Lower Triassic facts for kids
The Lower Triassic was the first part of the Triassic period. It started about 252.2 million years ago and ended around 247.2 million years ago. This makes it the oldest time period in the Mesozoic era, often called the "Age of Dinosaurs."
This important time came right after the huge Permian–Triassic extinction event. This event caused many types of plants and animals to disappear from Earth. In some older books, the Lower Triassic was called the Scythian stage. In Europe, many rocks from this time are sandstone. These rocks are often reddish and show that they formed on land in desert areas.
Life in the Lower Triassic
The massive extinction event that ended the Paleozoic era made life very hard for the animals that survived. Many kinds of corals, brachiopods, molluscs, echinoderms, and other invertebrates had completely vanished.
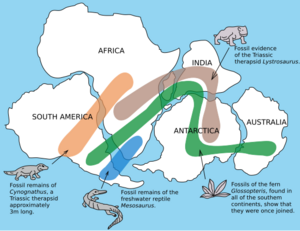
The most common hard-shelled sea animals that survived were bivalves (like clams), snails, ammonites, sea urchins, and some brachiopods. On land, the most common animal was a plant-eating reptile called Lystrosaurus.
The first animals of the Triassic period did not have much biodiversity. This means there were not many different types of animals. It took about 30 million years for life on land to fully recover after the big extinction. The first ichthyosaurs, which were large marine reptiles, also appeared during this time.
Climate during the Lower Triassic
The climate during the Lower Triassic was generally very dry. This was especially true in the middle of the supercontinent Pangaea. Huge deserts covered much of the land. However, areas near the North and South Poles had a more temperate climate. Scientists think the very hot climate of this time might have been caused by many volcanic eruptions happening around the world.
Images for kids
-
The Putorana Plateau is made of basalt rocks from the Siberian Traps.
-
Early Triassic and Anisian marine predators: 1. Wantzosaurus, 2. Fadenia, 3. Saurichthys, 4. Rebellatrix, 5. Hovasaurus, 6. Birgeria, 7. Aphaneramma, 8. Bobasatrania, 9. Hybodontiformes, 10. Mylacanthus, 11. Tanystropheus, 12. Corosaurus, 13. Ticinepomis, 14. Mixosaurus, 15. Cymbospondylidae, 16. Neoselachii, 17. Omphalosaurus skeleton, 18. Placodus
-
Early Triassic brittle stars (echinoderms)
-
Fossils of the bivalve Claraia clarai
-
Early Triassic ammonoid Hedenstroemia
-
Fossil of the Early Triassic neopterygian Candelarialepis argentus
See also
 In Spanish: Triásico Inferior para niños
In Spanish: Triásico Inferior para niños









