Darmstadt facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Darmstadt
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
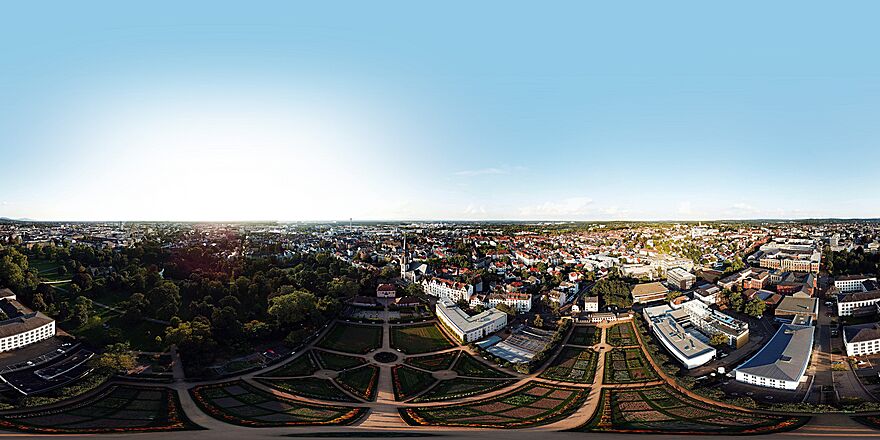
Central Darmstadt in January 2005
Residential Palace
Headquarters of Merck Group
Bessungen old town
European Space Operations Centre
UNESCO World Heritage Site Artists' Colony
|
|||
|
|||
|
Location of Darmstadt within Hessen
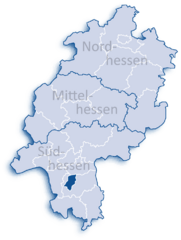 |
|||
| Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 530: Unable to find the specified location map definition: "Module:Location map/data/Germany Hessen" does not exist. | |||
| Country | Germany | ||
| State | Hesse | ||
| Admin. region | Darmstadt | ||
| District | Urban district | ||
| Subdivisions | 9 boroughs | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 122.23 km2 (47.19 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 144 m (472 ft) | ||
| Population
(2022-12-31)
|
|||
| • Total | 162,243 | ||
| • Density | 1,327.36/km2 (3,437.84/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) | ||
| Postal codes |
64283–64297
|
||
| Dialling codes | 06151, 06150 | ||
| Vehicle registration | DA | ||
| Official name: Mathildenhöhe Darmstadt | |||
| Type: | Cultural | ||
| Criteria: | (ii)(iv) | ||
| Designated: | 2021 | ||
| Reference #: | [1] | ||

Darmstadt is a cool city in Germany. It is in the state of Hesse. You can find it in the southern part of the Rhine-Main-Area. About 160,000 people live here. This makes Darmstadt the fourth largest city in Hesse. Only Frankfurt am Main, Wiesbaden, and Kassel are bigger.
Darmstadt is known as the "City of Science." It has many important science places. There are universities and companies that work with high-tech stuff. For example, the European Space Agency's European Space Operations Centre (ESA ESOC) is here. This is where they control spacecraft! Also, the GSI Centre for Heavy Ion Research is in Darmstadt. Scientists there discovered several new chemical elements. These include darmstadtium (named after the city!), bohrium, and meitnerium. The world's oldest medicine company, Merck, is also in Darmstadt. It is the city's biggest employer.
A special place called the Mathildenhöhe is in Darmstadt. It includes the Darmstadt artists' colony. This was a big center for the Jugendstil art style. It is also known as Art Nouveau. The buildings and art here are so important that UNESCO made it a World Heritage Site in 2021. This means it is a place of special cultural value to the world.
Darmstadt used to be the capital of a state called the Grand Duchy of Hesse. Later, it was the capital of the People's State of Hesse. Because it was a capital, the city became quite famous. It is still one of the richest cities in Europe. In the 1900s, industries like chemicals, electronics, and information technology became very important. These are still a big part of the city's economy today. Darmstadt is also home to the SV Darmstadt 98 football club.
Contents
History of Darmstadt
How Darmstadt Started
The name Darmstadt first appeared a long time ago. It was around the end of the 1000s. Back then, it was called Darmundestat.
Darmstadt became an official city in 1330. This happened thanks to Ludwig the Bavarian. At that time, the city belonged to the counts of Katzenelnbogen. Darmstadt, then called Darmstait, became a second home for these counts. They built a small castle there.
In 1479, the Katzenelnbogen family line ended. The city then went to the Landgraviate of Hesse. It became the main city for the rulers there. Later, it was the home of the grand dukes of Hesse until 1918.
Growing with Industry
Darmstadt grew a lot in the 1800s. Its population went from about 10,000 to 72,000 people. A special school for technology opened in 1877. This school later became the TU Darmstadt. It is a very important university today.
In the early 1900s, Darmstadt was a big center for the Jugendstil art style. This is also known as Art Nouveau. In 1937, the city grew even more. It added the nearby areas of Arheilgen and Eberstadt.
World War II and Rebuilding
Darmstadt faced very tough times during World War II. The city was bombed many times. A very big bombing raid happened on September 11, 1944. This attack destroyed most of the old city center. Many buildings were burned down. About 11,000 to 12,500 people lost their lives. Also, 66,000 to 70,000 people lost their homes.
After the war, the city was rebuilt. Many historic buildings were restored to look like they did before. Today, about 30% of Darmstadt's buildings are from before World War II.
A City of Science Today
After World War II, Darmstadt became a hub for technology. It also became a research center. Since 1997, it has called itself the "City of Science." It is known for its high-tech work. This includes spacecraft operations, chemistry, and information technology.
The Darmstadt University of Applied Sciences started in 1876. It is now the largest University of Applied Sciences in Hesse. The TU Darmstadt is also a top technical school. It is famous for engineering. These universities bring many students to the city. In 2004, there were over 33,000 students here.
Areas of Darmstadt
Darmstadt has nine official areas, called 'Stadtteile'. These are:
- Darmstadt-Arheilgen
- Darmstadt-Bessungen
- Darmstadt-Eberstadt
- Darmstadt-Kranichstein
- Darmstadt-Mitte (Central Darmstadt)
- Darmstadt-Nord (North)
- Darmstadt-Ost (East)
- Darmstadt-West
- Darmstadt-Wixhausen
Population Changes
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1871 | 33,800 | — |
| 1890 | 55,883 | +65.3% |
| 1900 | 72,381 | +29.5% |
| 1925 | 89,465 | +23.6% |
| 1933 | 93,222 | +4.2% |
| 1945 | 69,539 | −25.4% |
| 1956 | 123,306 | +77.3% |
| 1975 | 137,018 | +11.1% |
| 1990 | 138,920 | +1.4% |
| 2000 | 138,242 | −0.5% |
| 2010 | 144,402 | +4.5% |
| 2020 | 159,174 | +10.2% |
| Rank | Nationality | Population (31 December 2022) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4,308 | |
| 2 | 2,422 | |
| 3 | 1,836 | |
| 4 | 1,784 | |
| 5 | 1,715 | |
| 6 | 1,673 | |
| 7 | 1,322 | |
| 8 | 1,138 | |
| 9 | 1,078 | |
| 10 | 1,034 |
Getting Around Darmstadt
Darmstadt has great ways to travel. You can use major highways, fast trains, and a big international airport.
Roads
Darmstadt is connected to important roads. These include two Autobahnen (highways). The main road going west-east is the Bundesstraße 26. The Bundesstraße 3 runs north-south.
Public Transport
Darmstadt has a great public transport system. It is part of the RMV. This is the transport system for the Frankfurt area. The main way to get around Darmstadt is its modern tram system. It has 9 lines. There are also local buses that go everywhere in the city. Darmstadt is also connected to the Frankfurt S-Bahn system. This is a fast train network.
Train Connections
Darmstadt's main train station is Darmstadt Hauptbahnhof. It connects the city to the rest of Germany and Europe. You can catch fast Intercity-Express trains here. It is a busy station with 12 platforms. It serves as a major train hub for southern Hesse.
Airports
You can easily reach Darmstadt from around the world. Just fly to Frankfurt Airport. It is about 20 kilometers (12 miles) north of Darmstadt. You can get there by highway, train, or a direct express bus called the "Airliner." This airport is one of the busiest in the world.
- Frankfurt Egelsbach Airport
This airport is for smaller planes. It is 5 kilometers (3 miles) north of Darmstadt.
- Frankfurt Hahn Airport
This airport is quite far from Darmstadt. It is about 120 kilometers (75 miles) to the west. It is a major base for low-cost airlines. You can only reach it by car or bus.
Fun Things to See and Do
Castles and Old Buildings
Darmstadt used to be the capital of its own country. This means it has many old and grand buildings. Many were designed by Georg Moller. He was a famous builder for the Grand Duchy of Hesse. The last Grand Duke of Hesse was related to Queen Victoria of Britain. He was also brother to the Russian Empress Alexandra. So, you can see British and Russian styles in Darmstadt's buildings.
The Residential Palace Darmstadt is in the city center. It was once home to the rulers of Hesse. They also owned Jagdschloss Kranichstein. This was a hunting lodge. Now it is a fancy hotel. The most famous castle nearby is Frankenstein Castle. Some people think it might have inspired the name for Mary Shelley's famous monster story!
Cool Modern Buildings
Darmstadt also has cool modern buildings. One famous one is the Waldspirale ('Forest Spiral'). It is a unique apartment building. It was designed by Austrian artist Friedensreich Hundertwasser. It looks almost like a dream. It has no straight lines or sharp corners. Even the windows are all different shapes!
Art Nouveau Style
Darmstadt was a big center for the Art Nouveau movement. In Germany, this style is called Jugendstil. You can still see many examples of this art. The Rosenhöhe is a beautiful rose garden from the 1800s. The Mathildenhöhe is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It has the Hochzeitsturm ('Wedding Tower'). This tower is also called the 'Five-Finger-Tower'. The Russian Chapel in Darmstadt is also there. Many artists lived and worked in Darmstadt during this time.
City Squares
The Luisenplatz is the main square in the city. It is a central spot for public transport. In 1844, a tall column was put in the middle of the square. It is called the Ludwigsäule. People call it Langer Lui (Long Ludwig). It honors Ludwig I, the first Grand Duke of Hesse. Other important squares are the Marktplatz (Market Square) and the Sabaisplatz.
Parks and Gardens
Darmstadt has many beautiful parks. The Herrngarten is a large English-style park. It used to be a royal garden. Now, everyone can enjoy it. Other great parks include the Prinz-Georgs-Garten and the Orangerie. The Park Rosenhöhe is a peaceful place. It has two impressive mausoleums. The Botanischer Garten is a botanical garden. It has a wonderful collection of rare plants and trees.
Churches
The Protestant Stadtkirche Darmstadt was built in 1369. It is in the city center. It has Gothic, renaissance, and baroque styles. The most important Catholic Church is St. Ludwig. The Russian Chapel in Darmstadt is a Russian orthodox church. It is still used today. It was built for the last Tsar of Russia, Nicholas II. His wife, Alexandra, was born in Darmstadt. People say the chapel was built on Russian soil.
Festivals
Every year in July, the Heinerfest festival takes place. It is held around the old palace. It is a traditional German festival. You can find music, food, and fun rides. Another festival, the Schlossgrabenfest, happens in May. It focuses more on live music. Both festivals attract many visitors!
Culture and Arts
Darmstadt has a rich history of culture. The Staatstheater Darmstadt is a theater that dates back to 1711. The current building has three halls. The "Grand Hall" is for opera. The "Small Hall" is for plays and dance. There is also a smaller hall for chamber plays.
Darmstadt has many museums. The Hessisches Landesmuseum (Hessian State Museum) is very important. There is also a Porcelain Museum. The Schlossmuseum shows off the old royal residence. The Museum Künstlerkolonie is an Art Nouveau museum.
The Jazz-Institut Darmstadt is Germany's largest public jazz archive. The Internationales Musikinstitut Darmstadt has one of the world's largest collections of modern sheet music. It also hosts a summer school for contemporary classical music. Many famous composers have attended or taught there.
The Deutsche Akademie für Sprache und Dichtung is a place for writers and scholars. They research the German language here. The academy gives out the Georg Büchner Prize every year. It is a very important award for German writers.
Geography
Darmstadt is in the Upper Rhine Plain. This is a long, flat area. It is between Frankfurt in the north and Mannheim in the south. The southeastern parts of Darmstadt are in the Odenwald. This is a low mountain range.
Climate
Southern Hesse has a mild climate. This is why winegrowing is popular south of Darmstadt. Summers are warm and humid. They often have thunderstorms. Winters are usually mild. Snow is most likely in January and February.
| Climate data for Darmstadt (1981–2010 normals, extremes 1995–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.0 (60.8) |
19.6 (67.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
33.3 (91.9) |
37.6 (99.7) |
39.3 (102.7) |
39.5 (103.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
27.4 (81.3) |
22.6 (72.7) |
15.7 (60.3) |
39.5 (103.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5 (41) |
7 (45) |
11 (52) |
15 (59) |
20 (68) |
23 (73) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
20 (68) |
14 (57) |
8 (46) |
5 (41) |
15 (59) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.4 (34.5) |
2.1 (35.8) |
5.9 (42.6) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.3 (57.7) |
17.3 (63.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
18.7 (65.7) |
14.5 (58.1) |
10 (50) |
5.3 (41.5) |
2.2 (36.0) |
10.1 (50.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1 (30) |
1 (34) |
3 (37) |
6 (43) |
11 (52) |
13 (55) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
11 (52) |
7 (45) |
4 (39) |
1 (34) |
7 (45) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −19.3 (−2.7) |
−18.1 (−0.6) |
−15.8 (3.6) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
2.5 (36.5) |
4.7 (40.5) |
4.1 (39.4) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−19.4 (−2.9) |
−19.4 (−2.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 55 (2.2) |
53 (2.1) |
66 (2.6) |
49 (1.9) |
76 (3.0) |
67 (2.6) |
75 (3.0) |
66 (2.6) |
63 (2.5) |
66 (2.6) |
63 (2.5) |
66 (2.6) |
765 (30.1) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 47 | 80 | 120 | 176 | 208 | 214 | 232 | 218 | 158 | 103 | 50 | 37 | 1,643 |
| Source: Daily mean / Avg. precipitation / Mean sunshine hours (1981–2010), DWD | |||||||||||||
Education in Darmstadt
Schools
Darmstadt has many public schools. These include primary, secondary, and higher schools. There are also private schools. Some examples are the Edith-Stein-Schule and the Schulzentrum Marienhöhe.
Universities
TU Darmstadt
The Technical University of Darmstadt (TU Darmstadt) is a famous research university. It started in 1877. In 1882, it was the first university in the world to have a special program for electrical engineering. The university has 13 departments. They offer about 100 different courses. You can study engineering, computer science, math, and natural sciences. They also have courses in economics, history, and psychology.
Hochschule Darmstadt
The Darmstadt University of Applied Sciences is called Hochschule Darmstadt. It works closely with many industries. It is the largest University of Applied Sciences in Hesse. About 16,000 students attend here. They can study architecture, engineering, design, and more.
EHD Darmstadt
The Protestant University of Applied Sciences Darmstadt (EHD) is a church-supported university. It has about 1,700 students. They have 40 professors and many visiting teachers.
Sports in Darmstadt
The main professional sports team is the SV Darmstadt 98 football club. They play at the Merck-Stadion am Böllenfalltor.
Other football clubs are 1. FCA Darmstadt and Rot-Weiß Darmstadt.
The Darmstadt Diamonds are the city's american football team.
The ice hockey team is called the ESC Darmstadt Dukes.
Important Organizations
Technology and Science
Darmstadt is home to many research places. These include the Fraunhofer Society and the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI). The GSI has a particle accelerator. Scientists there discovered the chemical element darmstadtium. It is named after the city! They also made other elements like meitnerium and hassium.
The European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) is in Darmstadt. This is where the European Space Agency controls its spacecraft. They manage satellites that explore space and orbit Earth.
EUMETSAT is another important organization. It operates Europe's main weather satellites. These satellites help us understand the weather.
Darmstadt is also a center for medicine and chemicals. Companies like Merck have their main offices here. It is also a hub for IT and telecommunications. Companies like Software AG and Deutsche Telekom have labs here.
ATHENE is a big research center. It focuses on IT security and privacy. It is the largest IT security research center in Europe. The German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence also has a lab in Darmstadt.
Tourist Sights
In the City
- Mathildenhöhe with the Art Nouveau Museum
- Wedding Tower (Hochzeitsturm)
- The former private chapel of the last Tsar of Russia
- State Theatre and Opera House
- Waldspirale Hundertwasser Building
- City Center with Luisenplatz, the Residential Palace, and the Market Square
- Hauptbahnhof (Central Train Station)
- Parks
- Herrngarten Park
- Botanical Garden
- Vortex Garden
- Park Rosenhöhe (Rose Heights Park) with the Dukal Cemetery
- Porcelain Museum
- St. Ludwig Church
- Hessisches Landesmuseum (Hessian State Museum)
- Haus der Geschichte (House of History)
- Train Museum Kranichstein
- Bessungen old town
In the Region
- Odenwald (a low mountain range)
- Bergstrasse (a scenic route)
- Vineyards at Zwingenberg
- Frankenstein Castle
- Messel Pit Fossil Site (a UNESCO World Heritage Site with fossils)
- Melibokus (a mountain with great views)
Famous People from Darmstadt




Many famous people were born or lived in Darmstadt. Here are a few:
- Johann Heinrich Merck (1741–1791), an author.
- Justus von Liebig (1803–1873), a chemist who helped start organic chemistry.
- Georg Büchner (1813–1837), a writer and poet.
- Friedrich August Kekulé (1829–1896), an organic chemist who developed the idea of chemical structure.
- Ernest Louis, Grand Duke of Hesse (1868–1937), the last Grand Duke of Hesse.
- Alexandra Feodorovna (1872–1918), who became the Russian Empress.
- Beno Gutenberg (1889–1960), a German-American scientist who studied earthquakes.
- Karlheinz Stockhausen (1928–2007), a leading composer of electronic music.
- Andrea Petkovic (born 1987), a tennis player.
Sister Cities
Darmstadt is connected to many cities around the world. These are called sister cities. They work together to share culture and ideas.
 Alkmaar, Netherlands (1958)
Alkmaar, Netherlands (1958) Brescia, Italy (1991)
Brescia, Italy (1991) Bursa, Turkey (1971)
Bursa, Turkey (1971) Chesterfield, England, UK (1959)
Chesterfield, England, UK (1959) Freiberg, Germany (1990)
Freiberg, Germany (1990) Graz, Austria (1968)
Graz, Austria (1968) Gstaad (Saanen), Switzerland (1991)
Gstaad (Saanen), Switzerland (1991) Gyönk, Hungary (1990)
Gyönk, Hungary (1990) Liepāja, Latvia (1993)
Liepāja, Latvia (1993) Logroño, Spain (2002)
Logroño, Spain (2002) Nahariya, Israel (2023)
Nahariya, Israel (2023) Płock, Poland (1988)
Płock, Poland (1988) San Antonio, United States (2017)
San Antonio, United States (2017) Szeged, Hungary (1990)
Szeged, Hungary (1990) Trondheim, Norway (1968)
Trondheim, Norway (1968) Troyes, France (1958)
Troyes, France (1958) Uzhhorod, Ukraine (1992)
Uzhhorod, Ukraine (1992)
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Darmstadt para niños
In Spanish: Darmstadt para niños









































































