Zambia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Zambia
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto:
"One Zambia, One Nation" |
|
|
Anthem: "Stand and Sing of Zambia, Proud and Free"
|
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Lusaka 15°25′S 28°17′E / 15.417°S 28.283°E |
| Official languages | English |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups
(2010)
|
List
21.0% Bemba
13.6% Tonga 7.4% Chewa 5.7% Lozi 5.3% Nsenga 4.4% Tumbuka 4.0% Ngoni 3.1% Lala 2.9% Kaonde 2.8% Namwanga 2.6% Lunda (Northern) 2.5% Mambwe 2.2% Luvale 2.1% Lamba 1.9% Ushi 1.6% Bisa 1.6% Lenje 1.2% Mbunda 0.9% Lunda (Luapula) 0.9% Senga 0.8% Ila 0.8% Lungu 0.7% Tabwa 0.7% Soli 0.7% Kunda 0.6% Ngumbo 0.5% Chishinga 0.5% Chokwe 0.5% Nkoya 5.4% Other ethnics 0.8% Major racial 0.4% Unclassified |
| Religion
(2010)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Zambian |
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
| Edgar Lungu | |
| Inonge Wina | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
| History | |
|
• North-Western Rhodesia
|
27 June 1890 |
| 28 November 1899 | |
|
• North-Eastern Rhodesia
|
29 January 1900 |
| 17 August 1911 | |
|
• Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland
|
1 August 1953 |
| 24 October 1964 | |
|
• Current constitution
|
5 January 2016 |
|
• Established
|
1964 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
752,618 km2 (290,587 sq mi) (38th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1 |
| Population | |
|
• 2018 estimate
|
17,351,708 (65th) |
|
• 2010 census
|
13,092,666 |
|
• Density
|
17.2/km2 (44.5/sq mi) (191st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$75.857 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$4,148 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$23.946 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$1,307 |
| Gini (2015) | 57.1 high |
| HDI (2019) | medium · 146th |
| Currency | Zambian kwacha (ZMW) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (CAT) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +260 |
| ISO 3166 code | ZM |
| Internet TLD | .zm |
The Republic of Zambia is a country in southern Africa. It shares its borders with many other nations. These include the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, and Malawi to the east. To the south, it borders Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia. Angola is to the west.
Zambia was once called Northern Rhodesia. Its current name comes from the Zambezi River. This country is known for its amazing natural beauty. It is home to Victoria Falls, one of the world's seven natural wonders. Zambia is also rich in different cultures and has at least 72 spoken languages.
The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka. It is also the largest city in the country. Edgar Lungu is the current president. Zambia's motto is One Zambia, One Nation. Its national anthem is Stand and Sing of Zambia, Proud and Free. The official language is English.
Contents
Zambia's History
Zambia used to be a colony of Great Britain called Northern Rhodesia. In 1964, Zambia became an independent country. Its first president was Kenneth Kaunda. He led Zambia for 27 years with his party, the UNIP. During this time, Zambia was a one-party state. This meant UNIP was the only legal political party. All other parties were not allowed.
After many protests, new democratic elections were held in 1991. Kenneth Kaunda lost these elections. He peacefully handed over power to Frederick Chiluba, who used to be a union leader.
Today, Zambia is a multi-party democracy. This means many different political parties can exist. The country has held several democratic elections since 1991. The most recent presidential election was in 2016. Edgar Lungu won against Hakahende Hichilema.
Zambia's Geography and Climate
Zambia is a landlocked country in southern Africa. This means it has no coastline. It has a tropical climate. Most of the country is made up of high plateaus with some hills and mountains. These areas are cut through by river valleys. Zambia covers about 752,614 square kilometers (290,587 square miles). This makes it the 39th largest country in the world.
Rivers and Waterways
Zambia has two main river systems. The Zambezi/Kafue basin covers about three-quarters of the country. The Congo basin covers about one-quarter in the north.
Many important rivers flow through Zambia as part of the Zambezi basin. These include the Kabompo, Lungwebungu, Kafue, and Luangwa. The Zambezi River itself flows through the western part of the country. It then forms Zambia's southern border with Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe.
