters that can open or close an electric garage door from outside.
- Radio-controlled models are popular toys like model boats, cars, airplanes, and helicopters (like quadcopters) that you control with radio signals from a handheld device.
- Wireless doorbells are doorbells that don't need wires. The button outside has a small transmitter that sends a signal to a receiver inside the house, which then rings.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A variety of radio antennas on Sandia Peak near Albuquerque, New Mexico, US
-
Radio communication. Information like sound is changed by a microphone into an electrical signal, which then changes a radio wave made by the transmitter. A receiver catches the radio wave and gets the information, which is then changed back into sound by a loudspeaker.
See also
 In Spanish: Radiocomunicación para niños
In Spanish: Radiocomunicación para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |