Spanish West Indies facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Spanish West Indies
Las Antillas Occidentales
Las Antillas Españolas |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1492–1898 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spanish West Indies
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Colony of Spain (Territory of the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1492 to 1898) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Santo Domingo (1511–1764) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Spanish (official) Taíno, Guanahatabey, Macorix, Ciguayo |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monarch | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1492–1504
|
Ferdinand II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1492–1504
|
Isabella I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1896–1898
|
Alfonso XIII | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Spanish colonization | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1492 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1898 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Spanish colonial real, Spanish dollar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | ES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
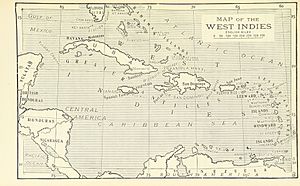
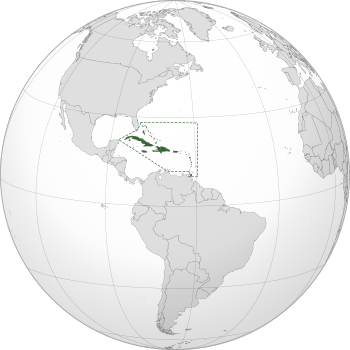
The Spanish West Indies were islands in the Caribbean that were once colonies of Spain. People also called them the Spanish Antilles. In Spanish, they were known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or "Las Antillas Españolas".
For a long time, these islands were part of the larger Spanish Empire. All of Spain's lands far away were called "The Indies." A group in Spain called the Council of the Indies helped manage them. Later, in 1535, the Spanish Crown created the Viceroyalty of New Spain. This was a big area that included the Caribbean islands.
Spain mainly controlled the larger islands, known as the Greater Antilles. These included Hispaniola (where Haiti and the Dominican Republic are today), Cuba, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico. By 1520, most native people on these islands had either died or mixed with the European settlers. Spain also claimed smaller islands, like the Lesser Antilles. But these smaller islands often stayed independent until other European countries took them over later.
The Spanish West Indies were very important because Christopher Columbus explored them first. Because of his trips, these islands were the first places in the Americas where Spain built lasting settlements. They were also the last part of Spain's American Empire to be given up. Spain lost them in 1898 after the Spanish–American War. For over 300 years, Spain used a network of ports in the Caribbean. These included Havana (Cuba), San Juan (Puerto Rico), and Veracruz (Mexico). These ports were connected by special ship routes.
Some smaller islands were taken by other European countries. This happened because of wars or agreements in the 1600s and 1700s. Other islands, like the Dominican Republic, became independent in the 1800s.
Contents
How Islands Changed Hands or Became Independent
Over time, many islands in the Spanish West Indies changed who ruled them. Some became independent countries. Here's how some of them changed:
Islands Gained by Other Countries
- The Bay Islands were given to England in 1643. Later, they went to Honduras in 1861.
- Jamaica was taken by England in 1655. This was made official in the Treaty of Madrid (1670).
- The Cayman Islands were also given to England in the Treaty of Madrid (1670).
- Haiti (the western part of Hispaniola) was given to France in 1697. This area became known as Saint-Domingue.
- Trinidad was captured by Britain in 1797. This was confirmed in the Treaty of Amiens in 1802.
Islands Gaining Independence
- The eastern part of Hispaniola (called Captaincy General of Santo Domingo) was given to France for a while. It later returned to Spain.
- It became independent from Spain as Spanish Haiti in 1821.
- Then it became independent from Haiti as the Dominican Republic in 1844.
- It gained independence from Spain again in 1865 after the Dominican Restoration War.
- Captaincy General of Cuba was lost to the United States in 1898. This happened after the Spanish–American War ended with the 1898 Treaty of Paris.
- Captaincy General of Puerto Rico was also lost to the United States in 1898. This was also part of the 1898 Treaty of Paris.
The Spanish Caribbean Today
Today, when people say Spanish Caribbean or Hispanophone Caribbean, they mean the places in the Caribbean Sea where Spanish is spoken. The main islands are Cuba, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico.
Sometimes, this term can also include the Spanish-speaking coasts of Mexico, Central America, and parts of South America. However, these areas are often culturally different from the Spanish-speaking islands. The Spanish Caribbean includes places where Spanish is the main language. It also includes areas where Spanish settlement has shaped the culture. This includes religion, language, and food. The type of Spanish spoken in this region is called Caribbean Spanish.
The Spanish Caribbean (Cuba, Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico) is a unique part of Latin America. It has its own culture, different from other Spanish-speaking countries on the mainlands. It's also different from other Caribbean islands where English, French, or Dutch are spoken.
People in the Spanish Caribbean often have mixed backgrounds. Many are of mixed Spanish, West African, and native Taíno ancestry. This group makes up most of the population, especially in the Dominican Republic. There are also many people of African descent. African culture has a strong influence here. The Spanish Caribbean also has more influence from the Canary Islands of Spain. French ancestry is also common because French people moved here from Haiti. This mix of cultures from Europe, Africa, and the Taíno people is very important to the region.
The term "Spanish Caribbean" helps us tell it apart from the Anglophone Caribbean (English-speaking), French Caribbean (French-speaking), and Dutch Caribbean (Dutch-speaking). The Hispanophone Caribbean is part of the larger Hispanic America. This includes all Spanish-speaking countries in the Americas. In the past, coastal areas like Spanish Florida and Caribbean South America were closely connected to the Spanish Caribbean. During the time Spain settled the New World, the Spanish West Indies meant the islands ruled by Spain. These territories were part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain until the early 1800s.
Today, the Colombian islands of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina can also be included. They are in the Caribbean but are not part of the Antilles island chain.
Islands of the Spanish West Indies
Below is a list of islands that were once under Spanish rule. These islands are part of the Greater Antilles and Lesser Antilles. Some islands that were Spanish are now ruled by France, England, or the Netherlands. These are no longer considered part of the Spanish Caribbean.
Also, the Colombian islands of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina are in the Caribbean. They were sometimes under Spanish rule. They were managed as part of the Spanish mainland territories.
| Political entity | Islands of the West Indies | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Isla de Cuba — Isla de la Juventud — Sabana-Camagüey Archipelago — Cayo Blanco del Sur — Cayo Levisa — Cayo Los Ensenachos — Cayo Largo del Sur — Jardines de la Reina — Cayo Guillermo — Cayo Coco — Cayo Romano — Cayo Guajaba — Cayo Sabinal — Cayo Santa María — Cayo Paredón Grande — Colorados Archipelago — Cayo Saetía — Cayo Blanco | Independent republic from Spain since 1898 | |
| Eastern Hispaniola — Saona — Beata — Catalina — Alto Velo — Cayo Levantado | Independent republic from Spain since 1821, independent from Haiti since 1844 | |
| Isla de Puerto Rico — Culebra — Vieques — Mona — Monito — Desecheo — Caja de Muertos — Isla de Cabras — Cayo Batata — Isla Cardona — Cayos de Caña Gorda — Culebrita — Icacos — Cayo Luis Peña — Isla Magueyes — Cayo Norte — Isla Palominos — Isla de Ratones — Isleta de San Juan — Cayo Santiago — Spanish Virgin Islands | Commonwealth of the United States, independent from Spain since 1898 | |
| Isla de Margarita — Coche — Cubagua (form the state of Nueva Esparta) Los Monjes — Las Aves — Los Roques (Gran Roque, Francisquí, Isla Larga, Nordisquí, Madrisquí, Crasquí, Cayo Espenquí, Cayo Carenero, Cayo de Agua, Dos Mosquises, Cayo Sal, Cayo Grande) — Los Hermanos — Los Frailes — Aves — La Sola — La Tortuga (Cayo Herradura — Islas Los Tortuguillos) — La Orchila — La Blanquilla — Los Testigos — Patos (ceded from British Trinidad in 1942, form the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela) | Independent republic from Spain since 1811, recognized by Spain in 1845 |
See Also
 In Spanish: Antillas españolas para niños
In Spanish: Antillas españolas para niños
- Antillean Confederation
- British West Indies
- Danish West Indies
- Dutch West Indies
- French West Indies
- New Spain
- Population history of American indigenous peoples
- Province of Tierra Firme
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
- Spanish East Indies
- Voyages of Christopher Columbus
- Culture of Cuba
- Culture of Dominican Republic
- Culture of Puerto Rico