United States Marine Corps facts for kids
Quick facts for kids United States Marine Corps |
|
|---|---|

Emblem of the United States Marine Corps
|
|
| Founded | 11 July 1798 (227 years, 7 months) (in current form) 10 November 1775 |
| Country | United States |
| Type | Maritime land force |
| Role |
|
| Size | |
| Part of | United States Armed Forces Department of the Navy |
| Headquarters | The Pentagon Arlington County, Virginia, U.S. |
| Nickname(s) | "Jarheads", "Devil Dogs" ("Teufels Hunde"), "Leathernecks" |
| Motto(s) | Semper fidelis ("Always faithful") |
| Colors | Scarlet and gold |
| March | "Semper Fidelis" |
| Mascot(s) | English bulldog |
| Anniversaries | 10 November |
| Equipment | List of USMC equipment |
| Engagements |
See list
American Revolutionary War
Quasi-War First Barbary War War of 1812 Second Barbary War West Indies Anti-Piracy Operations Seminole Wars African Anti-Slavery Operations Aegean Sea Anti-Piracy Operations First Sumatran expedition Second Sumatran expedition United States Exploring Expedition Capture of Monterey Mexican–American War Bombardment of Greytown Battle of Ty-ho Bay First Fiji Expedition Second Opium War Third Fiji expedition Paraguay expedition Reform War John Brown's raid American Civil War Bombardment of Qui Nhon Shimonoseki Campaign Formosa Expedition United States expedition to Korea Egyptian Expedition (1882) Bering Sea Anti-Poaching Operations Overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii Second Samoan Civil War Banana Wars
Philippine–American War Boxer Rebellion World War I Russian Civil War World War II Korean War Vietnam War 1958 Lebanon Crisis Occupation of the Dominican Republic (1965) Iranian hostage rescue Multinational Force in Lebanon Operation Urgent Fury 1986 bombing of Libya Tanker War
Operation Just Cause Persian Gulf War Somali Civil War |
| Decorations | Presidential Unit Citation
Vietnam Civil Actions Medal |
| Commanders | |
| Commander-in-Chief | |
| Secretary of Defense | |
| Secretary of the Navy | |
| Commandant | |
| Assistant Commandant | |
| Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps | |
| Insignia | |
| Flag |  |
| Seal |  |
| Emblem ("Eagle, Globe, and Anchor" or "EGA") |  |
| Wordmark | |
| Song | "The Marines’ Hymn" |
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), often called the U.S. Marines, is a special part of the United States Armed Forces. It acts as a land force that works closely with the Navy. The Marines are experts at fighting on land and sea, especially in quick missions far from home.
They use their own infantry (foot soldiers), artillery (big guns), air support, and special teams. The U.S. Marine Corps is part of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six main armed forces of the United States.
The Marine Corps has been linked with the United States Department of the Navy since 1834. Marines operate from bases on land and from special ships called amphibious warfare ships. Some Marine air squadrons also fly from Navy aircraft carriers.
The Marine Corps started on November 10, 1775, in Philadelphia. Back then, they were called the Continental Marines. They were soldiers who could fight both at sea and on shore. During World War II, Marines led many island-hopping battles in the Pacific. As of December 2024, there are about 169,000 active-duty Marines and 33,000 in the reserves.
Contents
What Do the Marines Do?
The U.S. Marine Corps has three main jobs, as set out by law. These jobs help them support the country's defense.
- They capture or defend naval bases and do other land operations to help Navy missions.
- They create new ways of fighting, equipment, and training for landing forces. They do this with the Army and Air Force.
- They perform any other duties the President or Department of Defense asks them to do.
This last point means Marines are often called upon for many different tasks. They are known for being ready to act quickly in foreign affairs. They use the Navy's ships to get to places fast.
The Marine Band plays music for important events at the White House. It is known as the "President's Own." Marines also guard presidential retreats like Camp David. Special Marine helicopters fly the President and Vice President. These helicopters are called "Marine One" and "Marine Two." Marines also protect American embassies around the world. They serve in over 140 locations.
How the Marine Mission Changed
The Marine Corps first started to protect ships and their crews. They fought during boarding actions and stopped mutinies. Their first landing was in 1776 during the American Revolutionary War. They took control of British forts in the Bahamas.
Over time, their role grew beyond just ship duties. They became experts in fighting on land. In the early 1900s, they focused on taking bases and supporting Navy campaigns. Today, Marines no longer serve on every Navy ship. Their main focus is on being a rapid response force.
Marine Strengths and Abilities
The Marine Corps is vital for amphibious warfare. This means they can attack from the sea onto land. They can quickly send a team with ground troops, air support, and supplies anywhere in the world. This team is called a Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF).
Marines believe that "Every Marine is a rifleman." This means all Marines, no matter their job, learn basic combat skills. During World War II, pilots fought as ground officers when their planes were destroyed. This shows how flexible and ready Marines are. They are taught to understand the goal of an order, then figure out the best way to achieve it.
The Marines developed special ways to attack from the sea. They also pioneered using helicopters to move troops. They are known for their "Operational Maneuver from the Sea" strategy. This allows them to project power from ships.
The Marine Corps relies on the Navy for sealift. This helps them deploy quickly. Marine expeditionary units (MEU) are often at sea. They are ready to respond to global events. The Maritime Pre-Positioning System also helps. It places ships with supplies around the world. These ships carry enough gear for a marine expeditionary force to operate for 30 days.
A Look at Marine History
Early Days and the Revolutionary War
The U.S. Marine Corps began on November 10, 1775. Captain Samuel Nicholas formed two battalions of Marines during the American Revolutionary War. This date is celebrated as the Marine Corps birthday. In 1776, Marines made their first landing in the Bahamas. They captured a British port. They also fought on land with General George Washington at the Battle of Princeton in 1777.
After the Revolution, the Marines were disbanded. They were brought back on July 11, 1798. This was to prepare for a conflict with France. Their most famous early action was in the First Barbary War (1801–1805). They fought against pirates in North Africa. This event is remembered in the Marines' Hymn.
War of 1812 and Growth

During the War of 1812, Marines fought on Navy ships. They also helped defend New Orleans in 1815. They earned a reputation as skilled marksmen. After the war, Archibald Henderson became Commandant in 1820. He helped the Corps take on missions around the world. In the Mexican–American War (1846–1848), Marines famously stormed Chapultepec Palace in Mexico City. This is also mentioned in the Marines' Hymn as the "Halls of Montezuma."
Civil War to World War I

The Marine Corps played a small part in the American Civil War (1861–1865). They helped with blockades and captured New Orleans. After the war, the Corps focused on protecting American interests overseas. They were involved in many missions around the world. In 1868, the Corps adopted its famous emblem. Around 1883, they adopted their motto, "Semper fidelis" (Always Faithful).
During the Spanish–American War (1898), Marines led landings in the Philippines, Cuba, and Puerto Rico. They showed they were ready for quick deployments. From 1899 to 1916, they served in places like China (during the Boxer Rebellion), Panama, and Haiti. They learned a lot about fighting in small conflicts.
World War I and World War II
In World War I, Marines joined the American Expeditionary Forces. They grew a lot during this time. At the Battle of Belleau Wood in 1918, German soldiers supposedly called them Teufel Hunden, or "Devil Dogs." This nickname stuck with the Marines. Opha May Johnson was the first woman to join the Marines in 1918.
In World War II, Marines were crucial in the Pacific War. They fought fiercely in battles like Guadalcanal and Iwo Jima. The Battle of Iwo Jima in 1945 was one of the most famous. Marines faced strong resistance but raised the American flag on Mount Suribachi. About 600,000 Americans served as Marines in World War II. Nearly 87,000 became casualties, and 82 received the Medal of Honor.

Korean War and Vietnam War
The Korean War (1950–1953) saw Marines make a famous landing at Inchon. This helped turn the tide of the war. Later, the 1st Marine Division fought bravely during the difficult Battle of Chosin Reservoir. Marines played a key role in many battles until the war ended in 1953. Over 30,000 Marines were killed or wounded.
Marines also served in the Vietnam War. They took part in major battles like the Battle of Hue and the Battle of Khe Sanh in 1968. They fought both against guerrilla forces and the North Vietnamese Army. Marines left Vietnam in 1971. They returned briefly in 1975 for rescue missions. This was the longest war for the Marines at that time.
Recent Operations
After Vietnam, Marines continued their role as an expeditionary force. In 1983, a bombing in Beirut caused many Marine casualties. This led to the American withdrawal from Lebanon. Marines also helped in Grenada and Panama. During the Gulf War (1990–1991), Marines helped free Kuwait. They also provided humanitarian aid in Somalia (1992–1995).

After the attacks of September 11, 2001, Marines joined the Global War on Terrorism. They served in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2014. They fought in places like Helmand Province and the Battle of Marjah. Marines also served in the Iraq War. They led the 2003 invasion and later took responsibility for Al Anbar Province. They fought in intense battles in cities like Fallujah. Marines returned to Iraq in 2014 to help with growing challenges. They also supported operations in Africa to counter extremism and piracy.
Adapting for New Challenges
In the 2020s, the Marine Corps began to focus more on challenges in the Indo-Pacific region. They are strengthening their forces to operate in island environments. This includes working with the Australian military in Darwin.
Helping at Home
Marines have also helped within the United States. In 1992, Marines were deployed to Los Angeles to help restore order during civil unrest. In 2025, Marines were again deployed to Los Angeles to protect federal personnel and property during protests.
How the Marines Are Organized
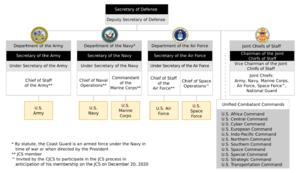
The Marine Corps is part of the United States Department of the Navy. This department also oversees the Navy. The top Marine officer is the Commandant. The Commandant makes sure the Marines are ready for missions.
Marine Headquarters and Forces
The Headquarters Marine Corps (HQMC) includes the Commandant and other leaders. They manage the Marine Corps's daily operations.
The main fighting forces are called the Operating Forces. These include Fleet Marine Forces (FMF) that work with Navy fleets. They also have Security Forces that guard important Navy bases. Additionally, Security Guard detachments protect American embassies worldwide.
Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF)
The basic way Marines organize for missions is called a Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF). A MAGTF is a flexible team. It includes ground troops, air support, and logistics (supplies). This team can work on its own or with larger groups. MAGTFs help the Marines be self-sufficient and ready for any mission.
Support and Training
The Supporting Establishment helps the Marines in many ways. It includes commands for training, logistics, and development. It also includes the famous Marine Band.
Marine Corps Bases
The Marine Corps has many important bases. Key bases include Camp Pendleton in California and Camp Lejeune in North Carolina. Camp Butler is in Okinawa, Japan. Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms in California is their largest training base. Marine Corps Base Quantico in Virginia is known as the "Crossroads of the Marine Corps."
Marine Reserves
The Marine Forces Reserve (MARFORRES) is made up of part-time Marines. They can form their own force or help active-duty Marines when needed.
Special Operations Marines
The United States Marine Forces Special Operations Command (MARSOC) includes the Marine Raider Regiment. These are highly trained special operations forces. They are experts in difficult and dangerous missions. MARSOC also has a training center to prepare these elite Marines.
Some Marine expeditionary units (MEUs) are also certified as "special operations capable" (MEU(SOC)). This means they have extra training for special missions.
Who Are the Marines?
Marine Leaders
The Commandant is the highest-ranking officer in the Marine Corps. The Commandant leads the Corps and reports to the Secretary of the Navy. The Assistant Commandant is the second-in-command. The Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps is the top enlisted Marine. They advise the Commandant on important matters.
Women in the Marines
Women have served in the Marine Corps since 1918. Opha May Johnson was the first woman to enlist. In 2017, women began joining infantry battalions for the first time. The Marine Corps started a program in 2020 to integrate women into recruit training in San Diego. By April 2021, 53 female recruits successfully graduated there. As of October 2019, women make up about 7.8% of Marine personnel.
Racial Integration
African Americans served in the Marines during the Revolutionary War. However, for many years, they were not allowed to join. In 1942, a presidential order led the Corps to begin recruiting African American Marines. They trained in separate units at a place called Montford Point. About 20,000 African Americans trained there until 1949. Montford Point was later renamed Camp Gilbert H. Johnson. Today, the Marine Corps is fully integrated, with people from all backgrounds serving together.
Marine Ranks
Marines have different ranks, like officers, warrant officers, and enlisted personnel.
| US DoD pay grade |
O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
| Insignia |  |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Service uniform insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Blue dress uniform insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Title | General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | First lieutenant | Second lieutenant |
| Abbreviation | Gen | LtGen | MajGen | BGen | Col | LtCol | Maj | Capt | 1stLt | 2ndLt |
- Commissioned Officers are leaders who hold a special authority from the President.
- Warrant Officers are experts in specific fields. They provide leadership in their specialty.
| US DoD pay grade |
Special | E-9 | E-8 | E-7 | E-6 | E-5 | E-4 | E-3 | E-2 | E-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | ||||
| Dress uniform insignia |
No insignia |
||||||||||||
| Service uniform insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Title | Senior Enlisted Advisor to the Chairman | Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps | Sergeant Major | Master Gunnery Sergeant | First Sergeant | Master Sergeant | Gunnery Sergeant | Staff Sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Private First Class | Private |
| Abbreviation | SEAC | SMMC | SgtMaj | MGySgt | 1stSgt | MSgt | GySgt | SSgt | Sgt | Cpl | LCpl | PFC | Pvt |
- Enlisted Marines make up most of the Corps. They include junior Marines, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and staff non-commissioned officers (SNCOs). NCOs and SNCOs supervise junior Marines and advise commanders. The Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps is the highest-ranking enlisted Marine.
Marine Jobs (MOS)
Every Marine has a Military Occupational Specialty (MOS). This is a four-digit code that describes their job. It tells what field and specific work a Marine does.
Training to Become a Marine
Each year, thousands of new Marines join the Corps. All new Marines are recruited by the Marine Corps Recruiting Command.
- Officers usually come from college programs or Officer Candidates School. After commissioning, they attend The Basic School. Here, they learn infantry and combat skills.
- Enlisted Marines go to boot camp. This training happens at Marine Corps Recruit Depot San Diego or Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island. Boot camp is 13 weeks long. After boot camp, Marines go to the United States Marine Corps School of Infantry. They learn combat skills before going to their specific job schools.
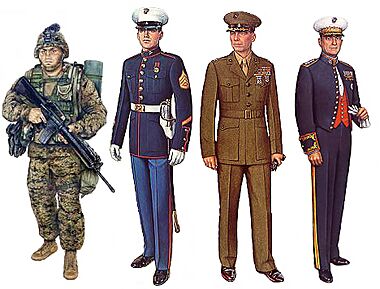
What Marines Wear
Marine uniforms are very distinct and have a long history. They have four main types of uniforms: dress, service, utility, and physical training.
- The dress uniform is the most formal. It is worn for special events. The "Blue Dress" uniform, often called "Dress Blues," is very famous.
- The service uniform is for daily work in offices or less formal settings. It is olive green and khaki.
- The utility uniform is for field work or dirty jobs. It uses MARPAT camouflage patterns. Marines wear these uniforms on base but not usually off-base.
Marine Corps Culture and Traditions
Marines have many traditions that make their service special. These traditions help build strong bonds among them. They also use many naval terms from their history with the Navy. Marines are called "Marines," not "soldiers" or "sailors."
Official Traditions
- The Marine Corps emblem is the Eagle, Globe, and Anchor (EGA). It was adopted in 1868.
- The official colors are scarlet and gold.
- The Marine motto is Semper Fidelis, which means Always Faithful in Latin. It is often shortened to Semper Fi.
- The "Marines' Hymn" is the oldest official song in the U.S. armed forces.
- The Marine Corps Birthday is celebrated every year on November 10. It includes a cake-cutting ceremony.
- Marines use two types of swords: the officers' Mameluke Sword and the Marine NCO sword.
Unofficial Traditions
Marines have several nicknames:
- Devil Dog: Legend says German soldiers called Marines "Teufelshunde" (Devil Dogs) in World War I.
- Gyrene: A common term among Marines.
- Leatherneck: Refers to a leather collar once part of the Marine uniform.
- Jarhead: A nickname with several possible origins.
Other traditions include:
- Oorah is a common shout among Marines.
- Semper Fi is a common greeting.
- Improvise, Adapt and Overcome is a popular saying.
Marine Martial Arts
In 2001, the Marine Corps started its own martial arts program (MCMAP). This program teaches Marines different fighting styles. It helps them control situations without always using lethal force. MCMAP also helps build a strong "Warrior Ethos" in Marines. Marines earn different colored belts, from tan to black, as they progress.
Marine Corps Equipment
Marines use a wide range of equipment for their missions.
Infantry Weapons
- The main rifle for infantry Marines is the M27 IAR. Other Marines use the M4 carbine.
- The standard pistol is the SIG Sauer M17/M18.
- Machine guns like the M249 SAW and M240 provide heavy fire.
- Grenade launchers like the M320 and mortars provide indirect fire.
- Heavy machine guns like the M2 .50 caliber and MK19 automatic grenade launcher are also used.
- Snipers use rifles like the M40 series and Barrett M107.
- Marines also use rockets and missiles like the SMAW and FGM-148 Javelin to fight armored vehicles.
Ground Vehicles
- Marines use the HMMWV, which is being replaced by the Joint Light Tactical Vehicle (JLTV).
- The LAV-25 is a wheeled armored vehicle for quick movement.
- The AAV-7A1 is an armored vehicle that can travel on land and water. It will be replaced by the Amphibious Combat Vehicle.
- Heavily armored vehicles called Mine Resistant Ambush Protected vehicles protect against bombs.
- They use the M777 155mm howitzer and High Mobility Artillery Rocket System for artillery support.
- In 2020, the Marine Corps removed its M1A1 Abrams tanks. This was to focus on different types of challenges.
Aircraft
Marine Corps Aviation provides air support for ground forces.
- Light attack and transport helicopters include the Bell UH-1Y Venom and Bell AH-1Z Viper.
- Medium-lift transport is done by the MV-22 Osprey tiltrotor aircraft.
- Heavy-lift helicopters are the CH-53E Super Stallion, being replaced by the CH-53K.
- Attack jets include the AV-8B Harrier II.
- Fighter/attack missions are handled by the F/A-18 Hornet. Both are being replaced by the F-35 Lightning II.
- The KC-130 Hercules refuels aircraft and transports equipment.
- Marines also use unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) for scouting.
- Special helicopters like the VH-3D Sea King and VH-60N Whitehawk transport the President. These are known as Marine One.
- A Marine Corps C-130 aircraft, "Fat Albert," supports the Navy's "Blue Angels" flight team.
Working with Other Military Branches
The Marine Corps works closely with other parts of the U.S. military.
The Navy and Marine Corps have a very close relationship. They are often called the "Navy-Marine Corps Team." Both report to the Secretary of the Navy. The Navy provides transport, supplies, and combat support for Marine missions. Many Marine pilots and medical staff are trained by the Navy. Sailors who work with Marines, like Hospital Corpsmen, often wear Marine uniforms with Navy badges.
With the U.S. Army
The Marine Corps and Army both conduct land operations. However, the Army has much larger and more varied forces. The Marines focus on smaller, faster-deploying units with their own air support.
With the U.S. Air Force
The Air Force helps the Marine Corps with airlift (moving Marines and equipment by air). They also provide close air support for Marines on the ground.
With the U.S. Coast Guard
The Marine Corps and Coast Guard share some training. They work together at facilities like the Joint Maritime Training Center.
Marine Corps Budget
The Marine Corps gets its funding from the Department of the Navy. For the year 2019, the Marine Corps received $43.2 billion in funding. In 2013, the USMC was the first American military branch to have its annual budget fully checked.
| Area | FY2018 | FY2019 |
|---|---|---|
| Military Personnel | 13,197 | 13,888 |
| Reserve Personnel | 763 | 785 |
| Medicare-Eligible Retiree Health Fund Contribution | 903 | 831 |
| Medicare-Eligible Retiree Health Fund Contribution, Reserves | 81 | 74 |
| Operation and Maintenance | 8,118 | 7,843 |
| Operation and Maintenance, Reserve | 287 | 275 |
| Procurement | 2,019 | 2,858 |
| Procurement of Ammunition, Navy/Marine Corps | 1,038* | 1,182* |
| Military Construction, Navy and Marine Corps | 1,993* | 2,593* |
| Total Appropriated | 28,399 | 30,329 |
* not exact since certain fields are combined with Navy expenditures
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cuerpo de Marines de los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Cuerpo de Marines de los Estados Unidos para niños
- Marine Corps Key Volunteer Network
- Marine Corps Planning Process
- United States Marine Corps Women's Reserve
- List of United States Marine Corps acronyms and expressions