Outline of war facts for kids
War is a serious and often long-lasting armed conflict. It happens when groups of people, like countries or other large groups, fight each other using weapons. War involves a lot of violence, causes big problems for communities, and can destroy economies. Think of it as a planned, widespread fight between different groups, usually for political reasons.
Warfare is the general term for how wars are fought and what usually happens during them.
Contents
Different Kinds of War
Wars can be very different depending on how they are fought or what they are about. Here are some types:
- Cold War: A conflict where countries compete without direct fighting, often using threats or economic pressure.
- Colonial war: Fights where a country tries to control another land or people.
- Insurgency: A rebellion or uprising against a government.
- Civil war: A war fought between groups within the same country.
- Invasion: When an army enters another country's territory to take control.
- Proxy war: When two powerful countries support opposing sides in a conflict, but don't fight each other directly.
- Religious war: Conflicts fought over religious beliefs.
- Total war: A war where a country uses all its resources and people for the war effort.
- World war: A very large war involving many countries around the globe.
How Wars Are Fought
This describes the different ways armies fight and the strategies they use.
Fighting Styles and Goals
- Asymmetric warfare: When one side is much stronger than the other, so the weaker side uses unusual tactics like guerrilla warfare.
- Defensive warfare: Fighting to protect your own territory.
- Offensive warfare: Fighting to attack and take enemy territory.
War Strategies
These are the big plans armies use to win.
- Attrition warfare: Trying to win by slowly wearing down the enemy, causing more losses than they can handle.
- Conventional warfare: Using traditional armies, tanks, planes, and ships in direct battles.
- Unconventional warfare: Using methods that are not typical, like supporting rebel groups or guerrilla warfare.
- Economic warfare: Using money and trade to weaken an enemy, like blocking their supplies.
- Irregular warfare: Fighting by groups that are not regular armies, often using surprise attacks.
- Guerrilla warfare: Small groups using hit-and-run tactics against a larger, less flexible army.
- Psychological warfare: Using propaganda and other methods to affect the enemy's morale and beliefs.
- Terrorism: Using violence against civilians to create fear and achieve political goals.
Fighting in Different Places
Wars can be fought in many environments.
- Ground warfare: Fighting on land.
- Urban warfare: Fighting in cities.
- Jungle warfare: Fighting in dense forests.
- Mountain warfare: Fighting in mountains.
- Trench warfare: Fighting from long, narrow ditches, common in World War I.
- Naval warfare: Fighting at sea.
- Amphibious warfare: Attacks launched from the sea onto land.
- Aerial warfare: Fighting in the air using planes.
Wars Through Time
Warfare has changed a lot over history.
- Prehistoric warfare: Early fighting before written history.
- Ancient warfare: Wars from ancient times, like those of the Greeks or Romans.
- Medieval warfare: Wars during the Middle Ages, often involving castles and knights.
- Early modern warfare: Wars from the 1500s to 1700s, with new weapons like cannons.
- Industrial warfare: Wars from the 1800s and early 1900s, using factories to make many weapons.
- Modern warfare: Wars from the last century, with advanced technology.
History of War
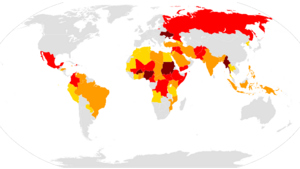
Major wars: 10,000+ deaths in a year Wars: 1,000–9,999 deaths in a year Minor conflicts: 100–999 deaths in a year Small clashes: fewer than 100 deaths.
War has been a part of human history for a very long time.
Wars by Time Period
- List of wars: before 1000
- List of wars: 1000–1499
- List of wars: 1500–1799
- List of wars: 1800–1899
- List of wars: 1900–1944
- List of wars: 1945–1989
- List of wars: 1990–2002
- List of wars: 2003–present
- List of ongoing armed conflicts
Wars by Location
Wars have happened all over the world.
- List of conflicts in North America
- List of conflicts in Europe
- List of conflicts in Asia
- List of modern conflicts in the Middle East
- List of conflicts in Africa
Famous Battles
- Lists of battles
- List of battles by casualties: Lists battles by how many people were killed or injured.
- List of sieges: When an army surrounds a city or fort to try and take it.
How Armies Are Organized
Armies need to be well-organized to fight effectively.
- Command and control (military): How leaders give orders and manage troops.
- Military branch: Different parts of the military, like the army, navy, or air force.
- Military intelligence: Gathering information about the enemy.
- Military logistics: Getting supplies, food, and equipment to soldiers.
- Military rank: The different levels of leadership in the military (e.g., private, sergeant, general).
- Military technology and equipment: The weapons and tools soldiers use.
Military Operations
Military operations are planned actions by armed forces. They can range from small attacks to huge campaigns.
- Military operation plan: A detailed plan for a military action.
Types of Military Operations
Military operations can be different sizes:
- Theater operation: A very large operation covering a huge area, like a whole continent. It involves many goals beyond just fighting, like economic and political aims.
- Campaign: A smaller part of a theater operation, or a more focused military effort in a specific area.
- Battle: A specific fight with clear military goals and a defined area, involving many troops.
- Engagement: A tactical fight for a specific area or objective between smaller units.
- Strike: A single attack on a specific target, often part of a larger engagement. For example, attacking an airport or an enemy leader.
Military Strategy and Tactics
- Military strategy: The overall plan for winning a war or campaign.
- Military tactics: The specific methods used by soldiers and units during a battle.
Big Picture Strategy
- Economic warfare: Using money and trade to weaken an enemy.
- Total war: When a country uses all its people and resources to win a war.
Battle Tactics
- Air combat manoeuvring: How fighter pilots fly to gain an advantage in a dogfight.
- Charge (warfare): A direct, fast attack on the enemy.
- Counter-insurgency: Efforts to fight against a rebellion or guerrilla group.
- Guerrilla warfare: Small groups using surprise attacks and ambushes.
- Siege: Surrounding an enemy position to force them to surrender.
The Politics of War
War is deeply connected to politics and how countries interact.
- Casus belli: A Latin phrase meaning the reason or justification for going to war.
- Declaration of war: A formal statement by a country that it is going to war.
- Surrender: When one side gives up fighting.
- Unconditional surrender: Giving up without any special conditions, except those protected by international law.
- Victory: Winning the war.
- Pyrrhic victory: A victory that comes at such a high cost that it feels almost like a defeat.
- War effort: All the activities a country does to support a war.
- War economy: How a country's economy changes to support the war effort.
Thinking About War
Philosophy of war looks at deeper questions about war, like why it happens, what it means, and if it's ever right or wrong.
- Militarism: The belief that military power is very important and that war can sometimes be good for a country.
- Pacifism: The belief that war is always wrong and should be avoided. Pacifists believe in solving problems without violence.
- Right of self-defence: The idea that a country has the right to defend itself and its citizens if attacked.
Rules of War
- Laws of war: International rules that try to limit the cruelty of war and protect people.
- War crimes: Actions during war that break the laws of war, like harming civilians on purpose.
Prisoners of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a soldier captured by the enemy during a conflict.
- Prison camps: Places where prisoners of war are held.
- Prisoner-of-war camp: A camp specifically for captured soldiers.
- Prison escape: When a prisoner tries to get away from a camp.
What Happens After War
Wars have many serious effects on people and places.
- Casualties: People who are killed, injured, or go missing during a war.
- List of genocides by death toll: Lists of times when large groups of people were killed because of their ethnicity or religion.
War in Culture
War is often shown in movies, books, and other forms of art.
- List of war films and TV specials: Movies and TV shows about wars.
- Wars in popular culture: How famous wars are shown in movies, games, and stories.
- World War I in popular culture
- World War II in popular culture
Books About War
- The Art of War: An ancient Chinese book about military strategy.
- On War: A famous book by Carl von Clausewitz about the philosophy of war.
Important People in War History
Many people have played key roles in wars, from inventors to leaders.
Inventors of Military Technology
- Archimedes: An ancient Greek inventor.
- Leonardo da Vinci: A famous artist and inventor.
- Richard Jordan Gatling: Invented the Gatling gun.
- Mikhail Kalashnikov: Designed the AK-47 rifle.
Famous Leaders and Commanders
Ancient Times
- Alexander the Great: A famous Greek king and military leader.
- Sun Tzu: A Chinese general and author of The Art of War.
- Hannibal: A Carthaginian general famous for fighting Rome.
- Julius Caesar: A Roman general and leader.
- Attila: A powerful leader of the Huns.
Middle Ages
- William the Conqueror: Led the Norman conquest of England.
- Richard the Lionheart: An English king and crusader.
- Saladin: A Muslim leader who fought against the Crusaders.
- Genghis Khan: The founder of the Mongol Empire.
- Joan of Arc: A French heroine who led armies in the Hundred Years' War.
Early Modern Period
- Mehmed the Conqueror: An Ottoman sultan who conquered Constantinople.
- Napoleon: A French emperor and military genius.
- George Washington: The first President of the United States and a general in the American Revolutionary War.
Modern Period
World War I Leaders
- Ferdinand Foch: A French general.
- John J. Pershing: An American general.
World War II Leaders
- Winston Churchill: The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
- Adolf Hitler: The leader of Nazi Germany.
- Franklin Roosevelt: The President of the United States.
- Joseph Stalin: The leader of the Soviet Union.
- Dwight D. Eisenhower: An American general who later became president.
- Douglas MacArthur: An American general.
- Bernard Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein: A British general.
- George S. Patton: An American general.
- Erwin Rommel: A German field marshal.
- Georgy Zhukov: A Soviet general.
See also
- List of ongoing armed conflicts
- List of terrorist incidents
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |

