Miami Beach, Florida facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Miami Beach
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| City of Miami Beach | |||

The southern portion of Miami Beach, known as South Beach (foreground), and Downtown Miami (background) in April 2006
|
|||
|
|||
Location of Miami Beach in Miami-Dade County and of Miami-Dade County in Florida
|
|||
U.S. Census Bureau map showing Miami Beach's city limits
|
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| County | |||
| Incorporated | March 26, 1915 | ||
| Named for | Miami River | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Commission-Manager | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 15.22 sq mi (39.42 km2) | ||
| • Land | 7.69 sq mi (19.92 km2) | ||
| • Water | 7.53 sq mi (19.49 km2) 62.37% | ||
| Elevation | 4 ft (1.2 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 82,890 | ||
| • Estimate
(2022)
|
80,017 | ||
| • Rank | 35th in Florida | ||
| • Density | 10,405.33/sq mi (4,016.92/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| Zip Codes |
33109, 33139, 33140, 33141.
|
||
| Area code(s) | 305, 786, 645 | ||
| FIPS code | 12-45025 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 286750 | ||
Miami Beach is a fun resort city in Florida, United States. It's part of the larger Miami metropolitan area. This city is special because it's built on both natural and human-made islands. These islands are located between the Atlantic Ocean and Biscayne Bay. The bay separates Miami Beach from the main city of Miami.
One of the most famous parts of Miami Beach is South Beach. This area, along with Downtown Miami, is a major center for business and tourism in South Florida. In 2020, about 82,890 people lived in Miami Beach. It has been a popular beach resort for visitors since the early 1900s.
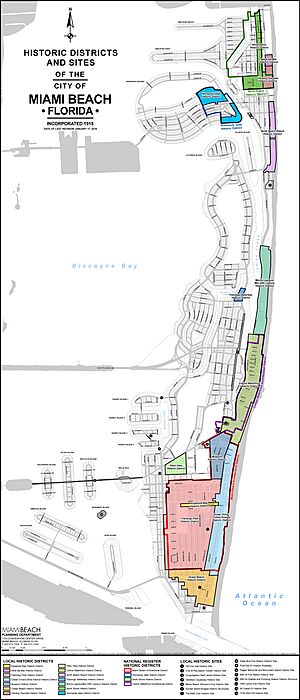
A very important part of Miami Beach is its Art Deco Historic District. This area was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. It's the biggest collection of Art Deco buildings in the world! Hundreds of hotels, apartments, and other buildings built between 1923 and 1943 are found here. You can see different styles like Mediterranean, Streamline Moderne, and Art Deco.
The Art Deco District is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Lenox Court to the west, 6th Street to the south, and Dade Boulevard to the north. A designer named Barbara Baer Capitman helped save these amazing buildings. Today, a street in the district is named after her.
Contents
History of Miami Beach
In 1870, a father and son, Henry and Charles Lum, bought the land that would become Miami Beach for a very low price. The first building there was the Biscayne House of Refuge in 1876. It was built to help shipwrecked people. Later, in the 1880s, some business people tried to grow coconuts, but it didn't work out.
However, one investor, John S. Collins, found success by growing avocados. His family saw how great the beach could be as a vacation spot. In the early 1900s, Collins, the Pancoast family, the Lummus brothers (who were bankers), and Indianapolis businessman Carl G. Fisher started developing the area. Before this, people could only visit the beach by taking a ferry from Miami.
By 1912, Collins and Pancoast were clearing land and building canals to transport their avocado crops. They also started the Miami Beach Improvement Company. The first hotel, Brown's Hotel, was built in 1915. Much of the land was a thick jungle of mangroves, which was expensive to clear.
Collins began building a long wooden bridge to connect the island to the mainland. It was the longest wooden bridge in the world at the time! When he ran out of money, Carl Fisher helped finish the bridge. This deal started the first big real estate boom on the island. Fisher promoted Miami Beach as a fun place for wealthy people to visit in the winter. By 1915, many important people lived on the island. There were also hotels, bath houses, an aquarium, and a golf course.
Miami Beach officially became a town on March 26, 1915, and a city in 1917. Carl Fisher was key to its growth in the 1920s. He wanted wealthy people from the north to build their winter homes there. Many grand hotels were built, like the Flamingo Hotel and the Roney Plaza Hotel.
In the 1920s, much of Miami Beach was created by adding land from dredging Biscayne Bay. Islands like Star, Palm, and Hibiscus Islands are all human-made. The great 1926 Miami hurricane slowed down this growth. But in the 1930s, Miami Beach still attracted tourists. Many smaller hotels were built, which now make up the famous "Art Deco" historic district.
After World War II, many people moved to South Florida, and Miami Beach's population grew a lot. Later, in 1959, many Cuban refugees came to South Florida, changing the area's population even more.
Geography of Miami Beach
Miami Beach covers about 15.22 square miles (39.42 square kilometers). About half of this area is land, and the other half is water.
Rising Sea Levels in Miami Beach

Miami Beach sometimes experiences "sunny day flooding" during very high tides, called king tides. This happens because some parts of the city are very low, almost at sea level. A study from the University of Miami showed that this type of flooding has become more common since the mid-2000s.
The city is working on a big plan to deal with sea level rise. This plan includes installing many pumps to remove water. They are also building taller sea walls and raising the level of roads. Some streets and sidewalks have already been raised by about 2.5 feet (0.76 meters). This project costs a lot of money, but it's important for protecting the city from future flooding.
People of Miami Beach
Miami Beach has a diverse population. In 2020, the city had about 82,890 residents. Over the years, the population has changed, with more people moving in from different parts of the world.
Many people in Miami Beach speak Spanish, in addition to English. This reflects the large number of residents with Hispanic or Latino backgrounds, especially from Cuba and other Latin American countries. There are also people from many other parts of the world, making Miami Beach a truly international city.
Economy and Tourism
Tourism is a huge part of Miami Beach's economy. More than half of all tourists who visit Miami-Dade County stay in Miami Beach. In 2017, over 15 million people visited the county, and most of them stayed in Miami Beach hotels.
The money from tourism, like resort taxes, helps fund many city services. This tax revenue brings in millions of dollars each year. Miami Beach has more than 26,600 hotel rooms, and they are usually very busy. A former mayor, Harold Rosen, helped bring Miami Beach back to life in the 1970s by ending rent control.
The Miami Beach Visitor and Convention Authority
This group helps promote Miami Beach as a great place to visit. It's made up of seven people chosen by the city. Their job is to tell the world about all the fun things to do in Miami Beach and support the tourism industry.
Arts and Culture in Miami Beach

South Beach (often called SoBe) is a very popular area in Miami Beach. It stretches from Biscayne Street to about 23rd Street. Years ago, before the TV show Miami Vice made it famous, South Beach had many empty buildings. Today, it's known for its shops and restaurants.
Miami Beach has also been featured in movies like Scarface and The Birdcage.
Lincoln Road is a famous street that runs east to west. It's a great place for outdoor dining and shopping. You can find art galleries featuring works by famous artists like Romero Britto. To keep it safe and enjoyable for everyone, the city passed a rule in 2015. It stops people from bicycling or rollerblading on Lincoln Road during busy times.
Places to Visit

- Bass Museum
- Eden Roc Miami Beach Hotel
- The Fillmore Miami Beach (a theater)
- Flagler Monument Island
- Fontainebleau Hotel
- Versace Mansion
- Holocaust Memorial
- Jewish Museum of Florida
- Lincoln Road
- Miami Beach Architectural District
- Miami Beach Botanical Garden
- North Beach
- Ocean Drive
- South Beach
- South Pointe Park
- Wolfsonian-FIU Museum
- The Setai Hotel
Saving Historic Buildings
In the 1970s, many people started flying to other warm places for vacations. This made Miami Beach's economy struggle. City planners wanted to tear down many old Art Deco buildings from the 1930s. There were over 800 of these unique buildings!
In 1976, Barbara Baer Capitman and other activists formed a group called the Miami Design Preservation League (MDPL). They fought to stop the destruction of these historic buildings. In 1979, they succeeded in getting the Miami Beach Art Deco District listed on the National Register of Historic Places. This helped bring attention to the buildings.
Because of this new awareness, tourists and even TV and movie crews started coming to South Beach. Investors began to fix up the old hotels, restaurants, and apartments.
Even though many people loved the historic buildings, there weren't strong laws to protect them. When demolition crews threatened buildings, MDPL members would protest. Sometimes, they even stood in front of hotels to block bulldozers!
After many years, Miami Beach created its first historic preservation districts in 1986. These districts covered areas like Espanola Way and parts of Ocean Drive. This helped protect buildings from being torn down and set rules for how they could be renovated.
Some investors, like Tony Goldman and Ian Schrager, bought Art Deco hotels and turned them into famous places in the 1980s and 90s. Many celebrities, including Madonna and Oprah Winfrey, visited Miami Beach. More historic districts were added later, protecting even more unique buildings, including those with MiMo (Miami Modern) style.
The Arts Scene
Famous comedian and actor Jackie Gleason moved his TV show to Miami Beach in 1964. He often praised the city on his show, calling the audience "the greatest in the world!" His show, The Jackie Gleason Show, was filmed at the Miami Beach Auditorium, which is now called the Fillmore Miami Beach.
Every December, Miami Beach hosts Art Basel Miami Beach. This is one of the biggest art shows in the United States. It brings together art galleries from all over the world. There are also special exhibitions, parties, and events featuring music, film, and design. The main show is at the Miami Beach Convention Center, but other events happen all around the city. The first Art Basel Miami Beach was held in 2002, and it now attracts tens of thousands of visitors.
Miami Beach is also home to the New World Symphony, a famous orchestra. In 2011, they moved into the amazing New World Center building, designed by the famous architect Frank Gehry. This building has a huge outdoor projection wall where visitors can watch concerts and events for free!
The Miami City Ballet, a ballet company started in 1985, has its home near the Bass Museum of Art. Miami Beach also hosts an annual outdoor art festival called the Miami Beach Festival of the Arts.
Jewish Community
Miami Beach has a strong Jewish community. There are many synagogues and schools, including the Landow Yeshiva, which has been open for over 30 years. Many Jewish families and retirees, especially those who come to Florida for the winter, enjoy the warm weather here. The famous writer Isaac Bashevis Singer lived in Miami Beach until he passed away in 1991.
You can find many kosher restaurants in Miami Beach. The city is also home to the Holocaust Memorial of the Greater Miami Jewish Federation, a place to remember those who suffered during the Holocaust.
LGBT Community
Miami Beach has been known as a very welcoming place for the lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender community for many years. It has many gay-friendly businesses and events. In the late 1980s and 1990s, many LGBT people moved to South Beach. They helped restore old Art Deco hotels and started new businesses, which helped the city become popular again.
Miami Beach has also passed laws to protect human rights, including for transgender people. This makes the city one of the most progressive in Florida. The annual Miami Beach Pride celebration has grown very popular since it started in 2009. It attracts over 130,000 people each year and has featured many celebrities.
Education in Miami Beach
The Miami-Dade County Public Schools system serves Miami Beach.
- North Beach Elementary
- Treasure Island Elementary
- South Pointe Elementary
- Mater Beach Academy
- Biscayne Elementary
- Fienberg/Fisher K–8 Center
- Nautilus Middle School
- Miami Beach Senior High School
There are also private schools like Rabbi Alexander S. Gross Hebrew Academy and St. Patrick Catholic School. The first high school building, Miami Beach High, was built in 1926.
Colleges and Universities
Florida International University has a campus on Lincoln Road in South Beach. Here, students can study architecture, art, music, and theater.
Getting Around Miami Beach
Transportation
Public transportation in Miami Beach is run by Miami-Dade Transit. Many people in Miami Beach use public transit, especially buses. The South Beach Local (SBL) bus is very popular. It connects all the main spots in South Beach to other bus lines in the city.
Bicycling
Riding bikes has become very popular in Miami Beach. Because the city is dense and has streets that are easy to walk on, many residents choose to bike.
In 2011, a public bicycle sharing system called Decobike started. It's one of the few programs like it in the United States. You can rent bikes from many stations throughout Miami Beach.
Famous People from Miami Beach
- George Abbott, playwright and director
- Desi Arnaz, entertainer
- Shmuley Boteach, rabbi and author
- Barbara Baer Capitman, historic preservation activist
- Al Capone, mobster (lived here)
- David Caruso, actor
- John S. Collins, horticulturist and developer
- Carl Graham Fisher, developer of Miami Beach
- Barry Gibb, singer (Bee Gees)
- Jackie Gleason, comedian and TV host
- Tony Goldman, real estate developer
- Meyer Lansky, mobster (lived here)
- Floyd Mayweather Jr., boxer
- Gianni Versace, fashion designer (lived here)
Sister Cities
Miami Beach has 13 sister cities around the world. This means they have special friendly relationships with these cities:
 Almonte, Spain
Almonte, Spain Marbella, Spain
Marbella, Spain Fortaleza, Brazil
Fortaleza, Brazil Santa Marta, Colombia
Santa Marta, Colombia Český Krumlov, Czech Republic
Český Krumlov, Czech Republic Nahariya, Israel
Nahariya, Israel Pescara, Italy
Pescara, Italy Fujisawa, Japan
Fujisawa, Japan Cozumel, Mexico
Cozumel, Mexico Ica, Peru
Ica, Peru Basel, Switzerland
Basel, Switzerland Brampton, Canada
Brampton, Canada Asmara, Eritrea
Asmara, Eritrea
See also
 In Spanish: Miami Beach para niños
In Spanish: Miami Beach para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |