Delhi facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Delhi
|
|
|---|---|
|
Megacity and union territory
|
|
| National Capital Territory of Delhi | |
|
From top, left to right: Humayun's Tomb; Qutub Minar; Jama Masjid; Red Fort's Lahori gate; India Gate; Digambar Jain Mandir with Gauri Shankar temple in the background; St. James' Church; Hyderabad House; Lotus Temple, a Baháʼí House of Worship
|
|
| Country | India |
| Region | North India |
| Capital, Delhi Sultanate | 1214 |
| Capital, Mughal Empire | 1526, intermittently with Agra |
| New Delhi, capital, British Indian Empire | 12 December 1911 |
| New Delhi, capital, Dominion of India | 1947 |
| New Delhi, capital, Republic of India | 26 January 1950 |
| Union Territory | 1 November 1956 |
| National Capital Territory | 1 February 1992 |
| Government | |
| • Body | Government of Delhi |
| Area | |
| • Megacity and union territory | 1,484 km2 (573 sq mi) |
| • Water | 18 km2 (6.9 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 200–250 m (650–820 ft) |
| Population
(2011)
|
|
| • Megacity and union territory | 16,787,941 |
| • Density | 11,312/km2 (29,298/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 16,349,831 (2nd) |
| • Megacity | 11,034,555 (2nd) |
| • Metro (includes part of NCR) (2018) | 28,514,000 (1st) |
| Languages | |
| • Official | |
| • Additional official | |
| GDP (2023–24) | |
| • Megacity and union territory | ₹11.08 trillion (US$190 billion) |
| • Per Capita | ₹513,131 (US$8,700) |
| • Metro (PPP) | $521.5 billion |
| Time zone | UTC+5.30 (IST) |
| PINs |
110000–110099
|
| Area code(s) | +91 11 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-DL |
| Vehicle registration | DL |
| International Airport | Indira Gandhi International Airport |
| Rapid Transit | Delhi Metro |
| HDI (2018) | |
| Literacy (2011) | 86.21% |
| Sex ratio (2011) | 868 ♀/1000 ♂ |
Delhi, also known as the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a big city and a special territory in India. It includes New Delhi, which is the capital city of India. Delhi is mostly located on the west side of the Yamuna river. It shares its borders with Uttar Pradesh to the east and Haryana in other directions. Delhi became a union territory in 1956 and the NCT in 1995.
The NCT covers an area of about 1,484 square kilometers. In 2011, Delhi's city population was over 11 million people. The total population of the NCT was around 16.8 million.
Delhi is part of a larger urban area called the National Capital Region (NCR). This area includes nearby cities like Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, and Noida. The NCR has an estimated population of over 28 million people. This makes it the largest metropolitan area in India and the second-largest in the world, after Tokyo.
For a long time, from the early 1200s to the mid-1800s, Delhi was the capital of two big empires: the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire. These empires ruled over large parts of South Asia. Three famous UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Delhi are from this time: the Qutub Minar, Humayun's Tomb, and the Red Fort. Delhi was also important for Sufism, a spiritual practice, and Qawwali music.
In 1911, New Delhi, a part of Delhi, became the capital of the British Indian Empire. After India became independent in 1947, New Delhi remained the capital. Today, Delhi is a major center for planning in the National Capital Region. It has also hosted many big events, like the 1951 Asian Games, 1982 Asian Games, and the 2010 Commonwealth Games.
Contents
What's in a Name?
There are many stories about how Delhi got its name. One story says it came from a king named Dhillu or Dilu. He built a city here around 50 BCE and named it after himself.
Another idea is that the name comes from the word dhili, meaning "loose." This might be because the iron pillar of Delhi was thought to have a weak base. Some old texts suggest the city's name was dilpat, which could be related to dil meaning "eminence."
People from Delhi are called Delhiites or Dilliwalas. There are also famous sayings about Delhi. For example, "Delhi is still far away" means a task is not yet finished. Another saying, "It pours all around, while Delhi lies parched," talks about being without something when there's plenty nearby.
A Look Back in Time
People traditionally link seven cities to the Delhi area. The oldest, Indraprastha, is described in an ancient Indian story called the Mahabharata. This story says a city was built on a hill by the Yamuna river. While the story describes a beautiful city, digs in the area haven't found signs of such an old city.
The oldest buildings found in Delhi are from the Maurya Empire around 300 BCE. In 1966, an inscription from Emperor Ashoka was found here. Later, in 1052 CE, a Rajput king named Anang Pal built a fort called Lal Kot.
Delhi's Medieval Capitals
In 1192, Muhammad of Ghor defeated Prithviraj Chauhan. After Ghori left, his general, Qutb al-Din Aibak, started the Delhi Sultanate in 1206 CE. He began building the Qutb Minar and the Quwwat-al-Islam mosque. The Qutb Minar, which is 72.5 meters tall, was finished by his successor, Iltutmish.
For the next 300 years, different groups ruled Delhi. They built many forts and towns, which are known as the "seven cities of Delhi." Delhi was also a big center for Sufism during this time. The Delhi Sultanate grew very large under Muhammad bin Tughluq. However, after Timur attacked and looted Delhi in 1398, the Sultanate became much smaller.
The Lodi dynasty later helped the Sultanate regain some power. But in 1526, Babur defeated the last Lodi ruler. This led to the start of the Mughal Empire.
The Mughal Era and Beyond

The Mughal Empire ruled Delhi for over 300 years. One famous Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan, built the seventh city of Delhi, called Shahjahanabad. This city is now known as Old Delhi.
After 1707, the Mughal Empire became weaker. The Maratha Empire from southern India grew stronger. In 1739, Nader Shah from Persia attacked and looted Delhi, taking away many treasures. This made the Mughal Empire even weaker. Later, the Marathas and Afghans fought for control of Delhi.
British Rule and Independence
In 1803, the British East India Company took control of Delhi. After the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the city came under direct British rule. In 1911, the British decided to move their capital from Calcutta to Delhi.
The new capital area was named "New Delhi" in 1927. It was officially opened in 1931. When India gained independence in 1947, New Delhi became the capital of the new country.

During the partition of India in 1947, many people moved to and from Delhi. Many Hindu and Sikh refugees came to Delhi from West Punjab. At the same time, many Muslim residents moved to Pakistan. Today, people from all over India continue to move to Delhi, making its population grow fast.
In 1991, Delhi became the National Capital Territory. It got its own legislative assembly, which is like a local government, but with limited powers. New Delhi is managed by both the national government of India and the local government of Delhi.
Where is Delhi?

Delhi is located in North India. It is surrounded by the state of Haryana on three sides and Uttar Pradesh (UP) to the east. The Yamuna River flows through Delhi. Its flood plains have fertile soil, good for farming, but they can flood sometimes. The Yamuna is a very important river in Hinduism.
Another important natural feature is the Delhi ridge. This ridge comes from the Aravalli Range and goes around parts of the city. It reaches a height of about 318 meters.
Delhi also has over 500 small ponds. These ponds are home to many different kinds of birds. Even though some ponds face challenges from trash and construction, they are important places for birds.
The National Capital Territory of Delhi covers about 1,483 square kilometers. Delhi is in India's seismic zone-IV, which means it can experience major earthquakes.
Delhi's Climate
Delhi has a climate with dry winters and hot summers. The warm season lasts from March to June, with daily temperatures often above 39°C. The hottest days are usually in late May, reaching around 42°C.
The cold season is from late November to early February, with daily temperatures below 20°C. The coldest days are in early January, with lows around 6.9°C. Heavy fog often happens in winter. The monsoon season, with more humidity, starts in late June. Delhi gets about 774.4 mm of rain each year.
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.5 (90.5) |
34.1 (93.4) |
40.6 (105.1) |
45.6 (114.1) |
47.2 (117.0) |
46.7 (116.1) |
45.0 (113.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
40.6 (105.1) |
39.4 (102.9) |
36.1 (97.0) |
30.0 (86.0) |
47.2 (117.0) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 25.8 (78.4) |
29.5 (85.1) |
35.8 (96.4) |
41.4 (106.5) |
44.3 (111.7) |
43.7 (110.7) |
40.1 (104.2) |
37.4 (99.3) |
37.1 (98.8) |
36.1 (97.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
27.3 (81.1) |
44.8 (112.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 20.1 (68.2) |
24.2 (75.6) |
29.9 (85.8) |
36.5 (97.7) |
39.9 (103.8) |
39.0 (102.2) |
35.6 (96.1) |
34.2 (93.6) |
34.1 (93.4) |
33.0 (91.4) |
28.4 (83.1) |
22.8 (73.0) |
31.4 (88.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 14.0 (57.2) |
17.8 (64.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
29.1 (84.4) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.3 (91.9) |
31.5 (88.7) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.7 (85.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.7 (69.3) |
15.7 (60.3) |
25.3 (77.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 7.5 (45.5) |
10.6 (51.1) |
15.6 (60.1) |
21.3 (70.3) |
25.8 (78.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.5 (81.5) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.0 (77.0) |
19.5 (67.1) |
13.0 (55.4) |
8.4 (47.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 3.5 (38.3) |
6.0 (42.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
16.3 (61.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
22.2 (72.0) |
24.3 (75.7) |
23.7 (74.7) |
21.9 (71.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
4.5 (40.1) |
3.1 (37.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −0.6 (30.9) |
1.6 (34.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.1 (59.2) |
17.6 (63.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
16.1 (61.0) |
9.4 (48.9) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 19.1 (0.75) |
21.3 (0.84) |
17.4 (0.69) |
16.3 (0.64) |
30.7 (1.21) |
74.1 (2.92) |
209.7 (8.26) |
233.1 (9.18) |
123.5 (4.86) |
15.1 (0.59) |
6.0 (0.24) |
8.1 (0.32) |
774.4 (30.5) |
| Average rainy days | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 2.7 | 4.8 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 5.5 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 40.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 57 | 46 | 37 | 25 | 28 | 43 | 63 | 68 | 60 | 47 | 52 | 59 | 49 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | 8 (46) |
11 (52) |
14 (57) |
14 (57) |
18 (64) |
22 (72) |
26 (79) |
25 (77) |
23 (73) |
18 (64) |
14 (57) |
10 (50) |
17 (62) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 220.1 | 223.2 | 248.0 | 276.0 | 285.2 | 219.0 | 179.8 | 176.7 | 219.0 | 260.4 | 246.0 | 220.1 | 2,773.5 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 7.1 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 7.3 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 7.1 | 7.6 |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 10.6 | 11.2 | 12.0 | 12.9 | 13.6 | 13.9 | 13.8 | 13.1 | 12.3 | 11.5 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 12.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 67 | 71 | 67 | 71 | 68 | 53 | 42 | 44 | 59 | 73 | 77 | 69 | 63 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 3 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 6 |
| Source 1: India Meteorological Department (sun 1971–2000); Time and Date (dewpoints, 2005–2015) Revised Rainfall data | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Météo Climat (mean temperature 1991-2020) Weather Atlas (UV Index) (Daylight) | |||||||||||||
Air Quality in Delhi
Air quality in Delhi is a big concern. In recent years, Delhi has been ranked among the most polluted cities in the world. This pollution can make it harder for people to breathe and can affect their health, especially children.
The air quality is usually moderate for most of the year. But from October to December, it gets much worse. This is due to things like smoke from burning farm waste in nearby states, firecrackers during festivals like Diwali, and cold weather trapping the pollution. Cars, factories, and construction also add to the problem.
The government and other groups are working to improve air quality. Delhi has many trees, which help clean the air. The city also has the world's largest fleet of buses that run on compressed natural gas (CNG), which is cleaner fuel. The Delhi Metro also helps by reducing the number of cars on the road.
However, challenges remain, especially from farm waste burning and the increasing number of diesel cars. It's important for everyone to be aware of air pollution and work together to make the air cleaner.
How Delhi is Governed
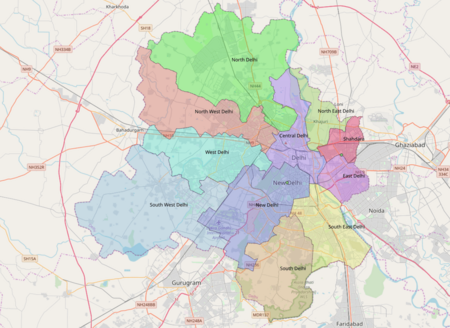
The National Capital Territory of Delhi is divided into 11 districts and three main municipalities:
- The Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) covers most of the area.
- The New Delhi Municipality covers the capital area.
- The Delhi Cantonment covers a military area.
Delhi has its own High Court and several other courts. For policing, Delhi is divided into 15 police districts with 180 police stations.
Delhi's Economy
Delhi is the biggest business center in northern India. It is one of the most productive metropolitan areas in India. Most of Delhi's economy comes from the service industry. This includes things like information technology, hotels, banking, media, and tourism. Construction and real estate are also important.
Delhi has a very large and fast-growing retail industry, with many shops and malls. Many companies have also set up their offices and factories in Delhi because it has a big market and many skilled workers.
City Services
The Delhi Jal Board manages Delhi's water supply. However, the city often needs more water than it can supply, especially as the population grows. Much of the sewage from the city flows into the Yamuna river without being fully treated.
Electricity in Delhi is managed by different companies. The city also gets a lot of its power from other states. The Delhi Fire Service has 43 fire stations that respond to many calls each year. Phone and mobile services are provided by both government and private companies.
Getting Around Delhi
By Air
The main airport for Delhi is Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA). It is one of the busiest airports in India and South Asia, handling millions of passengers each year. IGIA has won awards for being one of the best airports in the world.
There is also Hindon Airport in Ghaziabad, which serves as a second airport for the Delhi area. Plans are also being made for a new international airport in Jewar.
By Road
Delhi has a very dense road network. It is connected to other parts of India by several National Highways. Buses are the most popular way to travel by road in Delhi. The Delhi Transport Corporation (DTC) operates the world's largest fleet of CNG-fueled buses, which are better for the environment.
Personal cars are also very common in Delhi. The city has the highest number of registered cars compared to other big cities in India. Taxis, auto rickshaws, and cycle rickshaws are also widely used for shorter distances.
By Train
Delhi is a major hub for India's railway system. The main railway stations are New Delhi, Old Delhi, and Hazrat Nizamuddin.
By Metro
The Delhi Metro is a modern train system that connects many parts of Delhi and nearby cities like Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, and Noida. It is one of the largest metro systems in the world. The metro has many lines and stations, and it carries millions of passengers every day. All stations have escalators, lifts, and special tiles to help visually impaired people. The Delhi Metro helps reduce air pollution by encouraging people to use public transport instead of cars.
People and Languages
Population Growth
Delhi's population is growing very fast. In 2011, the NCT of Delhi had over 16.7 million people. Many people move to Delhi from other parts of India, which adds to its population growth. Delhi's urban area is now considered the second-largest in the world after Tokyo.
Some people in Delhi live in areas called slums or unauthorized colonies. These areas sometimes do not have enough basic services like water or proper sanitation.
Religions in Delhi
Most people in Delhi follow Hinduism, making up about 81.68% of the population. Other major religions include Islam (12.86%), Sikhism (3.40%), Jainism (0.99%), and Christianity (0.87%). There are also smaller numbers of people who follow Buddhism and other faiths.
| Religious group |
1881 | 1891 | 1901 | 1911 | 1921 | 1931 | 1941 | 1951 | 2011 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | |
| Hinduism |
97,601 | 55.02% | 108,058 | 56.11% | 114,417 | 54.86% | 121,735 | 52.28% | 325,551 | 66.65% | 400,302 | 62.92% | 567,264 | 61.8% | 1,467,854 | 84.16% | 13,712,100 | 81.68% |
| Islam |
74,159 | 41.81% | 79,238 | 41.15% | 88,460 | 42.41% | 102,476 | 44.01% | 141,758 | 29.02% | 206,960 | 32.53% | 304,971 | 33.22% | 99,501 | 5.71% | 2,158,684 | 12.86% |
| Jainism |
2,905 | 1.64% | 3,256 | 1.69% | 3,266 | 1.57% | 3,531 | 1.52% | 4,698 | 0.96% | 5,345 | 0.84% | 11,287 | 1.23% | 20,174 | 1.16% | 166,231 | 0.99% |
| Christianity |
997 | 0.56% | 1,700 | 0.88% | 2,164 | 1.04% | 3,075 | 1.32% | 13,320 | 2.73% | 16,989 | 2.67% | 17,475 | 1.9% | 18,685 | 1.07% | 146,093 | 0.87% |
| Sikhism |
869 | 0.49% | 289 | 0.15% | 229 | 0.11% | 1,939 | 0.83% | 2,764 | 0.57% | 6,437 | 1.01% | 16,157 | 1.76% | 137,096 | 7.86% | 570,581 | 3.4% |
| Zoroastrianism |
N/A | N/A | 31 | 0.02% | 35 | 0.02% | 74 | 0.03% | 72 | 0.01% | 126 | 0.02% | 284 | 0.03% | 164 | 0.01% | N/A | N/A |
| Judaism |
N/A | N/A | 6 | 0% | N/A | N/A | 7 | 0% | 17 | 0% | 11 | 0% | 55 | 0.01% | 90 | 0.01% | N/A | N/A |
| Buddhism |
N/A | N/A | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 6 | 0% | 76 | 0.01% | 150 | 0.02% | 503 | 0.03% | 18,449 | 0.11% |
| Others | 861 | 0.49% | 1 | 0% | 4 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 2 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 296 | 0.03% | 5 | 0% | 15,803 | 0.09% |
| Total population | 177,392 | 100% | 192,579 | 100% | 208,575 | 100% | 232,837 | 100% | 488,452 | 100% | 636,246 | 100% | 917,939 | 100% | 1,744,072 | 100% | 16,787,941 | 100% |
Languages Spoken
Hindi is the most spoken language in Delhi, with over 80% of people speaking it. Other languages spoken include Punjabi, Urdu, and Bengali. Hindi is the official language, while Urdu and Punjabi are also recognized as official languages.
Languages in NCT of Delhi (2011) Hindi (81.27%) Punjabi (5.20%) Urdu (5.17%) Bhojpuri (1.35%) Bengali (1.29%) Maithili (0.73%) Haryanvi (0.67%) Tamil (0.53%) Malayalam (0.49%) Rajasthani (0.46%) Gujarati (0.24%) Odia (0.23%) Nepali (0.22%) Sindhi (0.19%) Marathi (0.17%) Telugu (0.16%) Kashmiri (0.11%) Pahadi (0.09%) Awadhi (0.07%) Marwari (0.07%) Kannada (0.06%) Assamese (0.05%) Others (1.18%)
Delhi's Rich Culture
Delhi's culture is a mix of its long history and its role as India's capital. Many people from different parts of India have moved here, making it a "melting pot" of cultures.
The city has many important historical buildings. The Archaeological Survey of India lists 1,200 heritage buildings and 175 national heritage sites.
In Old Delhi, the Mughal rulers built amazing structures. These include the Jama Masjid, India's largest mosque, and the Red Fort. Other famous places are the India Gate, Jantar Mantar (an old observatory), and the Purana Qila (a 16th-century fort).
Modern buildings like the Laxminarayan Temple, Akshardham temple, Gurudwara Bangla Sahib, and the Baháʼí Faith's Lotus Temple are also very popular. Raj Ghat and associated memorials is a memorial to Mahatma Gandhi. New Delhi also has many government buildings with British-style architecture, like the Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Chandni Chowk, a market from the 1600s, is a famous shopping area. Delhi is also known for its arts and crafts, like Zardozi embroidery and Meenakari enameling.
-
The Hindu Laxminarayan Mandir was inaugurated by Mahatma Gandhi in 1933.
-
The Jama Masjid was built by the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan between 1650 and 1656.
-
The prayer hall of Sikh Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib in Chandni Chowk, Old Delhi which dates to 1783
Festivals and Celebrations
Because Delhi is the capital, national holidays are very important here. These include Republic Day, Independence Day, and Gandhi Jayanti. On Independence Day, the Prime Minister gives a speech from the Red Fort. The Republic Day Parade shows off India's culture and military.
Delhi has a special festival called Phool Walon Ki Sair in September. During this festival, flowers are offered to a Sufi saint's shrine and a temple.
People in Delhi celebrate many religious festivals. Some of these are Diwali, Holi, Eid ul-Fitr, and Christmas. The Qutub Festival is a cultural event with music and dance performances. Other fun events include the Kite Flying Festival and the International Mango Festival. The Auto Expo, Asia's largest car show, is also held in Delhi.
Delicious Delhi Food

Delhi's food has been shaped by its history as a capital city. Mughlai cuisine started here, with dishes like Kebab, biryani, and tandoori foods. Other classic dishes include butter chicken, dal makhani, and shahi paneer.
Street food is very popular in Delhi. You can find many tasty snacks like aloo chaat, samosa, and chole bhature. The Gali Paranthe Wali in Chandni Chowk is famous for its fried bread called paratha. Many important people, including prime ministers, have visited this street to try the food.
Learning in Delhi
Delhi has many schools and colleges. Private schools teach in English or Hindi. They are connected to different education boards like CISCE, CBSE, or NIOS. In 2004–05, over 1.5 million students were in primary schools.
Delhi has many colleges and universities. Some of the top colleges in India for management, medicine, and engineering are in Delhi. These include Faculty of Management Studies (Delhi), All India Institute of Medical Sciences Delhi, and Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi.
The University of Delhi, Jawaharlal Nehru University, and Jamia Millia Islamia are major universities. Many languages are taught in Delhi schools, including Hindi, Urdu, and English.
Media and News
As India's capital, Delhi is a big center for news. Many national news agencies and TV channels are based here. You can watch many Hindi, English, and regional language channels.
Newspapers are still very popular in Delhi. Some of the major Hindi newspapers are Navbharat Times and Hindustan Dainik. For English newspapers, Hindustan Times and The Times of India are very widely read.
Radio is also available, with many state-owned and private radio stations broadcasting from Delhi.
Sports in Delhi
Delhi has hosted many big sports events. It hosted the first 1951 Asian Games and again the 1982 Asian Games. In 2010, Delhi hosted the 2010 Commonwealth Games, which was the biggest sports event ever held in India. The opening ceremony was at the Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium.
Cricket and football are the most popular sports. The Arun Jaitley Stadium is a famous cricket ground where international matches are played. It is also the home ground for the Indian Premier League team Delhi Capitals. Many famous cricketers like Virender Sehwag and Virat Kohli are from Delhi.
The Ambedkar Stadium is a football stadium in Delhi. Delhi also has professional football and other sports clubs. The Buddh International Circuit near Delhi used to host the Formula 1 Indian Grand Prix.
City Sports Teams
| Club | Sport | League/Championship | Homeground | Founded |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dabang Delhi | Kabaddi | Pro Kabaddi League | Thyagaraj Sports Complex | 2014 |
| Delhi Dashers | Badminton | Premier Badminton League | Siri Fort Sports Complex | 2016 |
| Delhi Defenders | American Football | Elite Football League of India | Defenders Stadium | 2011 |
| Delhi Hurricanes Rugby Football Club | Rugby | All India & South Asia Rugby Tournament | Vasant Kunj Sports Complex | 2004 |
| Delhi Waveriders | Hockey | Hockey India League | Shivaji Hockey Stadium | 2011 |
| Delhi Capitals | Cricket | Indian Premier League | Arun Jaitley Cricket Stadium | 2008 |
| Delhi FC | Football | I-League | Ambedkar Stadium | 1994–present |
See also
 In Spanish: Delhi para niños
In Spanish: Delhi para niños