Sigmund Freud facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sigmund Freud
|
|
|---|---|
Freud c. 1921
|
|
| Born |
Sigismund Schlomo Freud
6 May 1856 Freiberg in Mähren, Moravia, Austrian Empire (Now Czech Republic)
|
| Died | 23 September 1939 (aged 83) Hampstead, London, England
|
| Alma mater | University of Vienna (MD, 1881) |
| Known for | Psychoanalysis, including the theories of id, ego and super-ego, repression, defense mechanism |
| Spouse(s) | |
| Children | Mathilde, Jean-Martin, Oliver, Ernst, Sophie, and Anna |
| Parents |
|
| Awards | Goethe Prize (1930) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Neurology, psychotherapy, psychoanalysis |
| Institutions |
|
| Academic advisors |
|
| Influences | |
| Influenced |
|
| Signature | |
Sigmund Freud ( froyd born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies seen as originating from conflicts in the psyche, through dialogue between patient and psychoanalyst, and the distinctive theory of mind and human agency derived from it.
Biography
Early life and education

Sigmund Freud was born to Ashkenazi Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire (now Příbor, Czech Republic), the first of eight children. Both of his parents were from Galicia, a historic province straddling modern-day West Ukraine and southeast Poland. His father, Jakob Freud (1815–1896), a wool merchant, had two sons, Emanuel (1833–1914) and Philipp (1836–1911), by his first marriage. Jakob's family were Hasidic Jews and, although Jakob himself had moved away from the tradition, he came to be known for his Torah study. He and Freud's mother, Amalia Nathansohn, who was 20 years younger and his third wife, were married by Rabbi Isaac Noah Mannheimer on 29 July 1855. They were struggling financially and living in a rented room, in a locksmith's house at Schlossergasse 117 when their son Sigmund was born.
In 1859, the Freud family left Freiberg. Freud's half-brothers immigrated to Manchester, England, parting him from the "inseparable" playmate of his early childhood, Emanuel's son, John. Jakob Freud took his wife and two children (Freud's sister, Anna, was born in 1858; a brother, Julius born in 1857, had died in infancy) firstly to Leipzig and then in 1860 to Vienna where four sisters and a brother were born: Rosa (b. 1860), Marie (b. 1861), Adolfine (b. 1862), Paula (b. 1864), Alexander (b. 1866). In 1865, the nine-year-old Freud entered the Leopoldstädter Kommunal-Realgymnasium, a prominent high school. He proved to be an outstanding pupil and graduated from the Matura in 1873 with honors. He loved literature and was proficient in German, French, Italian, Spanish, English, Hebrew, Latin and Greek.
Freud entered the University of Vienna at age 17. He had planned to study law, but joined the medical faculty at the university, where his studies included philosophy under Franz Brentano, physiology under Ernst Brücke, and zoology under Darwinist professor Carl Claus. In 1877, Freud moved to Ernst Brücke's physiology laboratory where he spent six years comparing the brains of humans and other vertebrates with those of frogs and invertebrates such as crayfish and lampreys. His research work on the biology of nervous tissue proved seminal for the subsequent discovery of the neuron in the 1890s. Freud's research work was interrupted in 1879 by the obligation to undertake a year's compulsory military service. The lengthy downtimes enabled him to complete a commission to translate four essays from John Stuart Mill's collected works. He graduated with an MD in March 1881.
Early career and marriage
In 1882, Freud began his medical career at Vienna General Hospital. Over a three-year period, Freud worked in various departments of the hospital. His time spent in Theodor Meynert's psychiatric clinic and as a locum in a local asylum led to an increased interest in clinical work. His substantial body of published research led to his appointment as a university lecturer or docent in neuropathology in 1885, a non-salaried post but one which entitled him to give lectures at the University of Vienna.
In 1886, Freud resigned his hospital post and entered private practice specializing in "nervous disorders". The same year he married Martha Bernays, the granddaughter of Isaac Bernays, a chief rabbi in Hamburg. The Freuds had six children: Mathilde (b. 1887), Jean-Martin (b. 1889), Oliver (b. 1891), Ernst (b. 1892), Sophie (b. 1893), and Anna (b. 1895). From 1891 until they left Vienna in 1938, Freud and his family lived in an apartment at Berggasse 19, near Innere Stadt, a historical district of Vienna.
Freud owned and made use of Charles Darwin's major evolutionary writings, and was also influenced by Eduard von Hartmann's The Philosophy of the Unconscious (1869). Other texts of importance to Freud were by Fechner and Herbart, with the latter's Psychology as Science arguably considered to be of underrated significance in this respect. Freud also drew on the work of Theodor Lipps, who was one of the main contemporary theorists of the concepts of the unconscious and empathy.
Though Freud was reluctant to associate his psychoanalytic insights with prior philosophical theories, attention has been drawn to analogies between his work and that of both Schopenhauer and Nietzsche. In 1908, Freud said that he occasionally read Nietzsche, and was strongly fascinated by his writings, but did not study him, because he found Nietzsche's "intuitive insights" resembled too much his own work at the time, and also because he was overwhelmed by the "wealth of ideas" he encountered when he read Nietzsche. His interest in philosophy declined after he had decided on a career in neurology.
Freud read William Shakespeare in English throughout his life, and it has been suggested that his understanding of human psychology may have been partially derived from Shakespeare's plays.
Freud's Jewish origins and his allegiance to his secular Jewish identity were of significant influence in the formation of his intellectual and moral outlook, especially concerning his intellectual non-conformism, as he pointed out in his Autobiographical Study.
Development of psychoanalysis

In October 1885, Freud went to Paris on a three-month fellowship to study with Jean-Martin Charcot, a renowned neurologist who was conducting scientific research into hypnosis. He was later to recall the experience of this stay as catalytic in turning him toward the practice of medical psychopathology and away from a less financially promising career in neurology research. Charcot specialized in the study of hysteria and susceptibility to hypnosis, which he frequently demonstrated with patients on stage in front of an audience.
Once he had set up in private practice back in Vienna in 1886, Freud began using hypnosis in his clinical work. He adopted the approach of his friend and collaborator, Josef Breuer, in a type of hypnosis that was different from the French methods he had studied, in that it did not use suggestion. The treatment of one particular patient of Breuer's proved to be transformative for Freud's clinical practice. Described as Anna O., she was invited to talk about her symptoms while under hypnosis (she would coin the phrase "talking cure" for her treatment). In the course of talking in this way, her symptoms became reduced in severity as she retrieved memories of traumatic incidents associated with their onset.
The inconsistent results of Freud's early clinical work eventually led him to abandon hypnosis, having concluded that more consistent and effective symptom relief could be achieved by encouraging patients to talk freely, without censorship or inhibition, about whatever ideas or memories occurred to them. In conjunction with this procedure, which he called "free association", Freud found that patients' dreams could be fruitfully analyzed to reveal the complex structuring of unconscious material and to demonstrate the psychic action of repression which, he had concluded, underlay symptom formation. By 1896 he was using the term "psychoanalysis" to refer to his new clinical method and the theories on which it was based.
Freud's development of these new theories took place during a period in which he experienced heart irregularities, disturbing dreams and periods of depression, a "neurasthenia" which he linked to the death of his father in 1896 and which prompted a "self-analysis" of his own dreams and memories of childhood. His explorations of his feelings of hostility to his father and rivalrous jealousy over his mother's affections led him to fundamentally revise his theory of the origin of the neuroses.
Freud described the evolution of his clinical method and set out his theory of the psychogenetic origins of hysteria, demonstrated in several case histories, in Studies on Hysteria published in 1895 (co-authored with Josef Breuer). In 1899, he published The Interpretation of Dreams in which, following a critical review of existing theory, Freud gives detailed interpretations of his own and his patients' dreams in terms of wish-fulfillments made subject to the repression and censorship of the "dream-work". He then sets out the theoretical model of mental structure (the unconscious, pre-conscious and conscious) on which this account is based. An abridged version, On Dreams, was published in 1901. In works that would win him a more general readership, Freud applied his theories outside the clinical setting in The Psychopathology of Everyday Life (1901) and Jokes and their Relation to the Unconscious (1905). The same year he published Fragment of an Analysis of a Case of Hysteria, which became one of his most famous case studies. Known as the 'Dora' case study, for Freud it was illustrative of hysteria as a symptom and contributed to his understanding of the importance of transference as a clinical phenomena. In other of his early case studies Freud set out to describe the symptomatology of obsessional neurosis in the case of the Rat man, and phobia in the case of Little Hans.
Transference is the process by which patients displace onto their analyst feelings and ideas which derive from previous figures in their lives. Transference was first seen as a regrettable phenomenon that interfered with the recovery of repressed memories and disturbed patients' objectivity, but by 1912, Freud had come to see it as an essential part of the therapeutic process.
Early followers

In 1902, Freud, at last, realised his long-standing ambition to be made a university professor. The title "professor extraordinarius" was important to Freud for the recognition and prestige it conferred, there being no salary or teaching duties attached to the post (he would be granted the enhanced status of "professor ordinarius" in 1920). Despite support from the university, his appointment had been blocked in successive years by the political authorities and it was secured only with the intervention of one of his more influential ex-patients, a Baroness Marie Ferstel.
With his prestige thus enhanced, Freud continued with the regular series of lectures on his work which, since the mid-1880s as a docent of Vienna University, he had been delivering to small audiences every Saturday evening at the lecture hall of the university's psychiatric clinic.
From the autumn of 1902, a number of Viennese physicians who had expressed interest in Freud's work were invited to meet at his apartment every Wednesday afternoon to discuss issues relating to psychology and neuropathology. This group was called the Wednesday Psychological Society (Psychologische Mittwochs-Gesellschaft) and it marked the beginnings of the worldwide psychoanalytic movement.

By 1906, the group had grown to sixteen members, including Otto Rank, who was employed as the group's paid secretary. In the same year, Freud began a correspondence with Carl Gustav Jung who was by then already an academically acclaimed researcher into word-association and the Galvanic Skin Response, and a lecturer at Zurich University, although still only an assistant to Eugen Bleuler at the Burghölzli Mental Hospital in Zürich. In March 1907, Jung and Ludwig Binswanger, also a Swiss psychiatrist, travelled to Vienna to visit Freud and attend the discussion group. Thereafter, they established a small psychoanalytic group in Zürich. In 1908, reflecting its growing institutional status, the Wednesday group was reconstituted as the Vienna Psychoanalytic Society with Freud as president, a position he relinquished in 1910 in favor of Adler in the hope of neutralizing his increasingly critical standpoint.
Freud's early followers met together formally for the first time at the Hotel Bristol, Salzburg on 27 April 1908. This meeting, which was retrospectively deemed to be the first International Psychoanalytic Congress, was convened at the suggestion of Ernest Jones, then a London-based neurologist who had discovered Freud's writings and begun applying psychoanalytic methods in his clinical work. There were, as Jones records, "forty-two present, half of whom were or became practising analysts." In addition to Jones and the Viennese and Zürich contingents accompanying Freud and Jung, also present and notable for their subsequent importance in the psychoanalytic movement were Karl Abraham and Max Eitingon from Berlin, Sándor Ferenczi from Budapest and the New York-based Abraham Brill.
Important decisions were taken at the Congress to advance the impact of Freud's work. A journal, the Jahrbuch für psychoanalytische und psychopathologische Forschungen, was launched in 1909 under the editorship of Jung. This was followed in 1910 by the monthly Zentralblatt für Psychoanalyse edited by Adler and Stekel, in 1911 by Imago, a journal devoted to the application of psychoanalysis to the field of cultural and literary studies edited by Rank and in 1913 by the Internationale Zeitschrift für Psychoanalyse, also edited by Rank. Plans for an international association of psychoanalysts were put in place and these were implemented at the Nuremberg Congress of 1910 where Jung was elected, with Freud's support, as its first president.
Freud turned to Brill and Jones to further his ambition to spread the psychoanalytic cause in the English-speaking world. Both were invited to Vienna following the Salzburg Congress and a division of labour was agreed with Brill given the translation rights for Freud's works, and Jones, who was to take up a post at the University of Toronto later in the year, tasked with establishing a platform for Freudian ideas in North American academic and medical life. Jones's advocacy prepared the way for Freud's visit to the United States, accompanied by Jung and Ferenczi, in September 1909 at the invitation of Stanley Hall, president of Clark University, Worcester, Massachusetts, where he gave five lectures on psychoanalysis.
The event, at which Freud was awarded an Honorary Doctorate, marked the first public recognition of Freud's work and attracted widespread media interest. Freud's audience included the distinguished neurologist and psychiatrist James Jackson Putnam, Professor of Diseases of the Nervous System at Harvard, who invited Freud to his country retreat where they held extensive discussions over a period of four days. Putnam's subsequent public endorsement of Freud's work represented a significant breakthrough for the psychoanalytic cause in the United States. When Putnam and Jones organised the founding of the American Psychoanalytic Association in May 1911 they were elected president and secretary respectively. Brill founded the New York Psychoanalytic Society the same year. His English translations of Freud's work began to appear from 1909.
Resignations from the IPA
Some of Freud's followers subsequently withdrew from the International Psychoanalytical Association (IPA) and founded their own schools.
From 1909, Adler's views on topics such as neurosis began to differ markedly from those held by Freud. As Adler's position appeared increasingly incompatible with Freudianism, a series of confrontations between their respective viewpoints took place at the meetings of the Viennese Psychoanalytic Society in January and February 1911. In February 1911, Adler, then the president of the society, resigned his position. At this time, Stekel also resigned from his position as vice president of the society. Adler finally left the Freudian group altogether in June 1911 to found his own organization with nine other members who had also resigned from the group. This new formation was initially called Society for Free Psychoanalysis but it was soon renamed the Society for Individual Psychology. In the period after World War I, Adler became increasingly associated with a psychological position he devised called individual psychology.

In 1912, Jung published Wandlungen und Symbole der Libido (published in English in 1916 as Psychology of the Unconscious) making it clear that his views were taking a direction quite different from those of Freud. To distinguish his system from psychoanalysis, Jung called it analytical psychology. Anticipating the final breakdown of the relationship between Freud and Jung, Ernest Jones initiated the formation of a Secret Committee of loyalists charged with safeguarding the theoretical coherence and institutional legacy of the psychoanalytic movement. Formed in the autumn of 1912, the Committee comprised Freud, Jones, Abraham, Ferenczi, Rank, and Hanns Sachs. Max Eitingon joined the Committee in 1919. Each member pledged himself not to make any public departure from the fundamental tenets of psychoanalytic theory before he had discussed his views with the others. After this development, Jung recognised that his position was untenable and resigned as editor of the Jahrbuch and then as president of the IPA in April 1914. The Zürich Society withdrew from the IPA the following July.
Later the same year, Freud published a paper entitled "The History of the Psychoanalytic Movement", the German original being first published in the Jahrbuch, giving his view on the birth and evolution of the psychoanalytic movement and the withdrawal of Adler and Jung from it.
The final defection from Freud's inner circle occurred following the publication in 1924 of Rank's The Trauma of Birth. Abraham and Jones became increasingly forceful critics of Rank and though he and Freud were reluctant to end their close and long-standing relationship. The break finally came in 1926 when Rank resigned from his official posts in the IPA and left Vienna for Paris. His place on the Committee was taken by Anna Freud. Rank eventually settled in the United States where his revisions of Freudian theory were to influence a new generation of therapists uncomfortable with the orthodoxies of the IPA.
Early psychoanalytic movement
After the founding of the IPA in 1910, an international network of psychoanalytical societies, training institutes, and clinics became well established and a regular schedule of biannual Congresses commenced after the end of World War I to coordinate their activities and as a forum for presenting papers on clinical and theoretical topics.
Abraham and Eitingon founded the Berlin Psychoanalytic Society in 1910 and then the Berlin Psychoanalytic Institute and the Poliklinik in 1920. The Poliklinik's innovations of free treatment, and child analysis, and the Berlin Institute's standardisation of psychoanalytic training had a major influence on the wider psychoanalytic movement. In 1927, Ernst Simmel founded the Schloss Tegel Sanatorium on the outskirts of Berlin, the first such establishment to provide psychoanalytic treatment in an institutional framework. Freud organised a fund to help finance its activities and his architect son, Ernst, was commissioned to refurbish the building. It was forced to close in 1931 for economic reasons.
The 1910 Moscow Psychoanalytic Society became the Russian Psychoanalytic Society and Institute in 1922. Freud's Russian followers were the first to benefit from translations of his work, the 1904 Russian translation of The Interpretation of Dreams appearing nine years before Brill's English edition. The Russian Institute was unique in receiving state support for its activities, including publication of translations of Freud's works. Support was abruptly annulled in 1924, when Joseph Stalin came to power, after which psychoanalysis was denounced on ideological grounds.
After helping found the American Psychoanalytic Association in 1911, Ernest Jones returned to Britain from Canada in 1913 and founded the London Psychoanalytic Society the same year. In 1919, he dissolved this organisation and, with its core membership purged of Jungian adherents, founded the British Psychoanalytical Society, serving as its president until 1944. The Institute of Psychoanalysis was established in 1924 and the London Clinic of Psychoanalysis was established in 1926, both under Jones's directorship.
The Vienna Ambulatorium (Clinic) was established in 1922 and the Vienna Psychoanalytic Institute was founded in 1924 under the directorship of Helene Deutsch. Ferenczi founded the Budapest Psychoanalytic Institute in 1913 and a clinic in 1929.
Psychoanalytic societies and institutes were established in Switzerland (1919), France (1926), Italy (1932), the Netherlands (1933), Norway (1933), and in Palestine (Jerusalem, 1933) by Eitingon, who had fled Berlin after Adolf Hitler came to power. The New York Psychoanalytic Institute was founded in 1931.
The 1922 Berlin Congress was the last Freud attended. By this time his speech had become seriously impaired by the prosthetic device he needed as a result of a series of operations on his cancerous jaw. He kept abreast of developments through regular correspondence with his principal followers and via the circular letters and meetings of the Secret Committee which he continued to attend.
The Committee continued to function until 1927 by which time institutional developments within the IPA, such as the establishment of the International Training Commission, had addressed concerns about the transmission of psychoanalytic theory and practice. There remained, however, significant differences over the issue of lay analysis – i.e. the acceptance of non-medically qualified candidates for psychoanalytic training. Freud set out his case in favour in 1926 in his The Question of Lay Analysis. He was resolutely opposed by the American societies who expressed concerns over professional standards and the risk of litigation (though child analysts were made exempt). These concerns were also shared by some of his European colleagues. Eventually, an agreement was reached allowing societies autonomy in setting criteria for candidature.
In 1930, Freud received the Goethe Prize in recognition of his contributions to psychology and German literary culture.
Escape from Nazism
In January 1933, the Nazi Party took control of Germany, and Freud's books were prominent among those they burned and destroyed. Freud remarked to Ernest Jones: "What progress we are making. In the Middle Ages they would have burned me. Now, they are content with burning my books." Freud continued to underestimate the growing Nazi threat and remained determined to stay in Vienna, even following the Anschluss of 13 March 1938, in which Nazi Germany annexed Austria, and the outbreaks of violent antisemitism that ensued. Jones, the then president of the International Psychoanalytical Association (IPA), flew into Vienna from London via Prague on 15 March determined to get Freud to change his mind and seek exile in Britain. This prospect and the shock of the arrest and interrogation of Anna Freud by the Gestapo finally convinced Freud it was time to leave Austria. Jones left for London the following week with a list provided by Freud of the party of émigrés for whom immigration permits would be required. Back in London, Jones used his personal acquaintance with the Home Secretary, Sir Samuel Hoare, to expedite the granting of permits. There were seventeen in all and work permits were provided where relevant. Jones also used his influence in scientific circles, persuading the president of the Royal Society, Sir William Bragg, to write to the Foreign Secretary Lord Halifax, requesting to good effect that diplomatic pressure be applied in Berlin and Vienna on Freud's behalf. Freud also had support from American diplomats, notably his ex-patient and American ambassador to France, William Bullitt. Bullitt alerted U.S. President Roosevelt to the increased dangers facing the Freuds, resulting in the American consul-general in Vienna, John Cooper Wiley, arranging regular monitoring of Berggasse 19. He also intervened by phone call during the Gestapo interrogation of Anna Freud.
The departure from Vienna began in stages throughout April and May 1938. Freud's grandson, Ernst Halberstadt, and Freud's son Martin's wife and children left for Paris in April. Freud's sister-in-law, Minna Bernays, left for London on 5 May, Martin Freud the following week and Freud's daughter Mathilde and her husband, Robert Hollitscher, on 24 May.
By the end of the month, arrangements for Freud's own departure for London had become stalled, mired in a legally tortuous and financially extortionate process of negotiation with the Nazi authorities. Under regulations imposed on its Jewish population by the new Nazi regime, a Kommissar was appointed to manage Freud's assets and those of the IPA whose headquarters were near Freud's home. Freud was allocated to Dr Anton Sauerwald, who had studied chemistry at Vienna University under Professor Josef Herzig, an old friend of Freud's. Sauerwald read Freud's books to further learn about him and became sympathetic toward his situation. Though required to disclose details of all Freud's bank accounts to his superiors and to arrange the destruction of the historic library of books housed in the offices of the IPA, Sauerwald did neither. Instead, he removed evidence of Freud's foreign bank accounts to his own safe-keeping and arranged the storage of the IPA library in the Austrian National Library, where it remained until the end of the war.
Though Sauerwald's intervention lessened the financial burden of the Reich Flight Tax on Freud's declared assets, other substantial charges were levied concerning the debts of the IPA and the valuable collection of antiquities Freud possessed. Unable to access his own accounts, Freud turned to Princess Marie Bonaparte, the most eminent and wealthy of his French followers, who had travelled to Vienna to offer her support, and it was she who made the necessary funds available. This allowed Sauerwald to sign the necessary exit visas for Freud, his wife Martha, and daughter Anna. They left Vienna on the Orient Express on 4 June, accompanied by their housekeeper and a doctor, arriving in Paris the following day, where they stayed as guests of Marie Bonaparte, before travelling overnight to London, arriving at London Victoria station on 6 June.
Among those soon to call on Freud to pay their respects were Salvador Dalí, Stefan Zweig, Leonard Woolf, Virginia Woolf, and H. G. Wells. Representatives of the Royal Society called with the Society's Charter for Freud, who had been elected a Foreign Member in 1936, to sign himself into membership. Marie Bonaparte arrived near the end of June to discuss the fate of Freud's four elderly sisters left behind in Vienna. Her subsequent attempts to get them exit visas failed; they all were murdered in Nazi concentration camps.

In early 1939, Sauerwald arrived in London in mysterious circumstances, where he met Freud's brother Alexander. He was tried and imprisoned in 1945 by an Austrian court for his activities as a Nazi Party official. Responding to a plea from his wife, Anna Freud wrote to confirm that Sauerwald "used his office as our appointed commissar in such a manner as to protect my father". Her intervention helped secure his release from jail in 1947.
The Freud's new family home was established in Hampstead at 20 Maresfield Gardens in September 1938. Freud's architect son, Ernst, designed modifications of the building including the installation of an electric lift. The study and library areas were arranged to create the atmosphere and visual impression of Freud's Vienna consulting rooms. He continued to see patients there until the terminal stages of his illness. He also worked on his last books, Moses and Monotheism, published in German in 1938 and in English the following year and the uncompleted An Outline of Psychoanalysis, which was published posthumously.
Death
By mid-September 1939, Freud's cancer of the jaw was causing him increasingly severe pain and had been declared inoperable. The last book he read, Balzac's La Peau de chagrin, prompted reflections on his own increasing frailty. Anna Freud wanted to postpone her father's death, but his doctor convinced her it was pointless to keep him alive; on 21 and 22 September, he administered doses of medicine that resulted in Freud's death at around 3 am on 23 September 1939.
Three days after his death, Freud's body was cremated at Golders Green Crematorium in North London, with Harrods acting as funeral directors, on the instructions of his son, Ernst. Funeral orations were given by Ernest Jones and the Austrian author Stefan Zweig. Freud's ashes were later placed in the crematorium's Ernest George Columbarium (see "Freud Corner"). They rest on a plinth designed by his son, Ernst, in a sealed ancient Greek bell krater painted with Dionysian scenes that Freud had received as a gift from Marie Bonaparte, and which he had kept in his study in Vienna for many years. After his wife, Martha, died in 1951, her ashes were also placed in the urn.
Ideas
In founding psychoanalysis Freud developed therapeutic techniques such as the use of free association and discovered transference, establishing its central role in the analytic process. His analysis of dreams as wish-fulfillments provided him with models for the clinical analysis of symptom formation and the underlying mechanisms of repression. On this basis Freud elaborated his theory of the unconscious and went on to develop a model of psychic structure comprising id, ego and super-ego. In his later work Freud developed a wide-ranging interpretation and critique of religion and culture.
Though in overall decline as a diagnostic and clinical practice, psychoanalysis remains influential within psychology, psychiatry, and psychotherapy, and across the humanities. It thus continues to generate extensive and highly contested debate concerning its therapeutic efficacy, its scientific status, and whether it advances or hinders the feminist cause. Nonetheless, Freud's work has suffused contemporary Western thought and popular culture.
Early work
Freud began his study of medicine at the University of Vienna in 1873. He took almost nine years to complete his studies, due to his interest in neurophysiological research, specifically investigation of the physiology of the fish nervous system, and because of his interest in studying philosophy with Franz Brentano. He entered private practice in neurology for financial reasons, receiving his M.D. degree in 1881 at the age of 25. Amongst his principal concerns in the 1880s was the anatomy of the brain, specifically the medulla oblongata. He intervened in the important debates about aphasia with his monograph of 1891, Zur Auffassung der Aphasien, in which he coined the term agnosia and counselled against a too locationist view of the explanation of neurological deficits. Like his contemporary Eugen Bleuler, he emphasized brain function rather than brain structure.
Freud was also an early researcher in the field of cerebral palsy, which was then known as "cerebral paralysis". He published several medical papers on the topic and showed that the disease existed long before other researchers of the period began to notice and study it. He also suggested that William John Little, the man who first identified cerebral palsy, was wrong about lack of oxygen during birth being a cause. Instead, he suggested that complications in birth were only a symptom.
The origin of Freud's early work with psychoanalysis can be linked to Josef Breuer. Freud credited Breuer with opening the way to the discovery of the psychoanalytical method by his treatment of the case of Anna O. In November 1880, Breuer was called in to treat a highly intelligent 21-year-old woman (Bertha Pappenheim) for a persistent cough and hallucinations that he diagnosed as hysterical. He found that while nursing her dying father, she had developed some transitory symptoms, including visual disorders and paralysis and contractures of limbs, which he also diagnosed as hysterical. Breuer began to see his patient almost every day as the symptoms increased and became more persistent, and observed that she entered states of absence. He found that when, with his encouragement, she told fantasy stories in her evening states of absence her condition improved, and most of her symptoms had disappeared by April 1881. Following the death of her father in that month her condition deteriorated again. Breuer recorded that some of the symptoms eventually remitted spontaneously and that full recovery was achieved by inducing her to recall events that had precipitated the occurrence of a specific symptom. In the years immediately following Breuer's treatment, Anna O. spent three short periods in sanatoria with the diagnosis "hysteria" with "somatic symptoms", and some authors have challenged Breuer's published account of a cure. Richard Skues rejects this interpretation, which he sees as stemming from both Freudian and anti-psychoanalytical revisionism — revisionism that regards both Breuer's narrative of the case as unreliable and his treatment of Anna O. as a failure.
The unconscious
The concept of the unconscious was central to Freud's account of the mind. Freud believed that while poets and thinkers had long known of the existence of the unconscious, he had ensured that it received scientific recognition in the field of psychology.
Freud states explicitly that his concept of the unconscious as he first formulated it was based on the theory of repression. He postulated a cycle in which ideas are repressed, but remain in the mind, removed from consciousness yet operative, then reappear in consciousness under certain circumstances.
In his account of the development and modification of his theory of unconscious mental processes he sets out in his 1915 paper 'The Unconscious' (Standard Edition XIV), Freud identifies the three perspectives he employs: the dynamic, the economic and the topographical.
The dynamic perspective concerns firstly the constitution of the unconscious by repression and secondly the process of "censorship" which maintains unwanted, anxiety-inducing thoughts as such. Here Freud is drawing on observations from his earliest clinical work in the treatment of hysteria.
In the economic perspective the focus is on the trajectories of the repressed contents as they undergo complex transformations in the process of both symptom formation and normal unconscious thought such as dreams and slips of the tongue. These were topics Freud explored in detail in The Interpretation of Dreams and The Psychopathology of Everyday Life.
Whereas both these former perspectives focus on the unconscious as it is about to enter consciousness, the topographical perspective represents a shift in which the systemic properties of the unconscious, its characteristic processes, and modes of operation such as Condensation and Displacement, are placed in the foreground.
This "first topography" presents a model of psychic structure comprising three systems:
- The System Ucs – the unconscious
- The System Pcs – the preconscious
- The System Cns – conscious thought governed by the reality principle
In his later work, notably in The Ego and the Id (1923), a second topography is introduced comprising id, ego and super-ego, which is superimposed on the first without replacing it. In this later formulation of the concept of the unconscious the id comprises a reservoir of instincts or drives, a portion of them being hereditary or innate, a portion repressed or acquired. As such, from the economic perspective, the id is the prime source of psychical energy and from the dynamic perspective it conflicts with the ego and the super-ego which, genetically speaking, are diversifications of the id.
