Russia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Russian Federation
Российская Федерация (Russian)
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem:
Государственный гимн Российской Федерации Gosudarstvennyy gimn Rossiyskoy Federatsii "State Anthem of the Russian Federation" |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
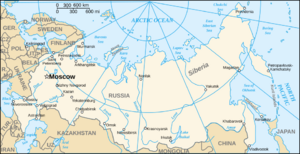
Moscow 55°45′21″N 37°37′02″E / 55.75583°N 37.61722°E |
| Official and national language | Russian |
| Recognised regional languages | 35 regional official languages |
| Ethnic groups
(2021; including Crimea)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Russian |
| Government | Federal semi-presidential republic |
| Vladimir Putin | |
| Mikhail Mishustin | |
| Legislature | Federal Assembly |
| Federation Council | |
| State Duma | |
| Formation | |
| 882 | |
| 1157 | |
|
• Principality of Moscow
|
1282 |
| 16 January 1547 | |
| 2 November 1721 | |
| 15 March 1917 | |
| 30 December 1922 | |
|
• Declaration of State
Sovereignty |
12 June 1990 |
|
• Russian Federation
|
12 December 1991 |
|
• Current constitution
|
12 December 1993 |
| 8 December 1999 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
17,098,246 km2 (6,601,670 sq mi)(within internationally recognised borders) |
|
• Water (%)
|
13 (including swamps) |
| Population | |
|
• 2025 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
8.4/km2 (21.8/sq mi) (187th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2020) | ▼ 36.0 medium |
| HDI (2023) | very high · 64th |
| Currency | Russian ruble (₽) (RUB) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 to +12 |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +7 |
| ISO 3166 code | RU |
| Internet TLD | |
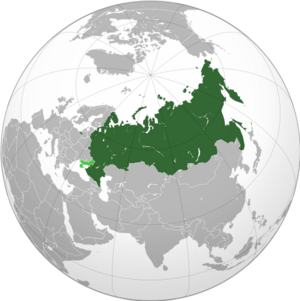
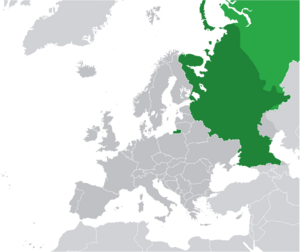
Russia, also known as the Russian Federation, is a large country that stretches across Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the biggest country in the world by area, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land. Russia crosses eleven time zones and shares borders with fourteen countries.
With over 140 million people, Russia is the most populated country in Europe and the ninth-most populated in the world. Many Russians live in cities. The capital and largest city is Moscow, which is also the biggest city in Europe. The second-largest city is Saint Petersburg, known as Russia's cultural center.
Russia has a long and rich history. Early Slavic people formed a state called Kievan Rus' in the 9th century. Over time, the Grand Duchy of Moscow grew stronger and united the Russian lands. This led to the Russian Empire, which became one of the largest empires in history. In the 20th century, Russia became the main part of the Soviet Union, a powerful country that competed with the United States during the Cold War. The Soviet Union was known for its achievements in science, including sending the first satellite and the first person into space.
After the Soviet Union broke apart in 1991, the country became the Russian Federation. Today, Russia is a major world power. It has one of the world's largest economies, thanks to its vast natural resources like oil and gas. Russia is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and is home to 32 UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
History
Early History and Kievan Rus'
People have lived in the area of modern Russia for a very long time. The ancestors of modern Russians were the East Slavs, who settled in the region over 1,500 years ago.
In the 9th century, a state called Kievan Rus' was formed. It became a large and successful state in Europe. In 988, its ruler, Vladimir the Great, adopted Orthodox Christianity, which became a very important part of Russian culture. After many years, Kievan Rus' broke up into smaller principalities.
In the 13th century, the Mongols invaded and ruled over the Russian lands for about 200 years. During this time, the city of Novgorod remained a center of trade and culture. Prince Alexander Nevsky of Novgorod became a hero for defending the land from invaders from the west.
Rise of Moscow

Over time, the Grand Principality of Moscow grew more powerful. In 1380, Prince Dmitry Donskoy of Moscow led a united Russian army to a major victory against the Mongol-Tatars at the Battle of Kulikovo.
Ivan III, also known as Ivan the Great, finally ended the Mongol-Tatar control. He united many Russian lands under Moscow's rule and called himself the "sovereign of all Russia."
Tsardom and Empire
In 1547, Ivan IV, also known as "Ivan the Terrible," was crowned the first Tsar (emperor) of Russia. During his rule, Russia grew much larger, expanding east into Siberia. After a period of trouble, the Romanov dynasty came to power in 1613 and ruled for over 300 years.
In the 18th century, Peter the Great turned Russia into a great European power. He founded the city of Saint Petersburg as the new capital and modernized the country. Later, Catherine the Great expanded the empire even more, making Russia the largest country in Europe.
During the Napoleonic Wars, Russia played a key role in defeating Napoleon. In 1812, Napoleon's army invaded Russia but was forced to retreat during the harsh Russian winter. This was a major turning point in European history.
In 1861, Tsar Alexander II made a very important change by freeing the serfs, who were farmers tied to the land. This helped Russia to start industrializing.
Revolution and the Soviet Union

In 1914, Russia entered World War I. The war was very difficult for the country and led to the Russian Revolution in 1917. Tsar Nicholas II was forced to give up his throne, and the monarchy ended.
A civil war followed, and the Bolshevik party, led by Vladimir Lenin, came to power. They created the world's first socialist state. In 1922, the Soviet Union (also called the USSR) was formed, with Russia as its largest and most important republic.
Under Joseph Stalin, the country industrialized very quickly. This was a difficult time for many people. During World War II, the Soviet Union fought against Nazi Germany on the Eastern Front. The war, known in Russia as the Great Patriotic War, caused immense destruction, but the Soviet Union emerged victorious and became a global superpower.
After the war, the Cold War began, a long period of competition between the Soviet Union and the United States. During this time, the Soviet Union achieved amazing things in science and technology. In 1957, it launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite. In 1961, cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first person to travel into space.
The Russian Federation
In the late 1980s, the Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced reforms to make the country more open. However, this led to big changes, and in 1991, the Soviet Union was dissolved. Russia became an independent country, the Russian Federation.
Boris Yeltsin became the first elected president of Russia. The 1990s were a challenging time as the country moved to a new economic system. In 1999, Yeltsin resigned, and Vladimir Putin became president.
Under Putin's leadership, the economy grew, and living standards improved. In recent years, Russia has been involved in conflicts with neighboring countries, including Georgia in 2008 and Ukraine since 2014.
Geography
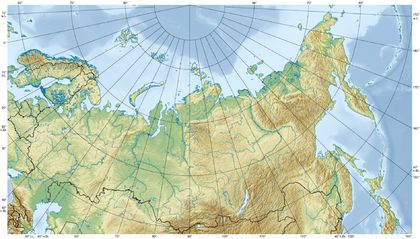
Russia is so big that it covers part of two continents: Europe and Asia. The Ural Mountains are often seen as the dividing line between the two. The country has a very long coastline, touching the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the east, and several seas in the west and south.
Most of Russia is made up of vast, flat plains. In the south, there are large mountain ranges like the Caucasus Mountains, where you can find Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in both Russia and Europe.
Siberia, the huge region in the east, is famous for its long, cold winters. It has some of the world's longest rivers, including the Ob, Yenisey, and Lena.
Russia is home to over 100,000 rivers and has a quarter of the world's liquid fresh water. Lake Baikal, the world's deepest and oldest freshwater lake, holds about one-fifth of the world's fresh surface water.
Climate
Because Russia is so large, its climate varies a lot. Most of the country has warm summers and very cold, snowy winters. The coldest inhabited places on Earth are in Siberia. In the south, near the Black Sea, the climate is much warmer, with mild winters.
Wildlife and Nature
Russia's diverse landscapes are home to a wide variety of plants and animals. The country has the world's largest forest area, known as the taiga. These forests are home to animals like brown bears, wolves, and moose.
In the far north, there is a cold, treeless region called the tundra, where polar bears and reindeer live. In the far east, you can find rare animals like the Siberian tiger and the Amur leopard. Russia has many national parks and nature reserves to protect its natural beauty and wildlife.
Government and Politics
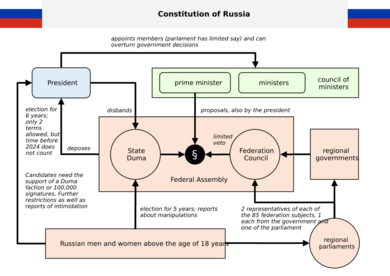
Russia is a federal republic with a semi-presidential system. This means it has both a president and a prime minister.
- The President is the head of state and is elected by the people for a six-year term. The president is the most powerful person in the government.
- The Prime Minister is the head of government and is in charge of the day-to-day running of the country.
The Russian parliament is called the Federal Assembly. It has two parts:
- The State Duma is the lower house, with 450 members who are elected by the people.
- The Federation Council is the upper house. Each region of Russia sends two representatives to it.
Russia is made up of many different regions, called federal subjects. These include republics, oblasts (provinces), and krais (territories). Each region has its own government but must follow federal laws.
Economy

Russia has a large, mixed economy. After the Soviet Union ended, the country moved from a planned economy to a market-based one. Today, the service industry is the largest part of the economy, followed by industry and agriculture.
The country is very rich in natural resources. It is one of the world's top producers of oil and natural gas, which are very important for its economy. Russia also has large amounts of coal, metals, and timber.
Russia's main trading partners include China and other European and Asian countries. The country has a skilled workforce and is known for its strong science and technology sectors.
Science and Technology
Russia has a long tradition of great achievements in science and technology.
- In chemistry, Dmitry Mendeleev created the Periodic table, which is used by scientists all over the world.
- Russian mathematicians like Nikolay Lobachevsky have made important discoveries.
- In physics, Russian scientists helped invent the laser.
Space Exploration

Russia is a world leader in space exploration. The Soviet space program achieved many "firsts":
- 1957: Launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit the Earth.
- 1961: Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space.
- 1963: Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space.
- 1965: Alexei Leonov performed the first spacewalk.
Today, Russia's space agency, Roscosmos, continues to play a key role in space exploration. It works with other countries on the International Space Station (ISS) and launches satellites and probes to explore the solar system.
Culture
Russian culture is famous around the world for its contributions to art, music, literature, and dance.
Art and Architecture

Russian architecture is known for its colorful onion domes, which can be seen on churches like Saint Basil's Cathedral in Moscow. The Moscow Kremlin and the beautiful palaces of Saint Petersburg are other famous examples.
Russian painting is famous for its religious icons and for the work of realist painters like Ilya Repin. In the 20th century, artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Marc Chagall became pioneers of modern art.
Music and Ballet
Russia has produced some of the world's greatest classical composers. Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky is famous for his symphonies and ballets like The Nutcracker and Swan Lake. Other famous composers include Sergei Rachmaninoff and Igor Stravinsky.
Russian ballet is considered among the best in the world. The Bolshoi Ballet in Moscow and the Mariinsky Ballet in Saint Petersburg are legendary.
Literature
Russian literature has had a huge impact on the world. The 19th century is known as the "Golden Age" of Russian literature.
- Alexander Pushkin is considered the father of modern Russian literature.
- Leo Tolstoy wrote epic novels like War and Peace and Anna Karenina.
- Fyodor Dostoevsky is known for deep, psychological novels like Crime and Punishment.
- Anton Chekhov was a master of short stories and plays.
Cuisine

Russian food is hearty and delicious, perfect for the country's long winters. Popular dishes include:
- Borsch: A beet soup often served with sour cream.
- Pelmeni: Dumplings filled with meat.
- Blini: Thin pancakes served with sweet or savory fillings.
- Beef Stroganoff: A dish of beef sautéed in a sour cream sauce.
A popular traditional drink is kvass, which is made from fermented rye bread.
Sports

Russians love sports. The most popular sports are football (soccer) and ice hockey. The Soviet national ice hockey team was one of the best in history.
Russia has also produced many world-class athletes in sports like rhythmic gymnastics, figure skating, and tennis. Chess is also very popular, and many world chess champions have come from Russia.
Russia has hosted major sporting events, including the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow and the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi. In 2018, it hosted the FIFA World Cup.