Electrical engineering facts for kids
Electrical engineers are engineers who create and design things that use electricity to help us. They work to fix or improve devices that run on electricity.
These engineers study many topics, including how to make power, how to control machines, semiconductors (special materials used in electronics), and information technology (like radio waves and computers). To meet new needs, electrical engineering has grown to include special areas like electronic engineering and software engineering.
Contents
What Electrical Engineers Do
Electrical engineering has many different areas, often called subdisciplines. While some electrical engineers focus on just one area, many work with a mix of them. Sometimes, fields like electronic engineering and computer engineering are even seen as separate subjects.
Power Engineering

Power engineering is all about how we make, send, and deliver electricity. It also includes designing things like transformers, electric generators, and electric motors.
Many places have a huge network called a power grid. This grid connects power plants to homes and businesses. Power engineers help design and maintain this grid. They also work on systems that connect to the grid, or even systems that work completely on their own, called off-grid systems.
Control Engineering
Control engineering focuses on making systems behave exactly how we want them to. Engineers use models to understand how different systems work. Then, they design controllers to guide these systems.
To make these controllers, electrical engineers use electronic circuits, special computer chips, and programmable logic control (PLCs). Control engineering is used in many places. It helps control airplanes and even the cruise control in many modern cars. It's also key in industrial automation, where machines do tasks automatically.
Control engineers often use something called feedback. Imagine a car with cruise control. The system constantly checks the car's speed. If the car goes too fast or too slow, the system adjusts the engine's power. This feedback helps the system keep the speed steady.
Electronics Engineering
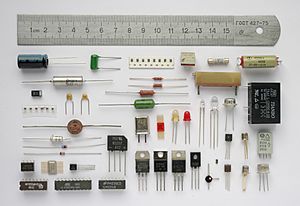
Electronic engineering involves designing and testing electronic circuits. These circuits use parts like resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and transistors. Each part has special properties to make the circuit do something useful.
For example, a special circuit in a radio lets you choose just one station to listen to. Before World War II, this field was mostly called radio engineering. It focused on things like communications, radar, and early TV. After the war, as more everyday devices were made, it grew to include modern TVs, audio systems, computers, and microprocessors.
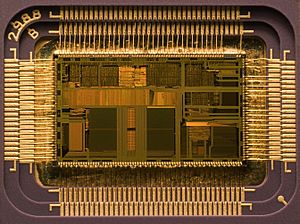
Before 1959, electronic circuits were made from separate, larger parts. These circuits took up a lot of space and used a lot of power. They were also slower. But then, the integrated circuit was invented. These tiny chips can hold millions of small electrical parts, mostly transistors. This invention made powerful computers and other small electronic devices possible.
Microelectronics Engineering
Microelectronics engineering is about designing and making very tiny electronic parts. These parts are used in integrated circuits or sometimes on their own. The most common microelectronic parts are semiconductor transistors. But all main electronic parts, like resistors and capacitors, can be made at a microscopic level.
Nanoelectronics takes this even further, making devices at the nanometer level. Modern devices are already very small, with parts smaller than 100 nanometers being common since about 2002.
Microelectronic parts are made by using chemicals on thin slices of materials like silicon. This process helps control how electricity moves through them. This field uses a lot of chemistry and material science. Electrical engineers in this area need to understand how quantum mechanics affects these tiny parts.
Signal Processing
Signal processing is about looking at and changing signals. Signals can be analog, meaning they change smoothly, like sound waves. Or they can be digital, meaning they are made of separate values, like computer data.
For analog signals, signal processing might make audio signals louder or filter out unwanted sounds. For digital signals, it can compress data to make files smaller. It can also find and fix errors in digital information.
Signal processing is a very math-heavy field. It is at the heart of digital signal processing and is growing fast. It's used in many areas of electrical engineering, like communications, control, radar, and biomedical engineering. Many old analog systems are now being replaced with digital ones.
DSP (Digital Signal Processing) chips are found in almost all modern electronic devices. These include SDTV and HDTV sets, radios, mobile phones, MP3 players, digital cameras, and noise cancelling headphones. They are also used in GPS systems, image processing, and speech processing.
Telecommunications Engineering
Telecommunications engineering focuses on sending information from one place to another. This can be through a coax cable, optical fiber, or even through air. When sending information through the air, it needs to be put onto a carrier signal. This process is called modulation.
Common ways to modulate signals are amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM). The way you choose to modulate affects how much it costs and how well the system works. Engineers must find a good balance.
Once the way information will be sent is decided, telecommunication engineers design the transmitters and receivers. Sometimes these are combined into one device called a transceiver. A key part of designing transmitters is how much power they use. This is linked to how strong the signal will be. If the signal is not strong enough, noise can mess up the information.
Instrumentation Engineering
Instrumentation engineering is about designing devices that measure physical things. These can be things like pressure, flow, or temperature. Designing these tools needs a good understanding of physics, not just electricity.
For example, flight instruments in an airplane measure things like wind speed and altitude. This helps pilots control the aircraft. Also, thermocouples use a special effect to measure temperature differences.
Often, these measuring tools are not used alone. They are usually part of larger electrical systems as sensors. For instance, a thermocouple might help make sure a furnace stays at a constant temperature. Because of this, instrumentation engineering is often seen as working hand-in-hand with control engineering.
Computer Engineering

Computer engineering deals with designing computers and computer systems. This can involve creating new hardware or designing devices like PDAs, tablets, and supercomputers. Computer engineers also use computers to control things like industrial plants.
Computer engineers might also work on a system's software. However, designing very complex software systems is often the job of software engineering, which is usually a separate field. Desktop computers are just a small part of what a computer engineer might work on. Computer-like systems are now found in many devices, including video game consoles and DVD players.
Related Fields
Mechatronics is a field that combines electrical and mechanical systems. These combined systems are called electromechanical systems and are used everywhere. Examples include automated manufacturing systems, heating and air-conditioning systems, and parts of aircraft and cars.
The term mechatronics usually refers to larger systems. But experts predict we will see very small electromechanical devices. These tiny devices, called Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), are already used in cars to deploy airbags. They also help digital projectors create sharper images and inkjet printers print in high definition. In the future, these devices might help create tiny medical implants and improve optical communication.
Biomedical engineering is another related field. It focuses on designing medical equipment. This includes large machines like ventilators and MRI scanners. It also includes smaller, portable devices like cochlear implants and artificial pacemakers.
Aerospace engineering and robotics are also related fields. For example, new electric propulsion and ion propulsion systems are being developed.
Images for kids
-
The discoveries of Michael Faraday helped create electric motor technology.
-
Guglielmo Marconi was a pioneer in long-distance radio transmission.
-
A replica of the first working transistor.
-
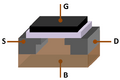
The Metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a basic part of modern electronics.
-
An Oscilloscope is used to see electrical signals.
-
The IEEE corporate office in New York City.
-
Satellite communications are a common area for electrical engineers.
-
A laser light bouncing inside an acrylic rod, showing how light travels in an optical fiber.
See also
 In Spanish: Ingeniería eléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Ingeniería eléctrica para niños