Canary Wharf facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Canary Wharf |
|
|---|---|
| Central business district | |
|
From top, left to right: Canary Wharf skyline; Canary Wharf DLR station; Canary Wharf tube station; Canada Square; Cabot Square; Crossrail Place; West India Quay |
|
| Population | 68,700 (Millwall, Blackwall and Cubitt Town, East India and Lansbury and Limehouse wards 2011 Census) |
| OS grid reference | TQ375802 |
| London borough | |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | LONDON |
| Postcode district | E14 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| UK Parliament |
|
| London Assembly | |
Canary Wharf is a modern area in London, England. It is located near the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. This area is a major part of London's central business district, which means it's a very important place for businesses.
Along with the City of London, Canary Wharf is one of the main financial centres in the United Kingdom and the world. It has many tall buildings, including One Canada Square, which was once the third-tallest building in the UK. This famous building opened on August 26, 1991.
Canary Wharf was built on the site of the old West India Docks in East London. Today, it has about 16 million square feet (1.5 million square meters) of offices and shops. You can also find many open spaces and gardens here, like Canada Square, Cabot Square, Westferry Circus, Jubilee Park, and the Crossrail Place Roof Garden. Canary Wharf, along with Heron Quays and Wood Wharf, forms the Canary Wharf Estate, covering about 97 acres (39 hectares).
Contents
- History of Canary Wharf
- London's Tallest Buildings
- Historic Buildings in Canary Wharf
- Companies and Organizations
- Things to Do in Canary Wharf
- Squares and Public Areas
- Parks and Green Spaces
- Shopping Malls
- Local Government
- Getting Around Canary Wharf
- Museums and Archives
- Fun Facts: Pokémon Go
- Events and Festivals
- Outdoor Public Art
- Local Media
- See also
- Images for kids
History of Canary Wharf
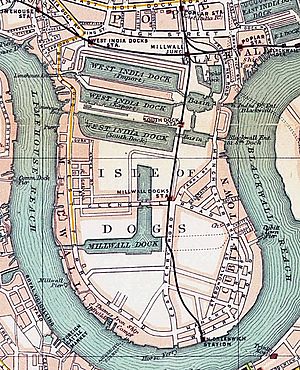
Canary Wharf is built on the land that used to be the West India Docks on the Isle of Dogs.
From Busy Docks to Modern Business Hub
From 1802 until the late 1980s, the area that is now Canary Wharf was one of the busiest docks in the world. It was part of the Isle of Dogs, Limehouse, and Poplar. A merchant named Robert Milligan helped develop the West India Dock Company.
The Port of London Authority took over the West India Dock in 1909. The name "Canary Wharf" comes from Sir Alfred Lewis Jones, a shipping businessman. Ships from the Canary Islands would arrive at London's South Quay Dock. A specific part of the dock, built in 1936 for fruit ships from the Mediterranean and Canary Islands, was named Canary Wharf.
Rebuilding the Docklands Area
After the 1960s, ships started using large containers for cargo. This meant the old docks were no longer needed, and they all closed by 1980. The British Government then decided to rebuild the area. They created the London Docklands Development Corporation (LDDC) in 1981. The Isle of Dogs was also made an "Urban Enterprise Zone" in 1982, which helped new businesses move in.
The idea for modern Canary Wharf came from Michael von Clemm, who thought the area could become a place for office work. Discussions led to plans for a new business district. The LDDC also helped build the Docklands Light Railway (DLR), a new train system, to make it easier to get to the area.
A Canadian company called Olympia & York started construction in 1988. The first buildings were finished in 1991, including One Canada Square. This building became the tallest in the UK at the time and a symbol of the area's new look. However, the property market in London faced problems, and Olympia and York Canary Wharf Limited went bankrupt in 1992.
At first, the City of London saw Canary Wharf as a competitor. The City changed its rules to allow more new offices, which led to too many offices being available. This contributed to Canary Wharf's early struggles.
Canary Wharf Group Takes Over
In 1995, a group of international investors bought control of Canary Wharf. Paul Reichmann became the chairman, and the company went public in 1999. The new company was named Canary Wharf Limited, and later became Canary Wharf Group.
In 1997, some people living nearby tried to sue Canary Wharf Ltd. They said the tall buildings were blocking their TV signals. However, they did not win the case.
The property market slowly got better, and there was a demand for large, modern office spaces. A big help was the start of work on the Jubilee Line Extension, a new underground train line. The government wanted it ready for the Millennium celebrations.
In 2004, a group of investors led by Morgan Stanley took over Canary Wharf Group plc.
London's Tallest Buildings


Canary Wharf is known for its many tall, modern buildings. It has become a major financial area in the UK. Starting from scratch in the early 1990s, the area is home to the first iconic skyscraper, One Canada Square. In just 20 years, Canary Wharf's new cluster of skyscrapers has completely changed London's skyline with its modern designs.
- As of 2023, Canary Wharf has five of the top 10 tallest buildings in the United Kingdom.
- One Canada Square (235 meters) and Landmark Pinnacle (233 meters) are the third and fourth tallest buildings in the UK.
- Other very tall buildings here include Newfoundland (220 meters), South Quay Plaza (215 meters), and One Park Drive (205 meters).
- The 75-storey Landmark Pinnacle is the tallest residential tower in the UK and all of Western Europe.
- Newfoundland is the tallest building in the UK designed specifically for renting.
- Novotel London Canary Wharf is the tallest hotel-only building in the UK and the tallest Novotel in the world.
- One Canada Square, at 235 meters, was the tallest building in the UK for 21 years (1991 to 2012). With its unique pyramid top, it's a famous London landmark seen in many films and TV shows.
This table shows completed buildings in Canary Wharf that are at least 100 meters tall.
| Ranking by height |
Image | Name | Height | Floors | Completion date | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metres | Feet | ||||||
| 1 |  |
One Canada Square | 235 | 771 | 50 | 1991 | The third-tallest completed building in the United Kingdom. It was the tallest in the UK when it was finished. Many companies have offices here. |
| 2 |  |
Landmark Pinnacle | 233 | 764 | 75 | 2020 | A residential tower. It is the tallest residential building in the UK and Western Europe. It has won several awards for its quality and design. |
| 3 |  |
Newfoundland | 220 | 722 | 60 | 2019 | The first residential building built on the private Canary Wharf estate. It's known as "the diamond tower" because of its unique steel design. It has won awards for its design. |
| 4 |  |
South Quay Plaza (Phase 1, Hampton Court) | 215 | 705 | 68 | 2020 | A residential tower, also called Valiant Tower. It won an award for its garden design. |
| 5 |  |
One Park Drive | 205 | 673 | 57 | 2019 | A residential tower and a main building in Wood Wharf. It has won many awards for its design and interiors. |
| 6 |  |
8 Canada Square | 200 | 655 | 42 | 2002 | One of the tallest buildings in the UK. It is the global headquarters for HSBC bank. |
| 7 |  |
25 Canada Square | 200 | 655 | 42 | 2001 | Another one of the tallest buildings in the UK. It forms a complex with 33 Canada Square and is mainly used by Citigroup. |
| 8 |  |
Wardian London (East Tower) | 187 | 614 | 55 | 2019 | A residential tower that won a Silver Award for Best Luxury Development. |
| 9 |  |
Amory Tower (The Madison) | 182 | 597 | 53 | 2019 | A residential tower that won an award for Best Residential Tall Building Project. |
| 10 |  |
Wardian London (West Tower) | 168 | 552 | 50 | 2019 | A residential tower, part of the Wardian London complex. |
| 11 |  |
One Churchill Place | 156 | 513 | 32 | 2005 | The global headquarters for Barclays bank. It was originally planned to be much taller. |
| 12= |  |
40 Bank Street | 153 | 502 | 33 | 2003 | Many different companies have offices here, including banks and law firms. |
| 12= |  |
25 Bank Street | 153 | 502 | 33 | 2003 | The European headquarters for JPMorgan Chase since 2012. |
| 14 |  |
10 Upper Bank Street | 151 | 495 | 32 | 2003 | The global headquarters for Clifford Chance law firm. Other companies also have offices here. |
| 15 |  |
10 Park Drive Wood Wharf |
150 | 492 | 43 | 2019 | A residential tower and the first new residential building in Wood Wharf. It won a Gold award for Best Apartment Scheme. |
| 16 |  |
Arena Tower (Baltimore Tower) | 149 | 489 | 45 | 2017 | A residential tower that won the Best Residential High Rise Award. |
| 17 |  |
Pan Peninsula (East Tower) | 147 | 484 | 48 | 2008 | A residential tower, considered one of the first "Ultra Luxury" developments in Canary Wharf. |
| 18 |  |
Maine Tower (Harbour Central Block D) | 144 | 472 | 42 | 2018 | A residential tower and the main building of the Harbour Central development. |
| 19 |  |
One & Five Bank Street | 143 | 469 | 28 | 2019 | A commercial tower that is very sustainable. The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development moved its headquarters here in 2022. |
| 20 |  |
24 Marsh Wall (Landmark East Tower) | 140 | 458 | 44 | 2010 | A residential tower. |
| 21= |  |
40 Marsh Wall (Novotel London Canary Wharf) | 128 | 420 | 39 | 2017 | A hotel operating as 'Novotel Canary Wharf'. |
| 21= |  |
10 George Street Wood Wharf |
