Concord, New Hampshire facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Concord, New Hampshire
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Main Street in Downtown Concord
View from Eagle Square
New Hampshire State Library
City Hall
St. Paul's School chapel
|
|||||
|
|||||
Location in Merrimack County, New Hampshire
|
|||||
| Country | United States | ||||
| State | New Hampshire | ||||
| County | Merrimack | ||||
| Region | New England | ||||
| Settled | 1659 | ||||
| Incorporated | 1733 | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | Mayor–council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total | 67.19 sq mi (174.02 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 63.96 sq mi (165.66 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 3.23 sq mi (8.36 km2) | ||||
| Elevation | 272 ft (83 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • Total | 43,976 | ||||
| • Density | 687.52/sq mi (265.46/km2) | ||||
| • μSA | 155,238 | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (Eastern) | ||||
| ZIP Codes |
03301, 03302, 03303, 03305
|
||||
| Area code(s) | 603 | ||||
| FIPS code | 33-14200 | ||||
| GNIS feature ID | 873303 | ||||
Concord is the capital city of New Hampshire, a state in the United States. It's also the main city of Merrimack County. In 2020, about 43,976 people lived here, making it the third largest city in New Hampshire. Only Manchester and Nashua are bigger.
Europeans first settled in this area in 1659. It was officially named Concord in 1765. This name was chosen to show peace after a disagreement with a nearby town called Bow. In 1808, Concord became the official capital of New Hampshire. The New Hampshire State House, where the state government meets, was finished in 1819. It's the oldest state capitol building in the U.S. where lawmakers still use their original meeting rooms.
Concord is located along the Merrimack River. The Soucook River forms the city's eastern border. The city includes its downtown area and four smaller villages: Penacook, Concord Heights, East Concord, and West Concord.
The biggest employer in Concord is the State of New Hampshire. The largest private employer is Concord Hospital. Concord is also home to the University of New Hampshire School of Law, which is New Hampshire's only law school. Other important schools include St. Paul's School, a private school, and NHTI, a community college. The Old North Cemetery in Concord is where Franklin Pierce, the 14th U.S. President, is buried.
You can get to Concord using Interstate 89 and Interstate 93, which are major highways. For air travel, Concord Municipal Airport handles smaller planes. The closest airport for commercial flights is Manchester–Boston Regional Airport, about 23 miles south.
Contents
History of Concord
The land where Concord now stands was first home to the Pennacook Native Americans thousands of years ago. They were part of the Abenaki tribe. They fished for salmon and other fish in the Merrimack River and used birch bark canoes to travel. The rich soil near the river was perfect for growing crops like beans, pumpkins, and corn.
Europeans first settled here in 1659. They called the area Penacook, which means "bend in the river" in the Abenaki language. This name described the curves of the Merrimack River. In 1725, the area was officially given to settlers from Massachusetts. It was settled between 1725 and 1727 by Captain Ebenezer Eastman and others. On February 9, 1734, it became a town called "Rumford."
In 1765, Governor Benning Wentworth renamed the town "Concord." This new name meant "harmony" or "agreement." It was chosen to end a long argument about the town's borders with its neighbor, Bow.
Concord grew in importance during the 1700s. After the American Revolution, its central location made it a good choice for the state capital. In 1807, a new canal system helped connect Concord to Boston by water. In 1808, Concord was chosen as the official state capital. The New Hampshire State House was built between 1815 and 1819. It's special because it's the oldest state capitol building in the U.S. where the state's lawmakers still meet in their original rooms. In 1823, Concord also became the main city for Merrimack County.
In the early 1800s, Concord's economy was known for making furniture, printing, and quarrying granite. Granite from Concord was used to build important buildings like the New Hampshire State House and the Library of Congress in Washington, D.C. In 1828, a company called Abbot and Downing started making their famous "Concord coach." These coaches were very important for travel in the American West and helped the city's economy grow a lot.
Later, Concord became a center for the railroad industry. The Penacook village area became a place for making textiles, using water power from the Contoocook River. The city also started to become a hub for healthcare. The New Hampshire State Hospital opened in 1842 as one of the first hospitals for mental health in the U.S. In 1891, Concord Hospital opened as the first general hospital in New Hampshire.
In the 1900s, Concord's economy changed as the railroad and textile industries became less important. The city became a key place for national politics because New Hampshire holds the first presidential primary election. Many presidential candidates still visit Concord during their campaigns. The city also became involved in the space industry. The McAuliffe-Shepard Discovery Center opened in 1990. It honors Alan Shepard, the first American in space, and Christa McAuliffe, a teacher from Concord High School who died in the 1986 Space Shuttle Challenger accident. Today, Concord is still important for politics, law, healthcare, and insurance.
Concord's Geography
Concord is located in the south-central part of New Hampshire. It is about 38 miles north of the Massachusetts border.
The city covers about 67 square miles. Most of this is land, with about 3.2 square miles of water. The Merrimack River flows through Concord from northwest to southeast. Penacook Lake is the biggest lake in the city and is its main source of drinking water. The highest point in Concord is Oak Hill, which is 860 feet above sea level.
Concord is entirely within the watershed of the Merrimack River. The downtown area is on a low flat area west of the river. To the east of the Merrimack is a flat, sandy area called Concord Heights. This area has seen a lot of new stores and businesses since 1960. The Soucook River forms the eastern border of Concord. The Turkey River flows through the southwestern part of the city. In the northern part of the city, the Contoocook River joins the Merrimack River near the village of Penacook.
Concord is about 16 miles north of Manchester, which is New Hampshire's largest city. It's also about 66 miles north of Boston.
Villages within Concord
The city of Concord includes its downtown area, with its North End and South End neighborhoods. It also has four distinct villages: Penacook, Concord Heights, East Concord, and West Concord.
Neighboring Towns
Concord shares borders with several other towns:
- Canterbury (north)
- Loudon (northeast)
- Pembroke (southeast)
- Bow (south)
- Hopkinton (west)
- Webster (northwest)
- Boscawen (north-northwest)
Concord's Climate
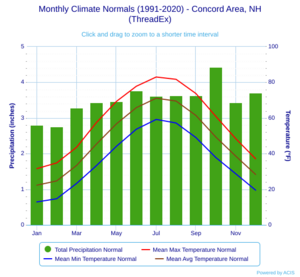
Concord has a humid continental climate. This means it has long, cold, and snowy winters. Summers are warm and sometimes humid. Spring and autumn are usually short. In winter, there's often a lot of snow, and temperatures can drop below 0°F about 15 nights a year. However, it often gets warmer, with temperatures reaching over 50°F some days in winter.
Summers can be humid with thunderstorms. Temperatures can reach over 90°F about 12 days a year. The first freezing temperatures usually happen around September 27, and the last around May 14.
The average daily temperature ranges from about 20.6°F in January to 70.0°F in July. The coldest temperature ever recorded was -37°F in February 1943. The hottest was 102°F in July 1966.
| Climate data for Concord Municipal Airport, New Hampshire (1981−2010 normals, extremes 1903–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 69 (21) |
67 (19) |
89 (32) |
95 (35) |
98 (37) |
101 (38) |
102 (39) |
101 (38) |
98 (37) |
90 (32) |
80 (27) |
73 (23) |
102 (39) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 50.8 (10.4) |
53.7 (12.1) |
66.6 (19.2) |
81.5 (27.5) |
88.7 (31.5) |
92.0 (33.3) |
93.1 (33.9) |
91.8 (33.2) |
87.7 (30.9) |
78.5 (25.8) |
68.7 (20.4) |
56.0 (13.3) |
95.5 (35.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 30.8 (−0.7) |
34.9 (1.6) |
43.8 (6.6) |
57.4 (14.1) |
68.9 (20.5) |
77.4 (25.2) |
82.3 (27.9) |
80.9 (27.2) |
72.6 (22.6) |
60.5 (15.8) |
48.4 (9.1) |
36.3 (2.4) |
58.0 (14.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 10.4 (−12.0) |
13.8 (−10.1) |
22.5 (−5.3) |
32.7 (0.4) |
42.6 (5.9) |
52.5 (11.4) |
57.7 (14.3) |
56.1 (13.4) |
47.4 (8.6) |
35.8 (2.1) |
28.2 (−2.1) |
17.2 (−8.2) |
34.8 (1.6) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −11.2 (−24.0) |
−8.2 (−22.3) |
0.8 (−17.3) |
19.4 (−7.0) |
28.1 (−2.2) |
37.9 (3.3) |
45.4 (7.4) |
42.0 (5.6) |
31.8 (−0.1) |
21.2 (−6.0) |
11.1 (−11.6) |
−2.8 (−19.3) |
−14.6 (−25.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −33 (−36) |
−37 (−38) |
−16 (−27) |
4 (−16) |
21 (−6) |
30 (−1) |
35 (2) |
29 (−2) |
20 (−7) |
10 (−12) |
−5 (−21) |
−22 (−30) |
−37 (−38) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.70 (69) |
2.62 (67) |
3.27 (83) |
3.41 (87) |
3.66 (93) |
3.69 (94) |
3.74 (95) |
3.18 (81) |
3.38 (86) |
4.04 (103) |
3.72 (94) |
3.20 (81) |
40.61 (1,033) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 18.1 (46) |
12.3 (31) |
11.1 (28) |
2.8 (7.1) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
trace | 2.6 (6.6) |
14.5 (37) |
61.4 (156) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.8 | 9.5 | 11.5 | 11.8 | 12.4 | 12.7 | 10.9 | 9.8 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 11.2 | 10.9 | 130.9 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 8.2 | 6.5 | 5.3 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.9 | 6.6 | 29.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67.9 | 66.0 | 64.8 | 62.0 | 65.0 | 70.9 | 71.8 | 74.5 | 76.3 | 72.8 | 73.3 | 72.3 | 69.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 162.8 | 171.8 | 210.5 | 223.2 | 258.4 | 274.3 | 295.8 | 261.9 | 214.7 | 183.4 | 127.8 | 134.8 | 2,519.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 56 | 58 | 57 | 56 | 57 | 60 | 64 | 61 | 57 | 54 | 44 | 48 | 56 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
People in Concord (Demographics)
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1767 | 752 | — |
| 1775 | 1,052 | +39.9% |
| 1786 | 1,402 | +33.3% |
| 1790 | 1,747 | +24.6% |
| 1800 | 2,052 | +17.5% |
| 1810 | 2,393 | +16.6% |
| 1820 | 2,838 | +18.6% |
| 1830 | 3,720 | +31.1% |
| 1840 | 4,897 | +31.6% |
| 1850 | 8,576 | +75.1% |
| 1860 | 10,896 | +27.1% |
| 1870 | 12,241 | +12.3% |
| 1880 | 13,843 | +13.1% |
| 1890 | 17,004 | +22.8% |
| 1900 | 19,632 | +15.5% |
| 1910 | 21,497 | +9.5% |
| 1920 | 22,167 | +3.1% |
| 1930 | 25,228 | +13.8% |
| 1940 | 27,171 | +7.7% |
| 1950 | 27,988 | +3.0% |
| 1960 | 28,991 | +3.6% |
| 1970 | 30,022 | +3.6% |
| 1980 | 30,400 | +1.3% |
| 1990 | 36,006 | +18.4% |
| 2000 | 40,687 | +13.0% |
| 2010 | 42,695 | +4.9% |
| 2020 | 43,976 | +3.0% |
| 2022 | 44,503 | +1.2% |
| Source: U.S. Decennial Census Population estimate U.S. Decennial Census |
||
In 2020, Concord had 43,976 residents. The city's population density was about 687 people per square mile. Most residents (84.5%) were White. Other groups included 4.9% Black or African American, 1.0% Native American, and 4.9% Asian. About 4.9% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
In 2010, there were about 17,592 households. About 28.7% of these households had children under 18 living with them. The average household size was 2.26 people.
The median age in Concord was 39.4 years. About 20.7% of the population was under 18.
The average yearly income for a household in Concord was about $52,695. For families, it was about $73,457. About 10.1% of the population lived below the poverty line.
| Race | Percentage |
|---|---|
| White, not Hispanic or Latino | 84.5% |
| Asian | 4.9% |
| Black or African American | 4.9% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 3.1% |
Concord's Economy
Major Employers
In 2020, the biggest employer in Concord was the State of New Hampshire, with over 6,000 workers. The largest private employer was Concord Hospital, which had almost 3,000 employees.
Here are the top 10 employers in Concord for the 2020 fiscal year:
| # | Employer | Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | State of New Hampshire | 6,069 |
| 2 | Capital Region Health Care – Concord Hospital | 2,998 |
| 3 | Concord School District | 809 |
| 4 | City of Concord | 556 |
| 5 | Lincoln Financial Group | 405 |
| 6 | Market Basket | 405 |
| 7 | Genesis HealthCare | 385 |
| 8 | NHHEAF Network Organizations | 332 |
| 9 | St. Paul's School | 330 |
| 10 | Merrimack Valley School District | 328 |
Getting Around Concord (Transportation)
Highways
Interstate 89 and Interstate 93 are the two main highways that serve Concord. They meet just south of the city. Interstate 89 connects Concord to Lebanon and Vermont to the northwest. Interstate 93 connects Concord to the White Mountains to the north and Manchester and Boston to the south.
Interstate 393 is a shorter highway that goes east from Concord. It joins with U.S. Route 4 and leads directly to New Hampshire's Seacoast region. U.S. Route 3 runs north-south and serves as Concord's Main Street. U.S. Route 202 and New Hampshire Route 9 cross the city from east to west. Other state routes like 13, 132, and New Hampshire Route 106 also serve the city.
Railroads
Concord used to be an important train station for the Boston and Maine Railroad. The old Concord Station was built in 1885. However, all passenger train services to Concord stopped in 1967. For a short time in 1980 and 1981, there were two daily train trips between Boston and Concord. Since then, there have been no passenger trains.
In 2021, Amtrak announced plans to bring back train service between Boston and Concord by 2035.
Bus Services
Local bus service in Concord is provided by Concord Area Transit (CAT), with three routes around the city. For longer trips, Concord Coach Lines and Greyhound Lines offer regional bus service from the Concord Transportation Center. You can take buses south to Boston or north to places like Littleton and Berlin.
Other Ways to Travel
For smaller planes, you can use Concord Municipal Airport, which is about 2 miles east of downtown. There are no commercial flights directly from Concord. The closest airport for commercial flights is Manchester–Boston Regional Airport, about 23 miles south.
Downtown Improvements
Concord's downtown area was greatly improved between 2015 and 2016. This project was called the "Complete Streets Improvement Project." It cost about $12 million. The goal was to fix old infrastructure, make the area more accessible, and make it safer for people walking, biking, and driving. It also aimed to help the local economy.
One big change was making the four-lane Main Street into two lanes with a turning lane in the middle. The extra space was used to make wider sidewalks and add areas for bikes. The city added special markings on the road to show where bikes should ride.
The project also made downtown more pleasant for pedestrians. Many power lines were buried. New street trees, colorful benches, and art were added. This made the area more welcoming for people. The project also added heated sidewalks, using steam from a local plant. This helps melt snow and ice in winter, reducing the need for sand and snow plows.
The funding for these improvements came from a grant and from the City of Concord itself.
Famous People from Concord
Media in Concord
Newspapers and Journals
- Concord Monitor (daily newspaper)
- Concord NH Patch (daily online news)
- New Hampshire Bulletin (daily online news)
- The Concord Insider (weekly newspaper)
- The Hippo (weekly entertainment paper)
Radio Stations
- WKXL 1450 AM (News Talk Information)
- WNHN-LP 94.7 FM (Jazz, Blues, Progressive Talk)
- WEVO 89.1 FM (Public radio)
- WCNH 90.5 FM (Classical Music)
- WJYY 105.5 FM (Top 40)
- WAKC 102.3 FM (Contemporary Christian)
- WICX 102.7 FM (Catholic Radio)
Concord also gets radio stations from the Manchester area. New Hampshire Public Radio has its main office in Concord.
Television
- WPXG-TV (Channel 21) (Ion Television)
- Concord TV Public-access television cable TV station
Places to Visit in Concord
The New Hampshire State House was designed by Stuart Park and built between 1815 and 1818. It is the oldest state house in the U.S. where lawmakers still meet in their original rooms. The building was updated in 1866 and expanded in 1910.
Across from the State House on Main Street is the Eagle Hotel. This hotel has been a famous landmark since it opened in 1827. Many U.S. Presidents, like Ulysses S. Grant and Franklin Pierce, stayed or dined there. Other famous guests included Charles Lindbergh and Eleanor Roosevelt. The hotel closed in 1961.
South of the Eagle Hotel on Main Street is Phenix Hall. The original hall burned down in 1893, and a new one was built. Both buildings had large rooms used for political speeches, plays, and fairs. Abraham Lincoln spoke at the old hall in 1860, and Theodore Roosevelt spoke at the new one in 1912.
North on Main Street, you can find the Walker-Woodman House, also known as the Reverend Timothy Walker House. It's the oldest two-story house still standing in Concord. It was built for Reverend Timothy Walker between 1733 and 1735.
At the north end of Main Street is the Pierce Manse. This is where President Franklin Pierce lived before and after he was president. This house, built in the 1830s, was moved in 1971 to save it from being torn down.
Beaver Meadow Golf Course, in northern Concord, is one of the oldest golf courses in New England. Other important sports places in Concord include Everett Arena and Memorial Field.
The SNOB (Somewhat North Of Boston) Film Festival started in 2002. It brings independent films and filmmakers to Concord. It also helps local filmmakers show their movies. The festival led to the building of Red River Theatres in 2007, which is a local, non-profit movie theater.
Other interesting places to visit include the Capitol Center for the Arts and the New Hampshire Historical Society. There's also the McAuliffe-Shepard Discovery Center. This science museum is named after Christa McAuliffe, the Concord teacher who died in the Space Shuttle Challenger accident, and Alan Shepard, the astronaut from nearby Derry who was the first American in space.
Education in Concord
Public Schools
Most of Concord's public schools are part of the Concord School District. However, schools in the Penacook area of the city are in the Merrimack Valley School District. This district also includes some towns north of Concord.
The only public high school in the Concord School District is Concord High School. In Fall 2023, it had about 1,450 students. Rundlett Middle School is the only public middle school in the district, with about 770 students in Fall 2023.
In 2012, Concord School District's elementary schools were reorganized. Three new schools opened, replacing six older ones. For example, Kimball School and Walker School were replaced by Christa McAuliffe School. Beaver Meadow School was not affected by these changes.
Concord schools in the Merrimack Valley School District include Merrimack Valley High School and Merrimack Valley Middle School, both in Penacook village. Penacook Elementary School is also in the village.
Private Schools
Concord has two religious schools: Bishop Brady High School and Saint John Regional School.
Other private schools in the area include Concord Christian Academy, Parker Academy, Trinity Christian School, and Shaker Road School. St. Paul's School is a private boarding school located in the city's West End.
Colleges and Universities
Concord is home to New Hampshire Technical Institute, which is the city's main community college. Granite State College offers online two-year and four-year degrees. The University of New Hampshire School of Law is located near downtown. The Franklin Pierce University Doctorate of Physical Therapy program also has a location in the city.
Concord Hospital plans to open a program with the New England College School of Nursing for a Bachelor of Nursing degree. Concord is also an important training site for Dartmouth College's Geisel School of Medicine, which is New Hampshire's only medical school.
See also
 In Spanish: Concord (Nuevo Hampshire) para niños
In Spanish: Concord (Nuevo Hampshire) para niños