Id, ego, and super-ego
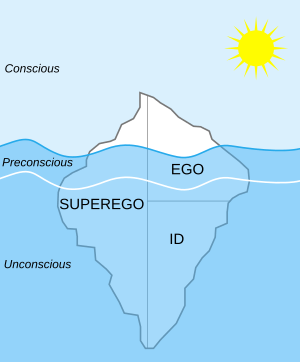
Freud proposed that the human psyche could be divided into three parts: Id, ego, and super-ego. The id is the unconscious portion of the psyche that operates on the "pleasure principle" and is the source of basic impulses and drives; it seeks immediate pleasure and gratification. Freud acknowledged that his use of the term Id (das Es, "the It") derives from the writings of Georg Groddeck.
The super-ego is the moral component of the psyche. The rational ego attempts to exact a balance between the impractical hedonism of the id and the equally impractical moralism of the super-ego; it is the part of the psyche that is usually reflected most directly in a person's actions. When overburdened or threatened by its tasks, it may employ defence mechanisms including denial, repression, undoing, rationalization, and displacement.
Freud compared the relationship between the ego and the id to that between a charioteer and his horses: the horses provide the energy and drive, while the charioteer provides direction.
Religion
Freud regarded the monotheistic God as an illusion based upon the infantile emotional need for a powerful, supernatural pater familias. He maintained that religion – once necessary to restrain man's violent nature in the early stages of civilization – in modern times, can be set aside in favor of reason and science.
Moreover, he perceived religion, with its suppression of violence, as mediator of the societal and personal, the public and the private, the forces of life and death. Later works indicate Freud's pessimism about the future of civilization.
Legacy

Freud's legacy, though a highly contested area of controversy, has been assessed as "one of the strongest influences on twentieth-century thought, its impact comparable only to that of Darwinism and Marxism," with its range of influence permeating "all the fields of culture ... so far as to change our way of life and concept of man."
Psychotherapy
Though not the first methodology in the practice of individual verbal psychotherapy, Freud's psychoanalytic system came to dominate the field from early in the twentieth century, forming the basis for many later variants. While these systems have adopted different theories and techniques, all have followed Freud by attempting to achieve psychic and behavioral change through having patients talk about their difficulties.
Philosophy
Freud has been compared to Marx by Reich, who saw Freud's importance for psychiatry as parallel to that of Marx for economics, and by Paul Robinson, who sees Freud as a revolutionary whose contributions to twentieth-century thought are comparable in importance to Marx's contributions to the nineteenth-century thought.
Works
Books
- 1891 On Aphasia
- 1895 Studies on Hysteria (co-authored with Josef Breuer)
- 1899 The Interpretation of Dreams
- 1901 On Dreams (abridged version of The Interpretation of Dreams)
- 1904 The Psychopathology of Everyday Life
- 1905 Jokes and Their Relation to the Unconscious
- 1907 Delusion and Dream in Jensen's Gradiva
- 1910 Five Lectures on Psycho-Analysis
- 1910 Leonardo da Vinci, A Memory of His Childhood
- 1915–17 Introductory Lectures on Psycho-Analysis
- 1921 Group Psychology and the Analysis of the Ego
- 1923 The Ego and the Id
- 1926 Inhibitions, Symptoms and Anxiety
- 1926 The Question of Lay Analysis
- 1927 The Future of an Illusion
- 1930 Civilization and Its Discontents
- 1933 New Introductory Lectures on Psycho-Analysis
- 1939 Moses and Monotheism
- 1940 An Outline of Psychoanalysis
- 1967 Thomas Woodrow Wilson: A Psychological Study, with William C. Bullit
See also
 In Spanish: Sigmund Freud para niños
In Spanish: Sigmund Freud para niños
- The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud
- Sigmund Freud Archives
- Freud Museum (London)
- Sigmund Freud Museum (Vienna)
- A Clinical Lesson at the Salpêtrière
- Afterwardsness
- Freudian slip
- Freudo-Marxism
- School of Brentano
- Hedgehog's dilemma
- Narcissism of small differences
- Hidden personality
- Histrionic personality disorder
- Psychoanalytic literary criticism
- Psychodynamics
- Saul Rosenzweig
- Signorelli parapraxis
- The Freudian Coverup
- Uncanny