128 | 420 | 35 | 2018 | A residential tower and the first "Build to Rent" property by the Canary Wharf group. It won a Gold award. |
| 23 |  |
Harbour Central Block C (Sirocco Tower) | 125 | 409 | 36 | 2018 | A residential tower and the first of seven buildings planned for the Harbour Central site. |
| 24 |  |
Pan Peninsula (West Tower) | 122 | 400 | 39 | 2008 | A residential tower, part of the Pan Peninsula development. |
| 25 |  |
25 Churchill Place | 118 | 387 | 24 | 2014 | This building housed the European Medicines Agency and Ernst & Young. |
| 26 |  |
Dollar Bay Tower | 109 | 358 | 31 | 2016 | A residential tower that has won many housing and architectural awards. |
| 27 |  |
1 West India Quay | 108 | 354 | 36 | 2004 | This building has both residential apartments and a Marriott Hotel. It was the tallest residential building in the UK when it was finished. |
| 28 |  |
33 Canada Square | 105 | 344 | 18 | 1999 | This building forms a complex with 25 Canada Square. |
Historic Buildings in Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf has 16 buildings that are "listed," meaning they are protected because of their historical importance. Two of these are Grade I listed, which is the highest level of protection.
- Grade I Listed Buildings
- Quay Walls, Copings and Buttresses to Import Dock and Export Dock: These are the original walls of the West India Docks. The Import Dock opened in 1800–02, and the Export Dock in 1803–06.
- Warehouses and General Offices at Western End of North Quay: Originally, there were nine warehouses built between 1800–04. Only two survived bombing during World War II.
These docks and warehouses are important examples of the first major building period in the London Docklands (1800–10).
- Grade II Listed Buildings
Most of the Grade II listed buildings in Canary Wharf are located north-west of West India Dock North. They are part of the West India Dock Conservation Area. These buildings are important not just for their architecture, but also for their connection to the history of the docks and the community that grew around them.
| Photograph | Building Name | Construction Date | Location (E14) | Listing Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
10 and 12, Garford Street E14 | Early 1800s | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | These early 19th-century brick houses were built for the officers and sergeants who worked at the Docks. |
 |
14, Garford Street E14 | Early 1800s | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | An early 19th-century brick house. |
 |
16 and 18, Garford Street E14 | Early 1800s | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | More early 19th-century brick houses. |
 |
Entrance Gates to West India Docks | Early 1800s | West India Dock Road | 19 July 1950 | Two large stone pillars that mark the entrance. |
 |
Former West Entrance Gate to West India Docks with Curved Walling and Bollards | Early 1900s | Westferry Road | 1 July 1983 | Curved brick walls and stone gate pillars. Old cast-iron posts with "WIDC" (West India Dock Company) written on them. |
 |
Railings to West of Main Gate at West India Docks | Early 1800s | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Cast iron railings about 70 yards long. |
 |
Former Excise Office | 1807 | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Also known as Dockmaster's House, designed by architect Thomas Morris. |
 |
Railings and Gatepiers to Former Excise Office | 1807 | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Iron railings and six decorated gate pillars at the street front. |
 |
Quadrangle Stores at West India Dock | 1825 | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Also known as Cannon Workshops, designed by engineer John Rennie the Younger. A rare example of an early building showing how the Docks Company worked. |
 |
Salvation Army Hostel | 1905 | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | A building in the Neo Georgian style. Also known as 20 Garford Street. |
 |
West India Dock Former Guard House | 1803 | West India Dock Road | 27 September 1973 | A small, round building designed by architect George Gwilt. It was originally a lock-up and armoury. |
 |
Former West Entrance Lock to South Dock, West India Docks | 1803-05 | Westferry Road | 1 July 1983 | Built by civil engineer William Jessop as an entrance lock to the City Canal. |
| Fitch and Sons Works | 1870-80 | Westferry Road | 1 July 1983 | A good example of the smaller warehouses in the historic West India Docks, with a rare retail shop on the ground floor. | |
 |
Cascades | 1987-88 | Westferry Road | 18 April 2018 | A 20-storey residential tower. It is a great example of British Post-Modernist architecture and an important building in the rebuilding of the London Docklands. It's a local landmark on the River Thames. |
Companies and Organizations
Canary Wharf has about 16 million square feet (1.5 million square meters) of office and retail space. The Canary Wharf Group owns about half of this. Around 105,000 people work here. It is home to the main offices for many big banks, business service companies, and media groups.
Some of these include Barclays, Citigroup, HSBC, JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley, The Economist Group, and Thomson Reuters. Until 2018, two important European Union agencies were also located here, but they moved to other cities.
Things to Do in Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf offers many activities for visitors and residents.
- Marinas
West India Quays and Poplar Dock are two marinas. These are places where barges and private boats can dock. The Canal & River Trust owns them.
- Library
There is a local public library called Idea Store Canary Wharf. It is inside the Churchill Place shopping mall. It opened in 2006 and is run by Tower Hamlets Council.
- Cinemas
Canary Wharf has two multiplex cinemas. One is at West India Quay and is run by Cineworld. The other is at Crossrail Place and is called Everyman Cinema.
Squares and Public Areas
Canary Wharf has many open spaces where people can relax and gather.
- Canada Square
Canada Square is one of the main squares in Canary Wharf. It's a large open area with grass. In winter, it turns into an ice rink! The square is named after Canada because the first developers of modern Canary Wharf, Olympia & York, were from Canada. Below the square is the Canada Place shopping mall.
- Westferry Circus
Westferry Circus is on the west side of Canary Wharf. It's a garden at ground level, with a roundabout underneath for cars. The garden has special ornamental railings and gates made by artist Giuseppe Lund. The area has a long history, dating back to 1812, when a horse ferry operated nearby.
- Cabot Square
Cabot Square is one of the largest squares in Canary Wharf. It has a big fountain in the middle and smaller fountains hidden by trees. The square is named after John Cabot and his son Sebastian, who were Italian explorers who settled in England.
- Churchill Place
Churchill Place is an area on the east side of Canary Wharf, named after Winston Churchill.
- Columbus Courtyard
This is a small square on the west side of Canary Wharf, named after Christopher Columbus. The first part of Canary Wharf was finished in 1992, 500 years after Columbus arrived in America.
- Chancellor Passage
A passageway south of Cabot Square, named after Richard Chancellor, an explorer who sailed to Moscow.
- Wren Landing
A small area north of Cabot Square, named after British architect Christopher Wren. It leads to a footbridge.
- Montgomery Square
Located at the east end of Jubilee Park, Montgomery Square is a place for social gatherings. It hosts events like street food markets, beach volleyball, and mini-golf.
Parks and Green Spaces
The Canary Wharf Group works hard to add more green spaces and gardens to the busy city area. Each year, they add 20 acres (8 hectares) of parks, gardens, and green squares. These include 1,000 trees, 4,000 shrubs, and 70,000 seasonal plants. Visitors can explore these areas for relaxation, social events, performances, and outdoor art.
- Jubilee Park
Jubilee Park is a 10,000 square meter (107,639 sq ft) roof garden. It is located above Jubilee Place shopping mall and the Canary Wharf Jubilee Station. The park opened in 2002 and was named to honor the Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II. The main feature of the park is a raised, winding water channel with rough stone walls. Its curved design is meant to be a contrast to the straight lines of the surrounding buildings. In 2023, Jubilee Park won the Green Flag Award, recognizing it as one of the UK's best parks.
- Crossrail Place Roof Garden
This is a 4,160 square meter (44,778 sq ft) roof garden on top of the seven-story Crossrail Place building. This building also contains the Elizabeth line Canary Wharf station. The garden opened in 2015 and sits almost exactly on the Meridian line. Plants from the eastern hemisphere are planted on the east side of the garden, and plants from the western hemisphere are on the west side. The Crossrail Place Roof Garden has won many international and UK awards for its design.
- Harbour Quay Garden
This is a newly opened garden at Wood Wharf. It has a boardwalk for walking by the water. The garden also has picnic spots and outdoor fitness equipment. Visitors can relax, see outdoor art, and watch the water. It also connects to a new garden square called Harbord Square Park.
- Harbord Square Park
Harbord Square Park is the newest garden square in Wood Wharf. It continues London's tradition of garden squares. It is open 24/7 and provides a green space for quiet activities and to support the well-being of nearby residents.
Shopping Malls
Canary Wharf has some of London's best shopping. It has five connected shopping malls: Canada Place, Cabot Place, Jubilee Place, Crossrail Place, and Churchill Place. These malls offer over 102,193 square meters (1.1 million sq ft) of shops. You can find more than 310 shops, including beauty, fashion, and luxury brands. There are also 70 cafés, bars, and restaurants, eight grocery stores, five health clubs, and a cinema. Many bars and restaurants at street level also offer outdoor seating with great views.
Local Government
Every four years, people living in the Canary Wharf area vote for two councillors to represent them on the Tower Hamlets Council.
Getting Around Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf has excellent transport links within London and to other parts of the UK.
Train Connections
Canary Wharf is in London fare zone 2. You can find several train stations here.

- The Docklands Light Railway (DLR) stops at Canary Wharf, Heron Quays, and West India Quay stations. This line opened in 1987.
- DLR trains go north to Bank in the City of London. They also go to Stratford. Southbound trains go to Lewisham, stopping at Greenwich.
- London Underground Jubilee line trains stop at Canary Wharf station. Eastbound trains go to Stratford. Westbound trains connect Canary Wharf to the West End and major stations like London Bridge and Waterloo.
- The Elizabeth line (built by the Crossrail project) also stops at Canary Wharf station. This line offers fast, direct connections to the City of London and the West End. Westbound trains go to Central London, Heathrow Airport, and Reading, Berkshire. Eastbound services go to Abbey Wood.
For regional and national train connections, you can travel from Canary Wharf to other major London stations like Liverpool Street or London Bridge.
Road Access
Major roads near Canary Wharf include:
- A12 - goes northeast towards Stratford and the M11 (for Stansted Airport
 ).
). - A13 (East India Dock Road) - goes west to the City of London and east towards Southend (
 ).
). - A102 (Blackwall Tunnel) - goes south to Greenwich and towards destinations in Kent.
- A1020 (Lower Lea Crossing) - goes east to London City Airport (
 ).
). - A1203 (Limehouse Link) - goes east to Shadwell and the City of London.
- A1205 (Burdett Road) - goes north to Mile End and Hackney.
- A1206 (Westferry Circus/Prestons Road) - circles the Isle of Dogs.
- A1261 (Aspen Way) - goes west to the A13 and east to the A1020 for City Airport.
Air Quality
Transport for London (TfL) and the London Borough of Tower Hamlets check the air quality around Canary Wharf. In 2017, a monitoring station in Blackwall found that the air quality did not meet UK National Air Quality Objectives for Nitrogen dioxide (NO2). However, other stations closer to Canary Wharf recorded cleaner air.
Buses
London Buses routes 135, 277, D3, D7, D8, N277, and N550 stop near Canary Wharf. Bus 135 connects directly to Liverpool Street in the City of London.
Riverboat Services
Several Riverboat services stop at Canary Wharf Pier.
- RB1 - goes east to North Greenwich and west to Tower, London Bridge City, and Westminster.
- RB1X - a faster service with fewer stops, going east to North Greenwich and west to Tower, London Bridge City, and Westminster.
- RB4 - the Canary Wharf – Rotherhithe Ferry crosses the Thames to Nelson Dock.
- RB6 - a limited service going east towards Putney.
You can use Oyster Cards for travel on TfL-coordinated riverboat services.
Airports
London City Airport is only 3 miles (4.8 km) from Canary Wharf. It serves flights to places within the UK and internationally, including New York. You can reach London City Airport by taking the DLR from Canary Wharf, changing trains at Poplar.
Cycling Paths
The Canary Wharf Group, London Borough of Tower Hamlets, and Transport for London (TfL) provide cycling infrastructure in and around Canary Wharf. Many routes for fun rides and commuting pass through or near the area.

- National Cycle Route 1 (NCR 1) - a leisure route from Dover, Kent to Shetland, Scotland. In London, it runs on low-traffic paths through Canary Wharf, Mile End, and Tottenham.
- EuroVelo 2 ("The Capitals Route") - an international leisure route from Moscow, Russia to Galway, Ireland. In London, it follows the same path as NCR 1.
- National Cycle Route 13 (NCR 13) - a leisure route from the City to Fakenham, Norfolk. It uses low-traffic paths through East London.
- Cycle Superhighway 3 (CS3) - a commuter route from Barking to West London. It runs east–west through nearby Poplar on low-traffic or residential streets. This route provides a direct link to Tower Hill, Blackfriars, Westminster, and Hyde Park Corner.
- Cycleway from Hackney to the Isle of Dogs - a planned cycle link that would connect Canary Wharf directly to Mile End on a traffic-free path.
- Limehouse Cut towpath - a shared path from nearby Limehouse to Stratford. It is traffic-free.
- Regent's Canal towpath - a shared path from nearby Limehouse to Angel. It is traffic-free and goes through Mile End and Islington.
Museums and Archives
The Museum of London Docklands is a major attraction in the area. It opened in June 2003 in a historic Georgian warehouse. The museum tells the story of London's river, port, and people from Roman times to today. It offers many activities for children and families, including interactive displays.
Fun Facts: Pokémon Go
Since 2017, Canary Wharf has been known as a great place to play Pokémon Go. It has some of the most popular Pokémon gyms in London, including at Canary Wharf DLR station and Montgomery Square. The Canary Wharf Group even made an official Pokémon map for PokéStops and Gyms. They noticed that the game brought more people to the area, especially to the food and drink places.
Events and Festivals
Canary Wharf hosts many exciting events throughout the year.
Winter Lights Festival
The Canary Wharf Winter Lights Festival started in 2014. Every January, visitors can see amazing outdoor light art and interactive displays created by artists from all over the world. The festival has won awards for being the Best Creative Lighting Event. The 2023 festival was described as the largest light art festival in London.
WaterAid Dragon Boat Race
This is an annual event that raises money for WaterAid, a charity that helps people get clean water and basic toilets. The Dragon Boat Race is based on an old Chinese tradition. It takes place in the South Dock of Canary Wharf in the summer. Teams of 11 to 17 people can join. In 2022, the event raised £26,000, and in 2023, it raised £31,744.
Festival14
Hosted by the Canary Wharf Group, Festival14 is a multi-day event. In 2022, it featured over 60 live acts, including music, theatre, dance, poetry, comedy, and family fun. Most events were free. The festival uses the area's parks and open spaces to host artists and performers from around the world. In 2023, the festival was extended to five days.
Open Water Swimming
Since summer 2022, Canary Wharf has offered outdoor swimming in the 220-year-old Middle Dock. This area provides 600 square meters (6,458 sq ft) of open water for swimming.
Outdoor Public Art
Canary Wharf has the largest outdoor public art collection in London. You can see over 100 sculptures and art pieces displayed outside buildings. The Canary Wharf Group provides two updated maps for visitors to find these artworks.
- Canary Wharf Art Map: This map shows over 100 artworks with descriptions and their locations.
- Children's Art Trail: A smaller trail with 12 sculptures and artworks designed for children.
The Canary Wharf website also has information about "Raise Your Art Rate." This event lets visitors explore the outdoor art collection while exercising. It offers 1 km, 3 km, and 5 km routes for walking, jogging, or running that pass by the artworks. The event is free and open to everyone.
Local Media
The East London Advertiser is a local newspaper that prints weekly and is also available online. Wharf life is another publication that comes out every two weeks. It focuses on Canary Wharf, Docklands, and East London.
See also
 In Spanish: Canary Wharf para niños
In Spanish: Canary Wharf para niños
- 1996 Docklands bombing
- The Wharf newspaper
- Cascades, Isle of Dogs
- Millwall
- List of tallest buildings and structures in London
- List of tallest buildings in the United Kingdom
Images for kids
-
East view from Cabot Square
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |