Bedford facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bedford |
|
|---|---|
| Town | |
 Clockwise from the top left: Bedford Castle Mound, Westbourne Road Mosque in the Queens Park area, Shire Hall, Bedford Town Bridge, Priory Lake, St Paul's Church and Britannia Iron Works former entrance |
|
| Population | 106,940 (2011 built-up area including Biddenham and Kempston) |
| OS grid reference | TL055495 |
| • London | 46 miles (74 km) S |
| Unitary authority | |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | Bedford |
| Postcode district | MK40–MK45 |
| Dialling code | 01234 |
| Police | Bedfordshire |
| Fire | Bedfordshire and Luton |
| Ambulance | East of England |
| EU Parliament | East of England |
| UK Parliament |
|
Bedford is a market town located in Bedfordshire, England. In 2011, about 106,940 people lived there. Bedford is the main town of Bedfordshire and where the local government for the Borough of Bedford is based.
The town of Bedford was started at a place where people could cross the River Great Ouse. It is believed that King Offa of Mercia, famous for building Offa's Dyke, was buried here. Bedford Castle was built by King Henry I, but it was later destroyed in 1224. Bedford became an official town in 1166 and has had representatives in Parliament since 1265. It is also known for having many people of Italian heritage.
Contents
- History of Bedford
- How Bedford is Governed
- Bedford's Geography and Climate
- People and Cultures in Bedford
- Famous Places in Bedford
- Getting Around Bedford
- Learning in Bedford
- Places of Worship
- Culture and Fun in Bedford
- Tourism and Future Plans
- New Technologies
- Media and News
- Sports in Bedford
- Bedford in Films and TV
- Public Services
- Notable People from Bedford
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Bedford
The name Bedford likely comes from a Saxon chief named Beda and a ford (a shallow place to cross) over the River Great Ouse. From the early Middle Ages, Bedford was an important market town for the farms around it.
The Anglo-Saxon King Offa of Mercia was buried in Bedford in 796. His tomb was likely near the Church of St Paul or by the river. In 886, Bedford became a border town between Wessex and Danelaw.
In 919, Edward the Elder built the town's first known fort south of the River Great Ouse. This fort was later destroyed by the Danes. William II then gave the area to Paine de Beauchamp, who built a strong new castle.
Key Events in Bedford's Past
Bedford received its town charter in 1166 from King Henry II. The new Bedford Castle was pulled down in 1224, and today only a mound remains. From the 1500s, Bedford became a major center for England's lace industry, which continued until the early 1900s.
In 1660, John Bunyan was put in Bedford Gaol for 12 years. While there, he wrote his famous book, The Pilgrim's Progress. The River Great Ouse became easy to travel on by boat up to Bedford in 1689.
In the 1800s, Bedford became an important place for engineering. A big fire in 1802 damaged 72 buildings in the St Loyes area. In 1823, a Great Flood covered most of the town when the river overflowed. You can still see a stone marker on a building in St Johns Street showing how high the water reached.
Gas lighting came to Bedford in 1832, and the railway arrived in 1846. The first corn exchange (a place for trading grain) was built in 1849. Drains and sewers were first dug in 1864. Mary Milligan became Bedford's first woman town councilor in 1919.
How Bedford is Governed
The main part of Bedford is the largest settlement in the wider Borough of Bedford. The local council is led by a 'Mayor of Bedford', who is chosen by the people. The current mayor is Tom Wootton.
The Bedford area is split into 10 areas called wards for local elections. These include Brickhill, Castle, and Goldington. Some parts of Bedford, like Kempston, have their own smaller local councils called parish councils.
Bedfordshire Police looks after safety in Bedford. The current Chief Constable is Trevor Rodenhurst. Bedford is also part of the Bedford constituency, which sends a representative to the UK Parliament. The current Member of Parliament (MP) for Bedford is Mohammad Yasin.
Bedford's Geography and Climate
Bedford is about 46 miles (74 km) north-northwest of London. It is also near other towns like Birmingham, Cambridge, and Northampton.
The town of Kempston and the village of Biddenham are part of Bedford's built-up area. Other nearby villages include Bromham and Elstow. Wixams is a new town being built south of Bedford.

Bedford's Weather
Like the rest of the United Kingdom, Bedford has a maritime climate. This means it has mild temperatures and rain spread throughout the year. The closest weather station is at Bedford (Thurleigh) airport.
Temperatures there have ranged from 39.5 °C (103.1 °F) in July 2022 to −15.3 °C (4.5 °F) in January 1982. Rainfall is about 585 mm (23.0 in) each year. The area gets around 1,500 hours of sunshine a year.
| Climate data for Bedford (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1980–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.9 (58.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
22.4 (72.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
39.5 (103.1) |
35.9 (96.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
28.1 (82.6) |
17.6 (63.7) |
15.7 (60.3) |
39.5 (103.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7.3 (45.1) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.6 (51.1) |
13.7 (56.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
19.8 (67.6) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.2 (72.0) |
19.0 (66.2) |
14.7 (58.5) |
10.2 (50.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
14.4 (57.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.4 (39.9) |
4.8 (40.6) |
6.7 (44.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
12.0 (53.6) |
15.0 (59.0) |
17.4 (63.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
14.6 (58.3) |
11.1 (52.0) |
7.2 (45.0) |
4.7 (40.5) |
10.4 (50.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
4.5 (40.1) |
7.3 (45.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
12.3 (54.1) |
12.3 (54.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
1.9 (35.4) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −15.9 (3.4) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
1.8 (35.2) |
4.9 (40.8) |
5.0 (41.0) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
−15.9 (3.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 52.4 (2.06) |
40.1 (1.58) |
37.3 (1.47) |
44.3 (1.74) |
47.0 (1.85) |
50.3 (1.98) |
51.2 (2.02) |
58.7 (2.31) |
50.0 (1.97) |
65.3 (2.57) |
56.9 (2.24) |
55.2 (2.17) |
608.6 (23.96) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 11.1 | 9.3 | 9.0 | 9.1 | 8.5 | 8.8 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 10.3 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 114.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 62.8 | 84.7 | 117.5 | 157.8 | 195.0 | 189.0 | 200.6 | 184.8 | 143.5 | 107.6 | 66.6 | 58.5 | 1,568.3 |
| Source 1: Met Office | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Starlings Roost Weather | |||||||||||||
People and Cultures in Bedford
Bedford has one of the largest groups of Italian immigrants in the UK. In 2001, almost 30% of Bedford's people had at least some Italian family. This happened because the London Brick Company hired many workers from Southern Italy in the early 1950s.
Besides Italians, many people have moved to Bedford from other places. These include India (8.1% of the population), Eastern Europe, Scandinavia, Ireland, Greece, Cyprus, and various parts of Africa and the Caribbean. This makes Bedford one of the most diverse towns in the UK outside of London.
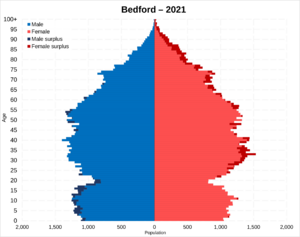
In 2011, the ethnic makeup of Bedford was about 74.4% white, 15% Asian, and 5% Black. About 50% of people said they were only English, 24% only British, and 15% had a non-UK identity.
Religious Groups in Bedford
In 2001, most people in Bedford (69%) were Christian. By 2021, this changed to 48% Christian, with 40% saying they had no religion. The number of Muslims grew from 3% in 2001 to 7% in 2021. Sikh people made up 2% of the population in both years.
| Religious group | 2021 | 2011 | 2001 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | |
| Christian | 88,178 | 47.61% | 93,346 | 59.28% | 101,720 | 68.77% |
| Muslim | 13,059 | 7.05% | 8,610 | 5.47% | 4,803 | 3.25% |
| Sikh | 4,114 | 2.22% | 3,336 | 2.12% | 2,740 | 1.85% |
| Hindu | 3,045 | 1.64% | 2,420 | 1.54% | 2,567 | 1.74% |
| Buddhist | 629 | 0.34% | 509 | 0.32% | 355 | 0.24% |
| Jewish | 232 | 0.13% | 171 | 0.11% | 180 | 0.12% |
| Other religion | 2,014 | 1.09% | 1,506 | 0.96% | 432 | 0.29% |
| Irreligious | 73,954 | 39.93% | 47,581 | 30.21% | 35,114 | 23.74% |
| Total responses | 185,225 | 100% | 157,479 | 100% | 147,911 | 100% |
Famous Places in Bedford
Bedford Park is the town's biggest park. It has many original features from its Victorian design, like a cricket pavilion and bandstand. Both are still used today. Priory Country Park is another large park by the River Great Ouse. Both parks have won Green Flag awards for being well-managed.
Bedford's main church is St Paul's, located in the town center. It is the main church for Bedford and Bedfordshire. It has a tall, famous spire that stands out in the town. The church has been there since at least 1066. John Bunyan and John Wesley both preached in this church. From 1941 to the end of Second World War, the BBC broadcast its daily service from St Paul's.
Another important church is St Peter's, which has some of the oldest building parts in Bedford. St Paul's Church also has the town's Visitor Information Centre.
Just outside Bedford are the Cardington airship hangars. These huge hangars have been used to film scenes for movies like Star Wars, Batman Begins, The Dark Knight, and Inception. You can see them from the Bedford Bypass.
The Old Town Hall was built in 1550 and was first used as a school.
The River Great Ouse
The River Great Ouse flows through the middle of Bedford. Its banks are lined with beautiful gardens called the Embankment. Here, you can find a war memorial for the men of Bedford who died in the First World War. The memorial was designed in 1921 and shows Lady Athelflaed, who ruled Mercia, fighting a dragon.
Bedford Castle Mound
Bedford Castle Mound is what's left of Bedford's old castle. It's near the town center, close to Bedford Bridge. Around 2000, the council built a wall on the south side facing the river. A path leads up to the top of the mound, which is a flat, grassy area.
Getting Around Bedford
Trains in Bedford
Bedford has two train stations. The main Bedford railway station is on the Midland Main Line. From here, you can catch trains to London St Pancras and the East Midlands. These are run by East Midlands Railway. Other trains, run by Thameslink, go through London to Gatwick Airport and Brighton.
Bedford's other station is Bedford St John's. This station is on the Marston Vale Line. Trains from here, run by London North Western Railway, go between Bletchley and Bedford's main station.
Roads in Bedford
Major roads like the A6 and A421 connect Bedford to other towns. The A6 goes to Kettering and Luton. The A421 connects to Milton Keynes and the M1 (a big highway) to the west. It also connects to the A1 to the east.
Buses in Bedford
The Bedford bus station serves the town. It was reopened on March 29, 2015, after a big upgrade. The main bus companies in Bedford are Stagecoach East and Stagecoach Midlands.
Learning in Bedford
Bedford used to have a "three-tier" school system (lower, middle, and upper schools). However, all schools in the borough have now changed to a "two-tier" system (primary and secondary schools).
Bedford has several secondary schools, including Bedford Academy, Bedford Free School, and St Thomas More Catholic School.
Private Schools
Bedford is home to four private schools run by the Harpur Trust charity. This charity was started by Sir William Harpur in the 1500s. These schools are:
- Bedford School for boys aged 7–18.
- Bedford Modern School, which became co-educational (for boys and girls) in 2003, for pupils aged 7–18.
- Bedford Girls' School for girls aged 7–18.
- Pilgrims Pre-Preparatory School.
Other private schools include Bedford Greenacre Independent School and Polam School.
Bedford also has a campus of the University of Bedfordshire. For further education after secondary school, students can go to Bedford College or The Bedford Sixth Form. Stella Mann College offers courses in performing arts.
Places of Worship

Bedford has many places of worship for different religions. These include the main St Paul's and St Peter's churches. There are also many Roman Catholic churches, Orthodox churches, Baptist churches, and other Christian churches.
The town has four Islamic mosques, and also Buddhist and Hindu temples. Bedford has the largest Sikh gurdwara (place of worship) in the UK outside London. There are also Guru Ravidass and Valmiki temples.
Other religious groups like Quakers, Jehovah's Witnesses, and Wiccans also have communities and meeting places in Bedford. The town used to be the headquarters of the Panacea Society, a religious group that believed Bedford would be important in the Second Coming of Jesus Christ. They even thought Bedford was the original Garden of Eden.
Culture and Fun in Bedford
The Higgins Art Gallery & Museum, Bedford, is in a Victorian home and a modern building. It has collections of local history, watercolours, drawings, ceramics, and lace.
Bedford has several public artworks, like the Statue of John Bunyan and the Statue of John Howard. The Panacea Museum tells the story of the Panacea Society.
The Bedford Corn Exchange is the biggest entertainment place in town. It hosts many shows, concerts, and events. Famous entertainers like Glenn Miller and Bob Hope have performed there.
The University of Bedfordshire Theatre is the largest theater in Bedford. Many local theater groups perform plays and musicals at places like the Place Theatre and the Corn Exchange. Esquires is a popular live music venue that hosts many bands.
Festivals and Events
Every two years, the "Bedford River Festival" takes place by the river in early July. This event lasts two days and attracts about 250,000 visitors. It includes sports, funfairs, and live music. It's the second-largest regular outdoor event in the UK. The Bedford Regatta in May is Britain's biggest one-day river rowing event.
Other yearly events include "Bedford by the Sea" (where sand is brought to the town center), the "Bedford International Kite Festival", and "Bedford Festival of Motoring" in June. "Proms in the Park" in early August is a popular music event.
Bedford has also appeared on TV and radio shows, like Mark Steel's in Town and The Late Show with Stephen Colbert.
Tourism and Future Plans
In December 2023, Universal Destinations & Experiences bought a large piece of land near Stewartby, just outside Bedford. The company is looking into building a theme park and resort there. They chose this spot because it's close to London and Luton Airport.
In 2024, Universal Studios Great Britain was announced. Plans are being approved, and construction could start as early as January 2025. The park might be finished around 2030.
New Technologies
In July 2022, Starship Technologies started using autonomous delivery robots in Bedford. These robots deliver items from three Co-op stores in Goldington, Queens Drive, and Kempston. This service covers about 45,000 residents and 20,000 homes.
Media and News
Television
Local news and TV shows for Bedford are provided by BBC East and ITV Anglia. These come from the Sandy Heath TV transmitter.
Radio
Local radio stations include BBC Three Counties Radio (95.5 FM), Heart East (96.9 FM), Greatest Hits Radio Bucks, Beds and Herts (96.2 FM), In2beats (106.5 FM), and Bedford Radio.
Newspapers
Bedford has two local newspapers: the Times & Citizen and the Bedford Independent. Both are given out for free in Bedford and nearby areas.
Sports in Bedford
Bedford has a long history of sports, especially rugby and football. The town has four rugby union teams: Bedford Blues, Bedford Queens, Bedford Swifts, and Bedford Athletic. Since 2004, Bedford also has a rugby league team, Bedford Tigers.
Bedford is one of the largest towns in England without a fully professional football team. Bedford Town F.C. plays at the seventh level of English football, and Real Bedford F.C. plays at the eighth level.
Rowing is also very popular. Many regatta events (boat races) are held throughout the year on the River Great Ouse. The most important is the Bedford Regatta, which is the second largest in the country by the number of teams. Olympic rower Tim Foster trained on Bedford's river. Many other sports champions, like Stephanie Cook and Paula Radcliffe, have come from Bedford.
Viking Kayak Club organizes the Bedford Kayak Marathon and national canoe slalom events at the Cardington Artificial Slalom Course (CASC). This was the first man-made whitewater course in the UK. CASC also hosts the UK's biggest canoe slalom event each year. Etienne Stott, an Olympic Gold Medallist in 2012, was part of this club.
Bedford was a major host for national teams getting ready for the 2012 Summer Olympics and Paralympics. Many countries, including the Maldives, Angola, and Jamaica, based their athletes in Bedford.
Bedford in Films and TV
- The popular BBC TV series Some Mothers Do 'Ave 'Em was filmed in and around Bedford in the 1970s.
- In 2017, The Late Show with Stephen Colbert featured a segment called "Bedford of Bedfordshire's Community Calendar." John Oliver, who grew up in Bedford, described the town as 'scrappy'. The segment showed places like the Shuttleworth Collection and the Bedford Corn Exchange.
Public Services
Bedford Hospital is a general hospital with two locations in town. It offers many services, but for very specialized care, patients might go to Addenbrooke's Hospital in Cambridge.
Bedfordshire Police is in charge of policing in Bedford and has a main police station in the town center. Fire and rescue services are handled by the Bedfordshire Fire and Rescue Service. Bedford's fire station is in the Newnham area and is open 24 hours a day.
Notable People from Bedford
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bedford para niños
In Spanish: Bedford para niños
- Transport in Bedford
- Healthcare in Bedfordshire
- List of twin towns and sister cities in the United Kingdom