Ancient history facts for kids
Ancient history is the story of everything we know that happened between the invention of writing and the start of the Middle Ages. Writing was a huge step for humans! It was invented around 3,300 BC, which is over 5,000 years ago, in the Middle East. The first people to use writing were the Sumerians and the Ancient Egyptians.
Before writing, we only have tools and monuments left by early people. This time is studied by archaeology, not history. Ancient history ends when the Middle Ages begin.
During ancient times (starting around 3000 BC), the world's population grew a lot. This was because of the Neolithic Revolution, when people started farming and living in towns. In 10,000 BC, there were about 2 million people. By 3,000 BC, it was 45 million! By 500 AD, at the end of ancient history, there were an estimated 209 million people. That's a huge increase!
Contents
Studying Ancient History
Finding out facts about ancient history can be tricky. People wrote less back then, and much of what they did write has been lost. There were no printing presses, so every copy had to be made by hand.
More people could read and write in Ancient Rome than in other places, but even much of their writing is now gone. Historians also study objects that were made and used in ancient times to learn more.
Archaeology
Archaeology is the study of things people made or used in the past to understand that time. Things like clay pots, strong tools, and metal weapons can last a very long time. But things like paper, wood, and cloth break down easily or get damaged.
Some incredible ancient things found by archaeologists include:
- The Egyptian pyramids – These are huge tombs built by the Ancient Egyptians for their kings and queens.
- The city of Pompeii – This was a city in Ancient Rome. A volcano erupted and buried the city and its people under rock and ash. This kept everything preserved for a very long time.
- The Terracotta Army – This is an army of clay soldiers found in the tomb of the First Qin Emperor in Ancient China.
Primary Sources
Primary sources are writings made by people who lived in ancient times. They tell us most of what we know about ancient history. However, people in ancient times might have had different beliefs or even been wrong sometimes.
Some famous people who wrote in ancient history are: Herodotus, Josephus, Livy, Polybius, Suetonius, Tacitus, Thucydides and Sima Qian.
Timeline of Ancient History
Prehistory
- About 200,000 to 250,000 years ago – Our species, Homo sapiens, developed in Africa.
- Around 90,000 years ago – People began to move into the Middle East.
- Around 60,000 years ago – People from Africa traveled to Asia.
- Around 40,000 years ago – People reached Australia and Europe.
- Around 14,000 to 10,000 BC – People arrived in America.
- Around 10,000 BC – People started farming.
- 4th millennium BC – Cuneiform writing appeared in cities like Uruk and Susa. Hieroglyphs (picture writing) started in Egypt.
- 1000 BC – The earliest writing about history began.
- 450 BC – Herodotus wrote what many consider the first true history book. It's still available today!
Older Ancient History

- c. 3300 BC – The Bronze Age began in the Near East and South Asia. Bronze tools and weapons spread to Europe and the Middle East.
- c. 3000 BC – Egyptians created papyrus, a type of paper made from reeds.
- c. 2800 BC – The Indus Valley Civilization began to grow.
- 2580 BC – Egyptians built the Great Pyramid of Giza.
- 2000 BC – People started using horses.
- 1600 BC – The Shang Dynasty began in China, and Chinese writing developed.
- 1600 BC – The Hittites started to rule parts of the Middle East.
- 1500 BC – The Rigveda, an important collection of hymns, was created.
- 1200 BC – The Hebrew people settled in Israel.
- c. 1200 BC – The legendary Trojan War took place.
- c. 1100 BC – King Saul united the 12 tribes of Israel.
- c. 1180 BC – The Hittite Empire ended.
- 1122 BC – The Zhou Dynasty began in China.
- 1004 BC – King David captured Jebus, renamed it Jerusalem, and made it the capital of Israel.
1000 BC to 100 BC
- 928 BC – Israel split into two kingdoms: Judah and Israel.
- 800 BC – City-states developed in Ancient Greece.
- 776 BC – People started writing about the Olympic Games.
- c. 753 BC – The city of Rome was founded.
- 728 BC – The Median Empire grew powerful.
- 653 BC – The first Persian state began to form.
- c. 600 BC – The Pandyan kingdom emerged in South India.
- c. 563 BC – Gautama Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama) was born.
- 546 BC – Cyrus the Great founded the Persian Empire.
- 539 BC – The Babylonian Empire ended, and Cyrus the Great freed the Jews.
- 525 BC – Cambyses II of Persia conquered Egypt.
- c. 512 BC – Darius the Great expanded the Persian Empire, making it the most powerful.
- 509 BC – The last king of Rome was removed, and the Roman Republic began.
- 490 BC – Greek city-states defeated the Persian attack at the Battle of Marathon.
- 403 BC – The Warring States Period began in China.
- 331 BC – Alexander the Great defeated Darius III of Persia in the Battle of Gaugamela.
- 323 BC – Alexander the Great died.
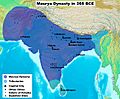
- 321 BC – Chandragupta Maurya founded the Maurya Empire in India.
- 273 BC – Ashoka the Great became emperor of the Mauryan Empire.
- 221 BC – Qin Shi Huang united China, ending the Warring States Period and starting the era of emperors in China.
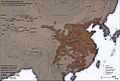
- 202 BC – The Han Dynasty began in China, and the Silk Road trade route was established.
- 202 BC – Scipio Africanus defeated Hannibal at the Battle of Zama.
- 146 BC – Rome conquered Greece.
100 BC to End of Roman Empire, 476 AD
- 49 BC – Julius Caesar and Pompey started the Roman Civil War.
- 44 BC – Marcus Junius Brutus and others assassinated Julius Caesar. The Roman Republic ended, and the Roman Empire began.
- 6 BC – Jesus of Nazareth was born.
- 14 AD – Emperor Augustus died, and Tiberius became emperor.
- 117 AD – Trajan was emperor of Rome. The Roman Empire was at its largest and most powerful.
- 220 AD – The Han Dynasty ended in China.
- 226 AD – The Parthian Empire ended, and the Sassanian Empire became powerful.
- 285 AD – Emperor Diocletian divided the Roman Empire into Eastern and Western parts.
- 313 AD – The Edict of Milan declared that the Roman Empire would allow people to worship freely.
- 378 AD – At the Battle of Adrianople, Germanic tribes defeated the Roman army.
- 395 AD – Roman Emperor Theodosius I made Christianity the official religion.
- 410 AD – Alaric and the Visigoths sacked Rome. This was the first time Rome had been defeated since 390 BC.
- 476 AD – Romulus Augustulus was removed as emperor of Rome, marking the end of the Western Roman Empire.
Some Groups of People in Ancient History
Europe and the Mediterranean
Mesopotamia
- Ancient Persia (including the Achaemenid Empire, Sassanid Empire, Seleucid Empire)
- Akkad
- Assyria
- Babylonia
- Elam
- Hittites
- Kassites
- Medes
- Mitanni
- Sumer
Central and Southwest Asia
Saharan and Sub-Saharan Africa
East Asia
- Ancient Turks
- Huns
America
End of the Period
The time period called Late antiquity is the bridge between Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages. It generally runs from the late 200s AD to the 600s AD.
The Middle Ages (also known as the post-classical age in Europe) began after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, roughly from 500 AD to 1500 AD.
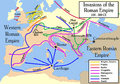
The Western Roman Empire in Europe, the Gupta Empire in India, and the Jin dynasty in North China were all taken over by invading tribes. These nomadic invasions, along with global climate change, the Plague of Justinian, and the rise of major religions, changed the world.
By 500 AD, the world had entered the Post-classical history era. Even though they are in different historical periods, the Ancient and Post-Classical eras are connected in the Old World. Trade routes often followed similar paths. Many inventions and religions that started before 500 AD, like Christianity, Judaism, Hinduism, and Buddhism, became even more important for people and societies.
Images for kids
-
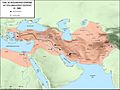
The Persian Achaemenid Empire at its largest, around 500 BC.
-
The biggest size of the Kingdom of Armenia under Tigranes the Great.
-
Khafre's Pyramid (4th dynasty) and the Great Sphinx of Giza (around 2500 BC or earlier).
-
Pharaohs of Nubia.
-
A map of the Maurya Empire, showing important cities like the capital Pataliputra, and where the Buddha found enlightenment.
-
Oracle bone script from the Shang Dynasty.
-
Terracotta Warriors from the time of Qin Shi Huang.
-
The Chinese Han dynasty was very powerful in East Asia at the start of the first millennium AD.
-
Gold stag with an eagle's head and ten more heads in its antlers. Inspired by Siberian Altai mountain art, possibly Pazyryk, found at Nalinggaotu, Shenmu County, near Xi'an, China. Possibly from Huns of the Northern Chinese prairie. 4th to 3rd centuries BC, or Han Dynasty period. Shaanxi History Museum.
-
The ruins of the Mesoamerican city Teotihuacan.
-
The Age of Migrations in Europe was very damaging to the late Roman Empire.
-
Roman cast terracotta of ram-horned Jupiter Ammon, a form of Zeus, 1st century AD. Gods were sometimes shared between civilizations and changed to fit local ideas.
See also
 In Spanish: Edad Antigua para niños
In Spanish: Edad Antigua para niños