Camden, New Jersey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Camden, New Jersey
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
City
|
|||
|
Campbell Soup Company headquarters
Rutgers University–Camden
|
|||
|
|||
| Motto(s):
In a Dream, I Saw a City Invincible
|
|||
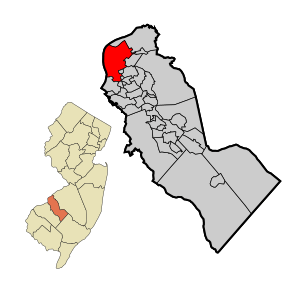
Location of Camden in Camden County highlighted in red (right). Inset map: Location of Camden County in New Jersey highlighted in orange (left).
|
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| County | Camden | ||
| Settled | 1626 | ||
| Incorporated | February 13, 1828 | ||
| Named for | Charles Pratt, 1st Earl Camden | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Faulkner Act (mayor–council) | ||
| • Body | City Council | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 10.34 sq mi (26.78 km2) | ||
| • Land | 8.92 sq mi (23.10 km2) | ||
| • Water | 1.42 sq mi (3.68 km2) 13.75% | ||
| Area rank | 208th of 565 in state 7th of 37 in county |
||
| Elevation | 16 ft (5 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 71,791 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
71,100 | ||
| • Rank | 532nd in country (as of 2023) 14th of 565 in state 2nd of 37 in county |
||
| • Density | 8,047.4/sq mi (3,107.1/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 50th of 565 in state 2nd of 37 in county |
||
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) | ||
| ZIP Codes |
08101–08105
|
||
| Area code(s) | 856 | ||
| FIPS code | 3400710000 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 0885177 | ||
Camden is a city in Camden County, New Jersey. It is part of the Delaware Valley area. The city was officially formed on February 13, 1828. Camden has been the main city, or county seat, of Camden County since 1844. The city is named after Charles Pratt, 1st Earl Camden. Camden has more than 20 neighborhoods and is part of the South Jersey region.
Camden grew a lot because of three big companies: RCA Victor, Campbell's Soup Company, and New York Shipbuilding Corporation. These companies later moved away from Camden. Even though the city faced challenges when industries left, it has worked hard to improve itself. Many projects have helped make the city better.
The waterfront area has been redeveloped. It now has three fun places to visit: the USS New Jersey, the Freedom Mortgage Pavilion, and the Adventure Aquarium. Camden is also home to Rutgers University–Camden, which started in 1926. Cooper Medical School of Rowan University opened in 2012. The city also has Cooper University Hospital and Virtua Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital. Camden County College and Rowan University have campuses downtown. These schools and hospitals provide about 45% of all jobs in Camden.
Camden was once known for high crime rates. However, the police force was reorganized in 2013. This change has helped reduce crime significantly. By January 2021, violent crime was down 46% from its highest point in the 1990s. It was at its lowest level since the 1960s. Overall crime reports in 2020 were down 74% compared to 1974.
Contents
History of Camden
Early Settlements and European Arrival
The area where Camden is located was first home to the Lenape people. They lived here for thousands of years before Europeans arrived. Between 1623 and 1627, a Dutch officer named Captain Cornelius Jacobsen May built Fort Nassau. This fort was near where the Delaware River meets Big Timber Creek. The fort was used for fur trading.
Later, in 1664, the British took control of the area. King Charles II of England gave the land to Lord John Berkeley and Sir George Carteret. They named the new colony Province of New Jersey. In 1674, Lord John Berkeley sold his part to two Quakers, John Fenwick and Edward Byllynge.
William Penn, another Quaker, helped manage the land for Byllynge's creditors. Quakers were looking for a place where they could practice their religion freely. In 1676, New Jersey was split into East Jersey and West Jersey. Quakers settled in West Jersey, including the Camden area, seeking religious freedom and fair government.
