Indigenous peoples of the North American Southwest facts for kids
The Indigenous peoples of the North American Southwest are the first people who lived in a large area of North America. This region includes parts of the United States like Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, and Nevada. It also covers parts of northern Mexico, such as Sonora and Chihuahua. This area is sometimes called the "American Southwest" or "Oasisamerica". For a very long time, people here have lived by hunting and gathering food, and also by farming.
Many different groups of Indigenous people live in the Southwest today. These include the Yuman-speaking peoples near the Colorado River. There are also the O'odham peoples in Arizona and Sonora. The Pueblo peoples live in Arizona and New Mexico. The Apache and Navajo peoples arrived in the Southwest around the 1300s and 1400s. Their ancestors came from Canada, and they are a big part of the region's culture today.
Contents
Indigenous Peoples of the Southwest
This list shows many of the different Indigenous groups who live or have lived in the North American Southwest.
- Ak Chin, Arizona
- Southern Athabaskan
- Chiricahua Apache, New Mexico and Oklahoma
- Jicarilla Apache, New Mexico
- Lipan Apache, Texas
- Mescalero Apache, New Mexico
- Navajo (Navaho, Diné), Arizona and New Mexico
- San Carlos Apache, Arizona
- Tonto Apache, Arizona
- Western Apache (Coyotero Apache), Arizona
- White Mountain Apache, Arizona
- Aranama (Hanáma, Hanáme, Chaimamé, Chariname, Xaraname, Taraname)
- Coahuiltecan, Texas, northern Mexico
- Cocopa, Arizona, northern Mexico
- Comecrudo Texas, northern Mexico
- Cotoname (Carrizo de Camargo)
- Halchidhoma, Arizona and California
- Hualapai, Arizona
- Havasupai, Arizona
- Hohokam, formerly Arizona
- Karankawa, Texas
- Kavelchadhom
- La Junta, Texas, Chihuahua
- Mamulique, Texas, northern Mexico
- Manso, Texas, Chihuahua
- Maricopa, Arizona
- Mojave, Arizona, California, and Nevada
- Pima, Arizona
- Pima Bajo
- Pueblo peoples, Arizona, New Mexico, Western Texas
- Ancestral Pueblo, formerly Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Utah
- Hopi-Tewa (Arizona Tewa, Hano), Arizona, joined the Hopi during the Pueblo Revolt
- Hopi, Arizona
- Keres people, New Mexico
- Acoma Pueblo, New Mexico
- Cochiti Pueblo, New Mexico
- Kewa Pueblo (formerly Santo Domingo Pueblo), New Mexico
- Laguna Pueblo, New Mexico
- San Felipe Pueblo, New Mexico
- Santa Ana Pueblo, New Mexico
- Zia Pueblo, New Mexico
- Tewa people, New Mexico
- Nambé Pueblo, New Mexico
- Ohkay Owingeh (formerly San Juan Pueblo), New Mexico
- Pojoaque Pueblo, New Mexico
- San Ildefonso Pueblo, New Mexico
- Tesuque Pueblo, New Mexico
- Santa Clara Pueblo, New Mexico
- Tiwa people, New Mexico
- Isleta Pueblo, New Mexico
- Picuris Pueblo, New Mexico
- Sandia Pueblo, New Mexico
- Taos Pueblo, New Mexico
- Ysleta del Sur Pueblo (Tigua Pueblo), Texas
- Piro Pueblo, New Mexico
- Towa people
- Jemez Pueblo (Walatowa), New Mexico
- Pecos (Ciquique) Pueblo, New Mexico
- Zuni people (Ashiwi), New Mexico
- Quechan (Yuma), Arizona and California
- Quems
- Solano, Coahuila, Texas
- Tamique
- Toboso
- Tohono O'odham, Arizona and Mexico
- Qahatika, Arizona
- Tompiro
- Ubate
- Walapai, Arizona
- Yaqui (Yoreme), Arizona, Sonora
- Yavapai, Arizona
- Tolkapaya (Western Yavapai), Arizona
- Yavapé (Northwestern Yavapai), Arizona
- Kwevkapaya (Southeastern Yavapai), Arizona
- Wipukpa (Northeastern Yavapai), Arizona
Related Indigenous Groups
Some groups are also connected to the Indigenous peoples of the Southwest.
- Genízaros: These people came from the Great Plains. They are recognized as an Indigenous group in New Mexico.
- Hispanos: Most Hispanos have mixed ancestry, especially in New Mexico. This means they have both Indigenous and Spanish roots.
- Californios: From California.
- Hispanos of New Mexico: From New Mexico.
- Tejanos: From Texas.
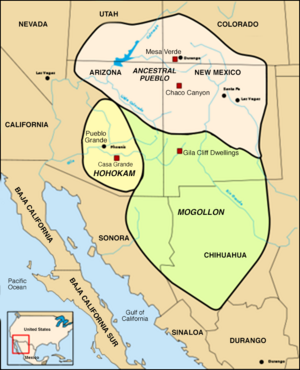
History of Ancient Cultures
Before Christopher Columbus arrived, the Southwest was home to three main ancient cultures. These are sometimes called Oasisamerica.
Ancestral Pueblo Peoples
The Ancestral Pueblo peoples are also known as the Anasazi. Their culture was centered around the Four Corners area. This is where the states of Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah meet. They started making unique pottery and building special homes around 750 CE. These people are famous for their amazing buildings. You can see them at places like Pueblo Bonito in Chaco Canyon. Other famous sites include Mesa Verde and Aztec Ruins.
Hohokam Culture
The Hohokam culture began around 200 CE. They lived near the Gila River and Salt River in Arizona. These people built amazing irrigation canals. These canals helped them water their crops in the desert. They grew many different kinds of plants. The Hohokam also traded with ancient cultures far to the south in Mesoamerica. This shows they had connections with other advanced societies.
Mogollon Culture
Mogollon peoples lived in the Southwest from about 200 CE to the 1400s or early 1500s. Their ancient sites are found in places like the Gila Wilderness and the Mimbres River Valley. You can also find their history at Paquime and Hueco Tanks.
Other Ancient Groups
Besides these three main cultures, other groups lived in different parts of the Southwest.
- The La Junta Indians lived where the Conchos River and Rio Grande meet. They lived there from 1200 CE into more recent times.
- The Patayan culture lived in parts of Arizona, California, and Baja California. They were present between 700 and 1550 CE.
- The Fremont culture lived in Utah and parts of Nevada, Idaho, and Colorado. They were there from 700 to 1300 CE.
Material Culture and Daily Life
The people of the Southwest grew many important foods. Their main crops included maize (corn), beans, squash, and sunflower seeds. The Tepary bean was a very important food. It could grow well even when there wasn't much water. These beans were often planted in floodplains that would dry out after heavy rains.
Foraging for Wild Foods
Finding and collecting wild foods was also a big part of their diet. For example, the fruit and seeds of the Saguaro cactus were eaten fresh or dried. Tribes like the Tohono O'odham and Pima also made drinks from them. The flower buds of the Cholla cactus were collected and roasted. Another key food was the seeds of the Pinyon pine, known as "pine nuts." These nuts were a vital source of protein in winter for the Ute and Paiute peoples.
Uses of the Agave Plant
The agave plant was very useful to Indigenous people. Its heart could be roasted for a sweet treat. Dried agave was eaten during the colder months. The strong fibers from agave were used to make baskets and mats. Agave is also famous for being used to make drinks like tequila and mezcal.
Animals and Livestock
Historically, Indigenous peoples in the region raised turkeys. They also hunted animals like deer, antelope, and rabbits. After Europeans arrived, they started to raise sheep, goats, and cattle too.
Society and Culture
Today, Pueblo Indians still organize their communities based on clans. Clans are groups of families who share a common ancestor. These clans are important for community activities and special ceremonies. For example, some eastern Pueblos are divided into "Summer people" and "Winter people." Western Puebloans have many different family lines and clans. Many Pueblo peoples still practice the kachina (katsina) religion. This religion involves spirits and ceremonies.
Images for kids
-
Puebloan from San Ildefonso Pueblo, New Mexico
-
Navajo family
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |