Treaty of Versailles facts for kids
The Treaty of Versailles was a very important peace treaty signed after World War I. It was agreed upon in 1919 by six main nations: France, Germany, Britain, Austria-Hungary, Japan, and the United States.
Germany was not allowed to help create the treaty. Instead, they were told to either sign it or face their country being taken over by Allied soldiers. This was called a "diktat," meaning a forced peace. Many Germans felt this was very unfair because they believed they were not fully to blame for starting the war.
France wanted to make sure Germany could not start another war. So, the treaty made Germany much weaker. Germany had to shrink its army from 6 million soldiers to just 100,000. They also had to get rid of their submarines, military planes, and most of their big guns like artillery. Their Navy could only have six small battleships.
Germany also had to give back land it had taken from France, like Alsace-Lorraine. It also had to give large parts of its own land to a new country called Poland. All of Germany's colonies (lands it ruled overseas) were taken away too. A huge problem for Germany was having to pay a very large amount of money, called World War I reparations, for the damage caused during the war, especially to France. This amount was not set at first, but 132 billion gold marks was just the first payment. Germany finally finished paying this debt in 2010.
Many people saw this treaty as a one-sided deal that was very harsh on Germany. Later, German nationalists and Adolf Hitler used this anger to gain support. They promised to break the "chains of Versailles," which eventually led to World War II.
The treaty also created the League of Nations. This group was meant to help solve problems between countries without war. It did help with some international disagreements, but it was not strong enough to stop World War II.
Contents
What Happened to Germany and Other Countries?
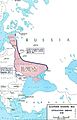
The Treaty of Versailles changed the map of Europe.
Germany's Land Changes
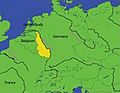
Germany had to give back Alsace-Lorraine to France. This land was taken by Germany after the Franco-Prussian War. France was still upset about losing it. Germany also had to remove its troops from the Rhineland. This was an important area along Germany's border with France, where the Rhine river flows. Many factories were there. If Germany ever put troops back, France could invade.
Germany also gave many areas to Poland. Poland was a new country made from parts of old Russian and Austrian lands. It was home to Polish and Lithuanian people. Poland had been a strong kingdom centuries ago but was later divided by Austria, Prussia, and Russia.
Belgium received some small areas from Germany, including Moresnet, Eupen, and Malmedy. This is why Belgium now has a German-speaking community.
Empires Breaking Apart
The Treaty of Versailles also broke up many large empires that were on the losing side of the war. U.S. President Woodrow Wilson thought this was a good idea. He believed many people in Europe wanted to be free from big empires. But this also created new problems.
Austria-Hungary Splits
The large empire of Austria-Hungary was divided into many new countries:
- Austria: This was meant to be the home for Austrians, who spoke German. Its capital was Vienna. Many Austrians, including Adolf Hitler, believed Austria should be part of Germany. This later led to Germany taking over Austria.
- Hungary: Like Poland, Hungary had been a strong country centuries before. Its capital is Budapest.
- Czechoslovakia: This new country was created for the Czechs and Slovaks. The Czech part included lands once called Bohemia and Moravia. Its capital was Prague. Many Germans lived on its borders in an area called the Sudetenland. Adolf Hitler later demanded this land for Germany.
- Yugoslavia: This country was formed by combining Bosnia, Slovenia, Croatia (from Austria-Hungary), northern Macedonia (from Bulgaria), Serbia, and Montenegro. It was meant to be a homeland for Slavic people. However, it had many different religions, languages, and national groups.
New Countries by the Baltic Sea
New countries were created near the Baltic Sea: Estonia, Finland, Latvia, and Lithuania. These lands were once controlled by Russia. The Russian Revolution happened during World War I, leading to a Communist state. Russia lost control of these western territories. During World War II, the Soviet Union (Russia's new name) took back Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and half of Poland.
Italy and Turkey
Italy gained some parts of Austria.
Another treaty, the Treaty of Sèvres, decided that Greece would take parts of Western Turkey (called Ionia) and its important city, Constantinople. Greece took these areas at first. But a new Turkish army fought back and drove the Greeks out. Greece did gain most of the islands in the Aegean Sea from Turkey and some parts of Bulgaria.
The League of Nations decided that parts of the old Turkish Empire would be looked after by France and Great Britain. Britain took control of Palestine, Iraq, and Transjordan (which later became Israel, Iraq, and Jordan). France took control of Syria and Lebanon.
Problems That Lasted a Long Time
The German Empire became a new government called the Weimar Republic. A huge problem for Germany was paying the enormous amount of money for war damages. This made Germany one of the poorest countries in Europe for nearly 20 years. It also caused a lot of political fighting. Germany officially finished paying its debt on October 3, 2010. Two main political groups, the Communists and the Nazis, fought for power for many years.
The debt to the Allies was made easier for Germany during the Great Depression. All remaining debt was cancelled in 1932. Many Germans hated the treaty. Some even wanted to keep fighting after it was signed.
The League of Nations, created by the treaty, was often not strong enough to stop wars. For example, Japan took a part of China called Manchuria, and the League could not stop it. Italy invaded Ethiopia, and even though the Ethiopian Emperor asked for help, the League did not act. Germany, Japan, and Italy later formed the Axis powers. By invading many peaceful countries, they caused World War II. The United States and the Soviet Union did not even join the League, even though it was the idea of U.S. President Woodrow Wilson. The League was never taken seriously, even though it was supposed to make sure the Treaty of Versailles was followed.
In the end, the treaty failed to keep peace. It became a reason for Nazi Germany and Adolf Hitler to gain support from poorer Germans. They promised to get rid of the "chains of Versailles," which led to World War II.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The heads of the "Big Four" nations at the Paris Peace Conference, 27 May 1919. From left to right: David Lloyd George, Vittorio Orlando, Georges Clemenceau, and Woodrow Wilson.
-
German Johannes Bell signs the Treaty of Versailles in the Hall of Mirrors, with various Allied delegations sitting and standing in front of him.
-
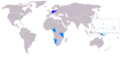
German colonies (light blue) made into League of Nations mandates.
-
Location of the Rhineland
-
Demonstration against the treaty in front of the Reichstag.
See also
 In Spanish: Tratado de Versalles (1919) para niños
In Spanish: Tratado de Versalles (1919) para niños