Colonial Times and the American Revolution
As more Quakers settled, the Lenape population declined. A ferry system on the Delaware River helped trade between Fort Nassau and Philadelphia. Families like the Coopers and Kaighns started settlements. In 1773, Jacob Cooper helped develop the area now known as Camden. It was named after Charles Pratt, the Earl of Camden.
During the Revolutionary War, Camden was held by the British. This slowed down the village's growth.
Becoming a City and Early Growth
In the 1800s, Camden changed from a transportation stop to a growing city. Camden officially became a city on February 13, 1828. It was formed from parts of Newton Township.
In 1830, the Camden and Amboy Railroad Company was started. This railroad connected New York City to Philadelphia by rail and ferry. Passengers would take the train to Camden's Waterfront, then a ferry across the Delaware River to Philadelphia. The railroad, which opened in 1834, helped Camden's population and businesses grow a lot.
Industrial Boom and Changes
At the start of the 1900s, industries in Camden grew quickly. Companies like the Victor Talking Machine Company (later RCA Victor), New York Shipbuilding Corporation, and Campbell Soup Company were major employers. They hired thousands of people. Camden's location on the Delaware River was perfect for building ships.
Camden's population also changed. By 1920, immigrants from Eastern Europe became the largest ethnic group. Before that, most immigrants were German, British, and Irish. In 1926, the Benjamin Franklin Bridge opened. This bridge connected New Jersey and Pennsylvania. It cost $37 million, shared equally by both states. The bridge helped reduce ferry traffic between Philadelphia and Camden.
During the 1930s, Camden faced economic challenges due to the Great Depression. But its strong industries helped it avoid bankruptcy. During World War II, the New York Shipbuilding Company became the largest shipyard in the world. Many African Americans moved to Camden from the South to work in factories for the war effort. This led to neighborhoods becoming separated by ethnicity and religion. In 1951, the Delaware River Port Authority was created to help trade and transportation between Camden and Philadelphia.
Industrial Decline and Challenges
By the 1950s, manufacturing slowed down. Industries moved away, and many jobs were lost. From 1950 to 1982, the number of manufacturing jobs dropped by 75%. Campbell's Soup Company and RCA Victor moved some of their production out of Camden. The New York Shipbuilding Company closed in 1967.
During this time, many white residents moved to the suburbs for better job opportunities. This is sometimes called "white flight." The building of the North-South Freeway also divided neighborhoods. About 1,289 families, mostly non-white, had to move because of the highway. The city also faced challenges with crime.
Efforts to Revitalize Camden
Efforts to improve Camden began in 1980 with Mayor Randy Primas. He tried to bring in money by building a state prison and a trash incinerator, but residents opposed these ideas. When Milton Milan became mayor, he declared the city bankrupt. This led to $60 million in aid and the state taking over Camden's finances. A non-profit group called The Parkside Business and Community In Partnership was formed in 1993 to help the city.
Redevelopment Projects
The idea of redeveloping Camden has been around since the 1980s. In 2013, the New Jersey Economic Development Authority offered special benefits to companies that moved to Camden. Other projects include improving the Waterfront, building the Philadelphia 76ers Training Complex, and the headquarters for Subaru of America.
Camden Today: Focus on Education and Healthcare
In recent years, Camden has shifted from manufacturing to an economy focused on education and healthcare. The "Eds-and-Meds Industry" is now the biggest source of jobs. This includes places like Cooper University Hospital, Rowan University, Rutgers-Camden, Camden County College, Virtua, Our Lady of Lourdes Medical Center, and CAMcare.
Culture and Community

Camden's history as an industrial city created unique neighborhoods and cultural groups. These groups have shaped the city over time. Camden has historic places that show its rich history in literature, music, and social work. These include the Walt Whitman House, the Walt Whitman Cultural Arts Center, and the Camden Children's Garden. The Camden County Historical Society also documents the city's past.
When industries declined from 1950 to 1970, many jobs were lost. This caused many residents, mostly white, to move away. New African American and Latino citizens moved in and helped reshape Camden's communities. Many non-profit groups like Hopeworks and the Neighborhood Center were formed to help Camden move forward.
Community Groups
The Black Community has been a key part of Camden since 1828. They have greatly contributed to the city's culture. Corinne's Place is a Black-owned soul food restaurant that opened in 1989. The Hispanic and Latino Community has also grown a lot in the last twenty years. They have a long history in Camden. Puerto Rican Unity for Progress is a group that helps the Hispanic community in Camden. It was started in 1976.
Arts and Entertainment
Arts and entertainment have always been important in Camden. In the early 1900s, Camden was a center for music and new ideas in entertainment. This was thanks to the Victor Talking Machine Company (later RCA Victor). Famous people like singer Russ Columbo and Broadway actress Lola Falana were born here. Today, many artists and groups help support the arts in Camden.
Religion in Camden
Camden has many religious places, including churches and their community centers. Examples are Little Rock Baptist Church, First Nazarene Baptist Church, and Kaighn Avenue Baptist Church. Other active groups include Newton Monthly Meeting of the Religious Society of Friends and the Masjid.
The first Scientology church was started in Camden in December 1953.
Father Michael Doyle, the pastor of Sacred Heart Catholic Church, has been very important in Camden's spiritual and social history. In 1971, Doyle was part of the Camden 28. This group of anti-Vietnam War activists planned to raid a draft board office. Father Doyle became known for his poetry and activism. He and Sacred Heart Church work to connect people from the surrounding suburbs with the city of Camden.
In 1982, Father Mark Aita started St. Luke's Catholic Medical Services. Aita, who was also a medical doctor, created the first medical system in Camden that did not use rotating doctors. St. Luke's now offers patient education and home medical services. It helps over seven thousand Camden residents.
Helping the Community (Philanthropy)
Camden has a long history of charity. The city's founding families were Quakers. They were interested in helping orphans and runaway slaves. In 1865, the Society of Friends founded the Camden Home for Friendless Children. They also opened the West Jersey Colored Orphanage in 1874.
Camden has many non-profit groups that help residents with health and social services. These services are often free or low-cost. Camden has one of the highest rates of poverty in New Jersey. In 2000, Camden's income per person was $9,815. This made it the poorest city in New Jersey and one of the poorest in the United States. Camden also has one of the highest rates of childhood poverty.
Economy and Jobs

About 45% of jobs in Camden are in the "eds and meds" sector. This means they are in educational and medical institutions.
In 2018, the average property tax bill in Camden was $1,710. This was the lowest in Camden County. The average bill in the county was $6,644, and statewide it was $8,767.
Major Employers
Some of the largest employers in Camden include:
- Campbell Soup Company
- Cooper University Hospital
- Delaware River Port Authority
- L3Harris Technologies
- Our Lady of Lourdes Medical Center
- Rutgers University–Camden
- State of New Jersey (including the New Jersey Judiciary)
- Subaru of America (moved from Cherry Hill in 2018)
- UrbanPromise Ministry (the largest private employer of teenagers)
Urban Enterprise Zone
Parts of Camden are in an Urban Enterprise Zone. This program offers benefits to encourage businesses to create jobs in the area. Shoppers can also pay a reduced sales tax rate of 3.3125% (half of the state's 6.625% rate) at eligible stores. Camden was one of the first cities chosen for this program in 1983. Its status is set to expire in December 2023.
The program had stopped in 2017 but was brought back in May 2018.
Geography and Neighborhoods
Camden covers about 10.34 square miles (26.78 km²). This includes 8.92 square miles (23.10 km²) of land and 1.42 square miles (3.68 km²) of water.
Camden shares borders with several towns in Camden County. These include Collingswood, Gloucester City, Oaklyn, Pennsauken Township, and Woodlynne. It also borders Philadelphia across the Delaware River in Pennsylvania. Pettys Island is just offshore of Camden. The Cooper River flows through Camden. Newton Creek forms the southern border with Gloucester City.
Neighborhoods of Camden
Camden has more than 20 recognized neighborhoods. Some of these are:
- Ablett Village
- Bergen Square
- Beideman
- Broadway
- Centerville
- Center City/Downtown Camden
- Central Waterfront
- Cooper
- Cooper Grant
- Cooper Point
- Cramer Hill
- Dudley
- East Camden
- Fairview
- Gateway
- Kaighn Point
- Lanning Square
- Liberty Park
- Marlton
- Morgan Village
- North Camden
- Parkside
- Pavonia
- Pyne Point
- Rosedale
- South Camden/Waterfront South
- Stockton
- Walt Whitman Park
- Yorkship
The Waterfront Area
The Waterfront has always been a key part of Camden. It was home to the New York Shipbuilding Company Shipyards until 1968. Since the 1990s, the Waterfront has been a symbol of the city's renewal. Its three main attractions are the USS New Jersey, the Freedom Mortgage Pavilion, and the Adventure Aquarium. The Waterfront also hosts the headquarters for Catapult Learning, the Philadelphia 76ers Training Complex, and American Water.
Other attractions at the Waterfront include Wiggins Park Riverstage and Marina, The Victor Lofts, the Walt Whitman House, the Walt Whitman Cultural Arts Center, the Rutgers–Camden Center for the Arts, the Camden Children's Garden, and Cooper's Poynt Park.
Port of Camden
The Port of Camden is on the Delaware River, with access to the Atlantic Ocean. It handles different types of cargo, like large items and some containers. The port receives hundreds of ships each year. It is one of the largest shipping centers in the USA for wood products, cocoa, and perishable goods.
Housing in Camden
The most common type of home in Camden is a rowhouse. These are similar to homes in Philadelphia. Saint Josephs Carpenter Society (SJCS) is a non-profit group that has fixed up 500 homes in the city.
Camden is home to the first federally funded planned community for working-class residents in the United States. It was called Yorkship Village (now Fairview). It was designed by Electus Darwin Litchfield. He was inspired by the "garden city" ideas popular in England.
In 2013, a company called Cherokee Investment Partners planned to build 5,000 new homes and a shopping center in North Camden. However, they stopped their plans due to local opposition and a slow real estate market.
Climate
Camden has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has hot summers and cool to cold winters.
| Climate data for Camden, New Jersey | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 41 (5) |
45 (7) |
54 (12) |
65 (18) |
74 (23) |
82 (28) |
87 (31) |
85 (29) |
78 (26) |
67 (19) |
57 (14) |
46 (8) |
65 (18) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 24 (−4) |
26 (−3) |
33 (1) |
42 (6) |
52 (11) |
61 (16) |
67 (19) |
65 (18) |
58 (14) |
46 (8) |
38 (3) |
29 (−2) |
45 (7) |
| Source: Weather.com | |||||||||||||
Education in Camden
Public Schools
Camden's public schools are run by the Camden City School District. This district is one of 31 in New Jersey where the state helps cover costs for school building and renovation projects. As of the 2020–21 school year, the district had 19 schools and 7,553 students. There were 668 teachers, meaning about 11 students per teacher.
High schools in the district include:
- Brimm Medical Arts High School (grades 9–12)
- Camden Big Picture Learning Academy (grades 6–12)
- Camden High School (grades 9–12)
- Creative Arts Academy (grades 6–12)
- Eastside High School (grades 9–12)
- Pride Academy (grades 6–12)
Charter and Renaissance Schools
In 2012, the Urban Hope Act allowed "renaissance schools" to open in Camden. These schools are run by charter companies. They enroll students based on their neighborhood, like public schools. This makes them a mix of charter and public schools. This act allowed Knowledge Is Power Program (KIPP), Uncommon Schools, and Mastery Schools to open in Camden.
Some public schools became part of these charter networks. For example, Henry L. Bonsall Family School became Uncommon Schools Camden Prep Mt. Ephraim Campus. Students could choose to stay or go to other schools.
In the 2013–14 school year, Camden city planned to give $72 million to charter schools. By 2019, about 3,850 Camden students were in renaissance schools. Another 4,350 students were in charter schools. Together, these students made up about 55% of all students in Camden.
Charter Schools
- Camden's Promise Charter School
- Environment Community Opportunity (ECO) Charter School
- Freedom Prep Charter School
- Hope Community Charter School
- LEAP Academy University Charter School
Renaissance Schools
- Uncommon Schools Camden Prep
- KIPP Cooper Norcross
- Lanning Square Primary School
- Lanning Square Middle School
- Whittier Middle School
- Mastery Schools of Camden
- Cramer Hill Elementary
- Molina Lower Elementary
- Molina Upper Elementary
- East Camden Middle
- Mastery High School of Camden
- McGraw Elementary
Private Education
Holy Name School, Sacred Heart Grade School, and St. Joseph Pro-Cathedral School are K–8 elementary schools. They are part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Camden. They are also part of the Catholic Partnership Schools, which is a new way of organizing urban Catholic education.
Higher Education (Colleges and Universities)

The University District, near downtown, is home to several colleges and universities:
- Camden County College – one of its three main campuses. It first came to Camden in 1969.
- Rowan University at Camden – a satellite campus. It started with a teacher program in 1969.
- Cooper Medical School of Rowan University (opened in 2012)
- Rutgers University–Camden – one of the three main Rutgers campuses. It started as South Jersey Law School in the 1920s.
- Camden College of Arts & Sciences
- School of Business – Camden
- Rutgers School of Law-Camden
- University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey (UMDNJ) – affiliated with Cooper University Hospital
- Coriell Institute for Medical Research – affiliated with Cooper University Hospital and Rowan University
Libraries
Camden once had two Carnegie libraries. These were the Main Building and the Cooper Library in Johnson Park. The city's library system faced financial problems and almost closed in 2010. It was then taken over by the county system. The main branch closed in February 2011. It later reopened in the Paul Robeson Library at Rutgers University.
Camden also has three academic libraries. The Paul Robeson Library at Rutgers University-Camden serves students from Rutgers, Camden County College, and Rowan University. Rutgers Law School has a law library, and Cooper Medical School has a medical library.
Sports and Recreation
Camden Athletic Complex
The Camden Athletic Complex was finished in 2022. It was built on the former site of Campbell's Field. This complex has a baseball field, a track and field area, a soccer field, and a lacrosse field. The Camden Riversharks were a professional baseball team that used to play at Campbell's Field. Rutgers University and the city of Camden invested $15 million to develop this area. It is used for city recreation and for the university's sports teams.
Philadelphia 76ers Training Facility

The Philadelphia 76ers basketball team built a training facility on the Camden Waterfront. The New Jersey Economic Development Authority approved an $82 million grant for its construction. The facility was completed in 2016. It includes two full-size basketball courts, a weight room, a hydrotherapy room, a restaurant for players, medical facilities, and a film room.
Government and Services
Since July 1, 1961, Camden has used a Mayor-Council form of government. The city is divided into four council districts. One council member is elected from each district. Three other council members are elected from the city as a whole.
As of 2024, the Mayor of Camden is Victor Carstarphen. His term ends on December 31, 2025.

Camden has faced challenges with political corruption in its history. Three Camden mayors have been jailed for corruption: Angelo Errichetti, Arnold Webster, and Milton Milan.
Federal, State, and County Representation
Camden is in New Jersey's 1st Congressional District. It is also part of New Jersey's 5th state legislative district.
Politics in Camden
Camden has historically supported the Democratic Party. As of November 6, 2018, there were 42,264 registered voters in Camden. Most of them were registered as Democrats. All Camden mayors since 1935 have been Democrats.
