Islam facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Islam |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Classification | Abrahamic |
| Scripture | Quran Prophetic traditions: Hadith |
| Theology | Monotheistic |
| Region | Middle East, North Africa, East Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Caucasus, Balkans, Guianas |
| Founder | Muhammad |
| Origin | 610 CE Jabal al-Nour, Mecca, Hejaz, Arabian Peninsula |
| Separations |
|
| Number of followers | est. 2 billion |
Islam is an Abrahamic religion that teaches there is only one God. People who follow Islam are called Muslims. With about 2 billion followers worldwide, Islam is the world's second-largest religion.
Muslims believe that God revealed his teachings to humanity through many prophets, including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. They believe the final and complete message was revealed to the prophet Muhammad in the 7th century. This message is recorded in the Quran, which Muslims consider the exact word of God.
The core of Islam is the belief in one God, called Allah in Arabic. Muslims show their devotion through five main duties called the Five Pillars of Islam. These include a declaration of faith, daily prayers, giving to charity, fasting during the month of Ramadan, and making a pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca.
Islam began in Mecca, a city in modern-day Saudi Arabia, around the year 610 CE. Today, Muslims live all over the world, with large communities in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia.
Contents
What Does "Islam" Mean?
In Arabic, the word Islam means "submission" or "surrender" to the will of God. A Muslim is a person who submits to God. These words come from the Arabic root S-L-M, which is also connected to the word for "peace."
In the past, some people in the English-speaking world called the religion Mohammedanism. This term is not used anymore because it wrongly suggests that Muslims worship Muhammad instead of God.
Core Beliefs of Islam
In Islam, there are six main articles of faith that all Muslims believe in.
Belief in One God
The most important belief in Islam is Tawhid, which means that there is only one God. Muslims believe God is unique, all-powerful, and merciful. They believe God has no partners, children, or equals.
Muslims refer to God as Allāh, an Arabic word that has no plural or gender. Arabic-speaking Christians and Jews also use the word Allah to refer to God.
Belief in Angels
Muslims believe in angels, which are spiritual beings created by God to serve Him. Angels do not have physical needs like eating or drinking. They carry out God's commands, such as delivering messages to prophets.
The most famous angel is Gabriel (called Jibrīl in Arabic), who revealed the Quran to Muhammad. Other angels are believed to record people's good and bad deeds.
Belief in Holy Books

The main holy book of Islam is the Quran. Muslims believe it is the direct word of God, revealed to Muhammad over 22 years. The Quran is divided into 114 chapters called surahs. It is considered the finest work of Arabic literature.
Muslims also respect other holy books that came before the Quran, such as the Tawrat (Torah) given to Moses and the Injil (Gospel) given to Jesus. However, they believe the Quran is the final and unchanged revelation from God.
Belief in Prophets
Prophets are people chosen by God to deliver His message to humanity. Muslims believe that thousands of prophets have been sent throughout history, including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus.
Muslims believe that Muhammad was the last and final prophet, often called the "Seal of the prophets". His life and teachings, known as the Sunnah, provide a model for how Muslims should live. These teachings are recorded in texts called hadith.
Belief in the Day of Judgment
Muslims believe in a Day of Judgment, or Yawm al-Qiyāmah, when all people who have ever lived will be brought back to life. On this day, God will judge everyone based on their actions.
Those who have lived good lives will be rewarded with a place in paradise, called Jannah. Those who have done wrong and did not repent will be sent to hell, called Jahannam.
Belief in Divine Decree
Muslims believe that everything that happens, both good and bad, is part of God's plan. This is known as divine decree or predestination (al-qadar). This belief encourages trust in God, and Muslims often say Inshallah ("if God wills") when talking about the future.
The Five Pillars of Islam
These are the five main duties that all Muslims are expected to perform. They are the foundation of Muslim life.
Declaration of Faith (Shahada)

The Shahada is the basic statement of Islamic belief. It says: "I testify that there is no god but God, and I testify that Muhammad is the messenger of God." Saying this with sincere belief is the first step to becoming a Muslim.
Prayer (Salah)
Muslims are required to pray five times a day. These prayers, called salah, are a way to communicate directly with God. Prayers are said in Arabic while facing the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca. Before praying, Muslims must perform a ritual washing called wudu.
Prayers can be performed anywhere, but it is encouraged to pray in a mosque, which is a Muslim place of worship.
Charity (Zakat)

Zakat is the practice of giving a portion of one's wealth to those in need. It is a duty for Muslims who can afford it to give 2.5% of their savings each year. Zakat is seen as a way to purify one's wealth and help the community.
Fasting (Sawm)
During the holy month of Ramadan, healthy adult Muslims are required to fast from dawn until sunset. This means not eating or drinking anything during daylight hours. Fasting, or sawm, is meant to teach self-discipline, thankfulness, and compassion for the poor.
Pilgrimage (Hajj)
The Hajj is a pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia. Every Muslim who is physically and financially able is expected to make this journey at least once in their lifetime. During the Hajj, pilgrims perform a series of rituals that remember the actions of the prophet Abraham and his family.
History of Islam
The Prophet Muhammad
According to Islamic tradition, Muhammad was born in Mecca in the year 570 CE. He was known for being honest and trustworthy. Around the age of 40, while meditating in a cave, he received his first message from God through the angel Gabriel.
Muhammad began to preach about the oneness of God. His message attracted many followers, but it also angered the powerful leaders of Mecca who believed in many gods. After facing persecution, Muhammad and his followers moved to the city of Medina in 622 CE. This event is known as the Hijra and marks the beginning of the Islamic calendar.
In Medina, Muhammad established the first Islamic community. After several battles, the Muslims conquered Mecca in 629 CE. By the time Muhammad died in 632 CE, most of the Arabian Peninsula had accepted Islam.
The Spread of Islam
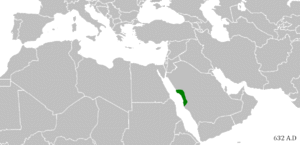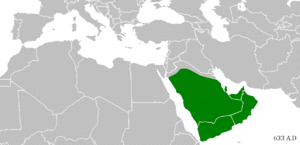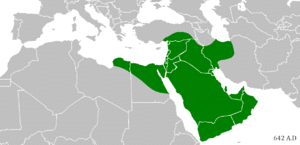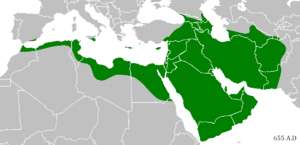
After Muhammad's death, his successors, known as Caliphs, continued to lead the Muslim community. The first four caliphs are called the "Rightly Guided Caliphs" by Sunni Muslims. Under their rule, the Islamic empire expanded rapidly, spreading from Spain in the west to India in the east.
This period, often called the Islamic Golden Age, was a time of great scientific, economic, and cultural growth. Scholars in the Muslim world made important advances in mathematics, medicine, astronomy, and philosophy.
Major Empires
Over the centuries, several powerful Islamic empires rose and fell.
- The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) was the first great Muslim dynasty.
- The Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258) ruled during the Islamic Golden Age from its capital in Baghdad.
- The Ottoman Empire (c. 1299–1922) was one of the longest-lasting empires in history, ruling large parts of the Middle East, North Africa, and Europe.
- The Safavid dynasty (1501–1736) established Shia Islam as the state religion of Iran.
- The Mughal Empire (1526–1857) ruled over most of the Indian subcontinent.
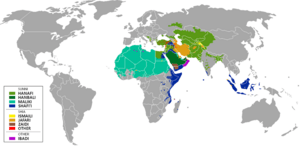
Branches of Islam
Like other major religions, Islam has different branches. The two largest are Sunni and Shia.
Sunni Islam

Sunni Muslims make up about 87–90% of all Muslims. They believe that the leaders of the Muslim community should be chosen from among those who are most qualified. They follow the teachings of the Quran and the Sunnah (the example of the Prophet Muhammad). Sunnis accept the first four caliphs as the rightful successors to Muhammad.
Shia Islam

Shia Muslims make up about 10–13% of the Muslim population. They believe that leadership should have stayed within Muhammad's family, starting with his cousin and son-in-law, Ali. Shias believe that Ali and his descendants, known as Imams, were the true spiritual leaders.
The split between Sunnis and Shias began over a disagreement about who should lead the Muslim community after Muhammad's death. Over time, this led to different religious and legal traditions.
Islamic Law and Culture
Sharia and Fiqh
Shariah is the religious law of Islam, based on the Quran and the Sunnah. It provides guidance on all aspects of life, from prayer and family matters to business and government. Fiqh is the human understanding and interpretation of Sharia. There are several different schools of Islamic law, or madhhabs, within both Sunni and Shia Islam.
Art and Architecture
Islamic art is known for its beautiful and complex patterns. Because creating images of living beings was often discouraged, artists focused on calligraphy (artistic handwriting), geometry, and patterns inspired by plants.
Islamic architecture is famous for its grand mosques with large domes, tall towers called minarets, and peaceful courtyards. Famous examples include the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem and the Taj Mahal in India.
Festivals
Muslims celebrate two major holidays each year.
- Eid al-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan. It is a time of feasting, prayer, and giving gifts.
- Eid al-Adha takes place during the Hajj. It honors the prophet Abraham's willingness to sacrifice his son and is celebrated with prayers and by sharing meat with family, friends, and the poor.
Interesting Facts About Islam
- Islam is the second-largest religion in the world. It has about 1.75 billion followers, which is about 24% of the world's population.
- Islam is also the fastest-growing religion in the world.
- Islam has three very holy sites: Jerusalem, Mecca, and Medina.
- Arabs make up about 20% of all Muslims worldwide.
- A Hafeez is a Muslim who has memorized the entire Quran. They can recite every word accurately without looking at the book.
Images for kids
-
The Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem was completed at the end of the 7th century.
-
Abdülmecid II, the last Caliph from the Ottoman dynasty.
-
The Imam Ali Shrine in Najaf, Iraq, is a holy site for Shia Muslims.
-
The Imam Hussein Shrine in Karbala, Iraq, is another important holy site for Shia Muslims.
-
The Imam Reza shrine in Mashhad, Iran, is the world's largest mosque by area.
-
The Whirling Dervishes of the Mevlevi Order, a Sufi group, performing a ceremony in Konya, Turkey.
See also
 In Spanish: Islam para niños
In Spanish: Islam para niños