Two of the Zambezi's longest rivers, the Kafue and the Luangwa, flow mostly within Zambia. The Zambezi River also creates the famous Victoria Falls. These falls drop about 100 meters (328 feet) over 1.6 kilometers (1 mile) wide. They are located in the southwest corner of Zambia. After the falls, the Zambezi flows into Lake Kariba.
The northern part of Zambia is very flat with wide plains. The Barotse Floodplain on the Zambezi is a good example. It floods from December to June each year. This flooding greatly affects the environment and the lives of people living there.
The southernmost source of the Congo River is in Zambia. It flows west through the northern area as the Chambeshi. After the Bangweulu Swamps, it becomes the Luapula. This river forms part of the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Lake Tanganyika is another major water feature in the Congo basin. Its southeastern end receives water from the Kalambo River. This river forms part of Zambia's border with Tanzania. It also has Africa's second highest uninterrupted waterfall, the Kalambo Falls.
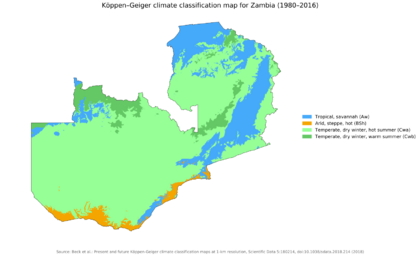
Zambia's Climate
Zambia is located on a high plateau in Central Africa. Its elevation is between 1,000 and 1,600 meters (3,280 and 5,250 feet) above sea level. This high elevation gives the country a generally mild climate. Zambia's climate is tropical, but the altitude makes it less hot.
There are two main seasons:
- The rainy season (November to April), which is summer.
- The dry season (May/June to October/November), which is winter.
The dry season is split into a cool dry season (May/June to August) and a hot dry season (September to October/November). Even in the cool season, average monthly temperatures stay above 20°C (68°F) for most of the year.
Wildlife and Nature

Zambia has many different natural environments. These include forests, thickets, woodlands, and grasslands.
In 2015, Zambia was home to about 12,505 identified species. Most of these were animals (63%), followed by plants (33%), and then bacteria and other tiny organisms (4%).
There are about 3,543 types of wild flowering plants in Zambia. The Northern and North-Western provinces have the most diverse plant life.
Zambia also has about 242 mammal species. Most of these live in the woodlands and grasslands. The Rhodesian giraffe and Kafue lechwe are types of animals found only in Zambia.
Around 757 bird species have been seen in the country. About 600 of these live there all year or migrate from other parts of Africa. The Zambian barbet is a bird species found only in Zambia.
About 490 known fish species live in Zambia's waters. Lake Tanganyika has the highest number of unique fish species.
Government and Administration

Zambia is a republic with a presidential system. This means the President of Zambia is both the head of state and the head of government. Zambia has a multi-party system, where different political parties can compete. The government holds executive power. The parliament, along with the government, has legislative power.
Zambia became a republic right after gaining independence in October 1964.
How Zambia is Divided
Zambia is divided into ten provinces. These provinces are then split into 117 districts. For elections, there are 156 constituencies and 1,281 wards.
The ten provinces are:
- Central Province
- Copperbelt
- Eastern Province
- Luapula
- Lusaka
- Muchinga
- North-Western Province
- Northern Province
- Southern Province
- Western Province
People and Culture
As of 2022, Zambia's population was 19,610,769 people. Most Zambians (99.2%) are black Africans. Other racial groups make up 0.8% of the population.
Zambia is one of the most urbanized countries in sub-Saharan Africa. About 44% of the people live in cities and towns. These areas are mostly along the main transportation routes. Rural areas have fewer people.
Largest Cities
The growth of copper mining in the Copperbelt region in the late 1920s led to fast growth in cities. Mining towns grew quickly after Zambia became independent. Even though the Copperbelt's economy slowed down later, many people still live near the railway and roads. These run south from the Copperbelt through Kapiri Mposhi, Lusaka, Choma, and Livingstone.
Religions in Zambia
Zambia is officially a "Christian nation" according to its 1996 constitution. However, it also protects freedom of religion for everyone. About 95.5% of Zambians are Christian. Most of these are Protestant (75.3%), and 20.2% are Roman Catholic.
About 2.7% of Zambians are Muslim. There are also smaller numbers of Hindus, Baha'is, Buddhists, and Sikhs. A small Jewish community once existed, but today there are fewer than 50 Zambian Jews.
Languages Spoken
The exact number of languages in Zambia is not known. However, most experts believe there are between 20 and 30 different languages.
English is the official language of Zambia. It is used for government business, education, and law. In Lusaka, the main local language is Nyanja (Chewa). Bemba is the second most common. In the Copperbelt region, Bemba is the main language, followed by Nyanja.
Other important local languages include Lozi, Tumbuka, Kaonde, Tonga, Lunda, and Luvale. These languages are also featured on the Zambia National Broadcasting Corporation (ZNBC).
Education System
The Zambian constitution guarantees the right to equal and good education for everyone. The Education Act of 2011 helps make sure this happens. As of 2018, the English-language literacy rate was 86.7%. This means most people can read and write in English.
Zambia's Economy
In 2022, Zambia exported goods worth between $7.5 billion and $8 billion each year. In 2018, this total was $9.1 billion. In 2015, about 54.4% of Zambians lived below the national poverty line. This was an improvement from 60.5% in 2010. Poverty rates are higher in rural areas (76.6%) than in cities (23.4%). Many people in cities struggle with unemployment. Most people in rural Zambia are subsistence farmers. This means they grow food mainly for themselves and their families.
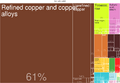
Zambia faced economic challenges when international copper prices dropped in the 1970s. The Zambian government is now working to make its economy less dependent on copper. They are trying to grow other parts of the economy. These include agriculture, tourism, gemstone mining, and hydroelectric power.
Mining Industry

Mining and quarrying made up about 13.2% of Zambia's economy in 2019. Historically, Zambia's economy has relied heavily on the copper mining industry. The industry was taken over by the government in 1973. After this, copper production went down a lot.
Besides copper, Zambia also mines other important minerals. These include gold, manganese, and nickel. The country also mines gemstones like amethyst, beryl, emerald, and tourmaline.
Agriculture
Agriculture is a very important part of Zambia's economy. It provides many more jobs than the mining industry. Some white Zimbabwean farmers moved to Zambia after being expelled from Zimbabwe. They brought their skills and helped boost Zambia's agriculture. They grow crops like tobacco, wheat, and chili peppers. In 2004, Zambia exported more corn than it imported for the first time in 26 years.
Tourism
Tourism made up 5.8% of Zambia's economy in 2021. The highest it ever reached was 9.8% in 2019. Most tourism focuses on wildlife areas. These include Zambia's 20 national parks and 34 game management areas.
The most famous tourist spot is Victoria Falls. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Zambian side of the falls is in Mosi-oa-Tunya National Park. The town of Livingstone, near Victoria Falls, is a major tourist hub. Other popular national parks are North Luangwa, South Luangwa, Kafue, and Liuwa Plain. The Zambian government wants to use tourism to help the economy grow, especially in rural areas. It also helps with wildlife conservation.
Energy Production
In 2009, Zambia produced 10.3 TWh of electricity. The country uses a lot of solar power and hydroelectricity (power from water). However, in early 2015, Zambia faced a serious energy shortage. This was because of low rainfall in 2014/2015, which led to low water levels at the Kariba Dam. In 2019, African Green Resources (AGR) announced plans to invest $150 million in a 50-megawatt solar farm. They also plan to build an irrigation dam and expand grain storage.
Zambian Culture
Before modern Zambia was formed, people lived in independent tribes. Each tribe had its own way of life. When Zambia became a colony, cities grew. Different ethnic groups started living together, influencing each other. They also began to adopt parts of global culture, like clothing styles. Much of Zambia's original cultures still exist in rural areas. Some outside influences, like Christianity, have also become part of the culture.
Zambia has many ceremonies and rituals. Some are nationally recognized, while others are important to specific groups. These ceremonies celebrate achievements, anniversaries, or mark important life events. They include coronations, graduations, weddings, funerals, and birth ceremonies.
As of December 2016, Zambia had 77 traditional ceremonies recognized by the government. Some well-known ones are:
- Kuomboka and Kathanga (Western Province)
- Mutomboko (Luapula Province)
- Kulamba and Ncwala (Eastern Province)
- Lwiindi and Shimunenga (Southern Province)
- Lunda Lubanza (North Western)
- Likumbi Lyamize (North Western)
- Mbunda Lukwakwa (North Western Province)
- Chibwela Kumushi (Central Province)
- Vinkhakanimba (Muchinga Province)
- Ukusefya Pa Ng'wena (Northern Province)
Popular traditional arts include pottery, basketry (like Tonga baskets), wooden carvings, and copper crafts. Most Zambian traditional music uses drums and other percussion instruments. It often involves a lot of singing and dancing. In cities, foreign music genres are popular. These include Congolese rumba, African-American music, and Jamaican reggae.
Sports and Games
Sports and games are important social activities in Zambia. They bring people together for fun, learning, and skill development. Popular sports include football (soccer), athletics, netball, and volleyball. There are also traditional games like nsolo, chiyenga, and hide and seek. These games help people socialize.
Zambia first took part in the Olympic Games in 1964. This was the same year it became independent. Zambia is the only country to enter an Olympic Games as one country and leave as another. Zambia has won two Olympic medals:
- In 1984, Keith Mwila won a bronze medal in boxing.
- In 1996, Samuel Matete won a silver medal in the 400-meter hurdles.
Zambia has never participated in the Winter Olympics.
Football is the most popular sport in Zambia. The Zambia national football team has had great moments. At the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul, the team beat the Italian national team 4–0. Kalusha Bwalya, Zambia's most famous football player, scored three goals in that match.
In 2012, Zambia won the African Cup of Nations for the first time. They beat Côte d'Ivoire in a penalty shoot-out. The game was played in Libreville, Gabon. This was just a few kilometers from where the Zambian national team had a tragic plane crash in 1993.
The Zambia women's national football team made its first appearance at the 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup. They won their first game in their first year. Lushomo Mweemba scored the fastest goal in the tournament. Barbara Banda scored the 1,000th goal in Women's World Cup history.

Rugby Union, boxing, and cricket are also popular sports. In the early 2000s, the captains of the Australian and South African national rugby teams were both born in the same hospital in Lusaka. Their names were George Gregan and Corné Krige.
In 2017, Zambia hosted and won the 2017 Africa U-20 Cup of Nations. This was a football tournament for players aged 20 and under.
Music and Dance
Zambia's culture is very important to its development. Music and dance are key parts of their cultural expression. They show the beauty of life in Zambia. Traditional music often uses talking drums and other percussion instruments. Dance brings people together.
Zamrock Music
Zamrock is a music style that started in the 1970s. It mixes traditional Zambian music with heavy, repeating guitar riffs. These riffs are similar to bands like Jimi Hendrix, James Brown, and Black Sabbath. Famous Zamrock groups include Rikki Ililonga and his band Musi-O-Tunya, WITCH, Chrissy "Zebby" Tembo, and Paul Ngozi and his Ngozi Family.
Notable People
- List of Zambians
- List of Zambian artists
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
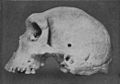
Skull of Broken Hill Man discovered in present-day Kabwe.
-
Three young Ngoni chiefs. The Ngoni came to Eastern Zambia from KwaZulu in South Africa.
-
An 1864 portrait of Scottish explorer and missionary David Livingstone.
-
Kenneth Kaunda, Zambia's first president, on a state visit to Romania in 1970.
-
President Edgar Lungu with Russian President Vladimir Putin, 26 July 2018.
See also
 In Spanish: Zambia para niños
In Spanish: Zambia para niños