In 2015, President Obama visited Camden. He said the city was "a symbol of promise for the nation." In the 2012 presidential election, Camden strongly voted for Barack Obama. In the 2016 presidential election, Hillary Clinton also received strong support from the city.
Camden Fire Department (CFD)
The Camden Fire Department (CFD) was officially started in 1869. It is the oldest paid fire department in New Jersey. The CFD operates from five fire stations. It has five engine companies, one squad, three ladder companies, and one rescue company. The department also has a fireboat on the Delaware River. Since 2010, the Fire Department has faced budget cuts.
Camden County Police Department (CCPD)
On May 1, 2013, the original Camden Police Department was disbanded. This was due to financial reasons. The Camden County Police Department was then formed to replace it. The new police force added 25 new officers. They trained in neighborhoods to build trust with local communities. The reorganized force has increased the number of police officers on the streets. They patrol and talk with residents. A CNN report suggested that Camden's police changes could be a model for other cities.
Transportation in Camden
Public Transportation Options

The Walter Rand Transportation Center opened in 1989. It was later named after former New Jersey State Senator Walter Rand in 1994. This center is a bus station located at Martin Luther King Boulevard and Broadway. It is open seven days a week. Most buses that stop here are NJ Transit buses. They provide affordable transportation to Philadelphia and nearby cities in Camden and Burlington Counties. The center also has Greyhound Lines buses for longer trips across the country.
The Walter Rand Transportation Center is also home to two train stations: the Walter Rand River Line station and PATCO, Broadway station. These stations make it easy to connect to the buses from the surrounding area.
Since March 14, 2004, NJ Transit's River Line has offered light rail service. It connects cities along the Delaware River, from North Camden to Trenton. There are four stations in Camden. The southernmost station is at Freedom Mortgage Pavilion. Other stops are at the Camden Adventure Aquarium, Rutgers University, and the Walter Rand Transportation Center. The River Line runs until 10 PM. Fares are $1.70. The River Line was the first railroad to use diesel LRV vehicles. These vehicles are cheaper to run and easier to stop frequently.
The PATCO Speedline offers frequent train service to Philadelphia and suburbs in Camden County. These suburbs include Collingswood, Haddon Township, Haddonfield, Cherry Hill, Voorhees, and Lindenwold. The PATCO Speedline runs 24 hours a day. It opened in 1926. It originally had six stops in Philadelphia and two in Camden: City Hall and Broadway station. In 1951, Pennsylvania and New Jersey agreed to expand the railroad. This included stations between Camden and Lindenwold. The PATCO uses automated fare collection. Some stations outside the cities offer free daytime parking.
The RiverLink Ferry opened in March 1992. It is a passenger ferry service that crosses the Delaware River. It connects the Camden Water Front with Philadelphia's Penn's Landing. The ferry runs daily from May through September. It also runs on Fridays through Sundays in April and October. The ferry docks at Wiggins Park in Camden. This provides access to the Adventure Aquarium, Battleship New Jersey, Camden's Children's Garden, and the Freedom Mortgage Pavilion. On the Philadelphia side, it docks at the Independence Seaport Museum. This gives access to many attractions at Penn's Landing and historic Center City Philadelphia. Round trip tickets cost $8 for children and seniors, and $10 for adults. Children under four ride free.
The RiverLink Ferry was not the first ferry in Camden. Before the Ben Franklin Bridge was built, many ferries operated from Camden's waterfront. These ferries transported goods and people across the Delaware River.
Roads and Highways

As of 2015, Camden had about 181.92 miles of roads. The city maintained 147.54 miles. Camden County maintained 25.39 miles. The New Jersey Department of Transportation maintained 6.60 miles. The Delaware River Port Authority maintained 2.39 miles.
Interstate 676 and U.S. Route 30 run through Camden to the Benjamin Franklin Bridge. Interstate 76 also passes through briefly and connects with Interstate 676.
Route 168 passes through the south of the city. Several County Routes also travel through the center of Camden. These include 537, 543, 551, and 561.
Environmental Concerns
Camden has faced environmental problems due to its history of heavy industry. These issues include air and water pollution, and soil contamination. There are several Superfund sites in the city. In recent years, illegal dumping has become a problem. This is due to many empty lots and a lack of security.
Population and Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 3,371 | — | |
| 1850 | 9,479 | 181.2% | |
| 1860 | 14,358 | 51.5% | |
| 1870 | 20,045 | 39.6% | |
| 1880 | 41,659 | 107.8% | |
| 1890 | 58,313 | 40.0% | |
| 1900 | 75,935 | 30.2% | |
| 1910 | 94,538 | 24.5% | |
| 1920 | 116,309 | 23.0% | |
| 1930 | 118,700 | 2.1% | |
| 1940 | 117,536 | −1.0% | |
| 1950 | 124,555 | 6.0% | |
| 1960 | 117,159 | −5.9% | |
| 1970 | 102,551 | −12.5% | |
| 1980 | 84,910 | −17.2% | |
| 1990 | 87,492 | 3.0% | |
| 2000 | 79,904 | −8.7% | |
| 2010 | 77,344 | −3.2% | |
| 2020 | 71,791 | −7.2% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 71,100 | −8.1% | |
| Population sources: 1840–2000 1840–1920 1840 1850–1870 1850 1870 1880–1890 1890–1910 1840–1930 1940–2000 2000 2010 2020 |
|||
Population Changes (2020 Census)
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 1990 | Pop 2000 | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 1990 | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 12,582 | 5,671 | 3,792 | 2,922 | 14.38% | 7.10% | 4.90% | 4.07% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 46,151 | 39,753 | 34,277 | 27,800 | 52.75% | 49.75% | 44.32% | 38.72% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 265 | 188 | 235 | 126 | 0.30% | 0.24% | 0.30% | 0.18% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 1,008 | 1,869 | 1,599 | 1,229 | 1.15% | 2.34% | 2.07% | 1.71% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | N/A | 20 | 15 | 11 | N/A | 0.03% | 0.02% | 0.02% |
| Other race alone (NH) | 213 | 129 | 109 | 315 | 0.24% | 0.16% | 0.14% | 0.44% |
| Mixed race or Multiracial (NH) | N/A | 1,255 | 938 | 1,476 | N/A | 1.57% | 1.21% | 2.06% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 27,273 | 31,019 | 36,379 | 37,912 | 31.17% | 38.82% | 47.04% | 52.81% |
| Total | 87,492 | 79,904 | 77,344 | 71,791 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 52.81% |
In the 2020 United States census, Camden had a population of 71,791. This was a decrease of 5,553 people from the 2010 census. The Census Bureau estimated the population to be 71,100 in 2023.
Population Details (2010 Census)
| Demographic profile | 1950 | 1970 | 1990 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 85.9% | 59.8% | 19.0% | 17.6% |
| —Non-Hispanic | N/A | 52.9% | 14.4% | 4.9% |
| Black or African American | 14.0% | 39.1% | 56.4% | 48.1% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | N/A | 7.6% | 31.2% | 47.0% |
| Asian | — | 0.2% | 1.3% | 2.1% |
The 2010 United States census counted 77,344 people in Camden. The population density was about 8,670 people per square mile. The racial makeup was 17.59% White, 48.07% Black or African American, and 27.57% from other races. People of Hispanic or Latino background made up 47.04% of the population. Camden is mostly populated by African Americans and Puerto Ricans.
In 2010, 31.0% of the population was under 18 years old. The median age was 28.5 years. The average household had 3.02 people.
The American Community Survey from 2006–2010 showed that the average household income was $27,027. About 36.1% of the population lived below the poverty line. This included 50.3% of those under 18.
In 2006, 52% of Camden's residents lived in poverty. This was one of the highest rates in the nation. The city's average household income was $18,007. This was the lowest among U.S. cities with more than 65,000 residents. A TV show called 20/20 featured Camden's poverty in 2007.
In 2011, Camden's unemployment rate was 19.6%. This was higher than the 10.6% rate for Camden County.
Places to Visit
- Corinne's Place is a Black-owned soul food restaurant. It is located on Haddon Avenue. Corinne Bradley-Powers opened it in 1989.
- Adventure Aquarium – This aquarium opened in 1992 and was updated in 2005. It has about 8,000 animals. It is the only aquarium in the world with hippopotamuses.
- Waterfront Music Pavilion – This is an outdoor and indoor music venue. It can hold 25,000 people.
- Battleship New Jersey Museum and Memorial – Opened in 2001. Visitors can explore the battleship USS New Jersey.
- Harleigh Cemetery – Started in 1885. It is the burial place of poet Walt Whitman and other important people.
- Walt Whitman House
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Camden County, New Jersey
Notable People from Camden
Actors and Actresses
- Christine Andreas (born 1951), Broadway actress and singer
- Joanna Cassidy (born 1944), actress
- Khris Davis (born 1987), actor
- Lola Falana (born 1942), singer and dancer
- Tasha Smith (born 1969), actress, director, and producer
Artists and Architects
- Vernon Howe Bailey (1874–1953), artist
- Alex Da Corte (born 1980), visual artist
- Mickalene Thomas (born 1970), artist
Athletes
- Jordan Burroughs (born 1988), Olympic champion in freestyle wrestling (won Gold in 2012)
- Sean Chandler (born 1996), safety for the New York Giants
- Donovin Darius (born 1975), professional football player for Jacksonville Jaguars
- Rachel Dawson (born 1985), field hockey midfielder
- Rawly Eastwick (born 1950), Major League Baseball pitcher
- Shaun T. Fitness (born 1978), motivational speaker and fitness trainer
- Haason Reddick (born 1994), linebacker for the Philadelphia Eagles
- Mike Rozier (born 1961), collegiate and professional football running back (won Heisman Trophy in 1983)
- Art Still (born 1955), professional football defensive end
- Devon Still (born 1989), professional football defensive end
- Sheena Tosta (born 1982), hurdler, Olympic silver medalist in 2008
- Dajuan Wagner (born 1983), professional basketball player
- Jersey Joe Walcott (1914–1994), boxing world heavyweight champion
Authors and Writers
- Betty Cavanna (1909–2001), author of teen romance novels and children's books
- Mary Chalmers (born 1927), author and illustrator of children's books
- Andrew Clements (1949–2019), writer of children's books, known for Frindle
- Walt Whitman (1819–1892), famous essayist, journalist, and poet
Musicians
- Graham Alexander (born 1989), singer-songwriter
- Cindy Birdsong (born 1939), vocalist for The Supremes
- Russ Columbo (1908–1934), baritone, songwriter, and actor
- Buddy DeFranco (1923–2014), jazz clarinetist
- Lola Falana (born 1942), singer and dancer
- Leon Huff (born 1942), songwriter and record producer
- Richard Sterban (born 1943), bass singer for the Oak Ridge Boys
- Tye Tribbett (born 1976), gospel music singer
- Crystal Waters (born 1967), house and dance music singer
Politicians and Public Officials
- Rob Andrews (born 1957), U.S. Representative (1990–2014)
- William T. Cahill (1912–1996), former Governor of New Jersey (1971–1975)
- Bonnie Watson Coleman (born 1945), U.S. Representative since 2015
- Donald Norcross (born 1958), U.S. Congressman
Other Notable People
- Richard Hollingshead (1900–1975), inventor of the drive-in theater
- Aaron McCargo Jr. (born 1971), chef and TV personality
- Dorcas Reilly (1926–2018), chef, known for popularizing the green bean casserole
- Phil Zimmermann (born 1954), programmer who developed Pretty Good Privacy (data encryption)
See also
 In Spanish: Camden (Nueva Jersey) para niños
In Spanish: Camden (Nueva Jersey) para niños
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |