Chocolate facts for kids

Chocolate most commonly comes in dark, milk, and white varieties, with cocoa solids contributing to the brown color.
|
|
| Main ingredients | Chocolate liquor, cocoa butter for white chocolate, often with added sugar |
|---|---|
Chocolate is a yummy food made from the seeds of the cacao tree. People use it in lots of desserts like pudding, cakes, candy, and ice cream. You can find chocolate as a solid bar or as a liquid drink like hot chocolate. Chocolate usually tastes sweet because makers add a lot of sugar and milk to it. Eating too much chocolate can be bad for your teeth and health, so it's best to enjoy it in small amounts.
After cacao beans are picked, they are dried, cleaned, and roasted. The outer shell is taken off to get "cacao nibs." These nibs are then ground into a thick paste called cocoa mass. When this cocoa mass is heated and becomes liquid, it's called chocolate liquor. This liquor can also be separated into two parts: cocoa solids and cocoa butter.
Baking chocolate, which is also called bitter chocolate, has cocoa solids and cocoa butter but no added sugar. Most chocolate we eat today is sweet chocolate. This is a mix of cocoa solids, cocoa butter (or other oils), and sugar. Milk chocolate is sweet chocolate that also has milk powder or condensed milk. White chocolate has cocoa butter, sugar, and milk, but it doesn't have any cocoa solids.
Chocolate is one of the most popular foods and flavors around the world! Many treats are made with chocolate, like cakes, pudding, mousse, chocolate brownies, and chocolate chip cookies. Lots of candies are filled with or covered in sweet chocolate. Solid bars and candy bars with chocolate coatings are popular snacks. People often give chocolate shaped like eggs or hearts as gifts on holidays like Easter and Valentine's Day. Chocolate is also used in drinks like chocolate milk and hot chocolate.
Even though cocoa trees first grew in the Americas, countries in Africa now produce most of the world's cocoa. Since the early 2000s, Western Africa makes almost two-thirds of all cocoa, with Ivory Coast growing nearly half of that amount.
Contents
How Chocolate Came to Be
People first discovered how useful cacao tree seeds were about 2,000 years ago. Early people in Central America and Mexico used cacao seeds to make a bitter drink. Only important people were allowed to drink it. The word "chocolate" in most languages comes from the Nahuatl language of Mexico, where it was called chocolatl.
Later, this bitter drink was made sweeter and became what we know today as hot chocolate. Spanish explorers brought it from North America to Spain, and it became very popular. When chocolate was made into candy, it became a favorite treat for many Europeans. At first, only rich people could afford chocolate. Now, many people around the world enjoy it. Most cocoa today is grown in Africa.
Different Kinds of Chocolate
There are several types of chocolate. Pure, unsweetened chocolate, often called "baking chocolate," mostly has cocoa solids and cocoa butter. Most chocolate eaten today is sweet chocolate, which mixes chocolate with sugar.
- Milk chocolate is sweet chocolate that also has milk powder or condensed milk.
- White chocolate looks similar to milk and dark chocolate, but it doesn't have any cocoa solids. Because of this, some countries don't even call white chocolate "chocolate." Since it has no cocoa solids, white chocolate doesn't have a substance called theobromine, which means some animals like dogs can eat it safely (though it's still best to check with a vet).
- Dark chocolate is made by adding fat and sugar to the cacao mix.
- Unsweetened chocolate is pure chocolate liquor. It's also called bitter or baking chocolate. It's just ground, roasted cacao beans, giving it a strong, deep chocolate flavor. It's usually used in baking where sugar and other ingredients are added later. Raw chocolate, or raw cacao, is always dark and has at least 75% cacao.
Sometimes, dark chocolate can get whitish spots called chocolate bloom. This happens if the chocolate isn't stored well, causing sugar or fat to separate. It's not harmful and is safe to eat!
How Chocolate is Made
Making chocolate involves many steps.
- First, cocoa beans are collected and put into piles or containers to ferment. Fermentation turns the sugar in the beans into alcohol.
- Then, the beans are dried and cleaned.
- Next, chocolate makers cook the beans and crush them. This process helps to get out the cocoa butter and chocolate liquor.
- After that, the chocolate maker mixes different ingredients to create different kinds of chocolate. Dark chocolate is made from sugar, cocoa butter, and chocolate liquor. Milk chocolate uses all those ingredients plus milk and vanilla. White chocolate doesn't have chocolate liquor; it only has cocoa butter, along with sugar, milk, and vanilla.
- The chocolate maker isn't finished yet! One of the last steps is called "conching." Before conching, chocolate feels rough in your mouth. Conching means crushing the chocolate very finely and keeping it warm so it stays liquid. Conching for several hours makes chocolate smooth and delicious.
- The very last step is called "tempering." The chocolate is heated, then shaken, and then cooled a few times. This makes the chocolate shiny and gives it a good "snap" when you break it.
What's in Chocolate?
The main ingredients for different types of chocolate are:
- Dark chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, and sometimes vanilla.
- Milk chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, milk or milk powder, and vanilla.
- White chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, milk or milk powder, and vanilla.
Often, a special ingredient like soy lecithin is added. This helps make the chocolate super smooth.
Who Makes Chocolate?
Many companies make chocolate products, from chocolate bars to fudge. Some big chocolate makers include Cadbury, Ferrero, Guylian, The Hershey Company, Lindt, Mars, Incorporated, Milka, and Neuhaus.
- Guylian is famous for its chocolate sea shells.
- Cadbury is known for its Dairy Milk bars and Creme Eggs.
- The Hershey Company, a big chocolate maker in North America, makes the Hershey Bar and Hershey's Kisses.
- Mars Incorporated makes popular bars like Mars Bar, Milky Way, M&M's, Twix, and Snickers.
- Lindt is known for its truffle balls and gold foil-wrapped Easter bunnies.
Big food companies like Nestlé and Kraft Foods also own chocolate brands. Nestlé makes Smarties and Kit Kat. Kraft Foods owns Milka and Suchard, and also bought Cadbury in 2010.
How People Use and Eat Chocolate

Chocolate is sold in chocolate bars, which come in dark, milk, and white chocolate kinds. Some bars mix in other ingredients like nuts, raisins, or crisped rice. Chocolate is a key part of many candy bars, which often have fillings like nougat, wafers, caramel, or nuts covered in chocolate.
Chocolate is also a popular flavor in many desserts, such as chocolate cakes, chocolate brownies, chocolate mousse, and chocolate chip cookies. Lots of candy and snacks have chocolate, either as a filling (like M&M's) or a coating (like chocolate-coated raisins or chocolate-coated peanuts).
Some drinks contain chocolate, such as chocolate milk, hot chocolate, and chocolate milkshakes. Chocolate is a favorite flavor for ice cream and pudding. Chocolate sauce is often added as a topping on ice cream sundaes.
Chocolate and Your Health
One hundred grams of milk chocolate has about 540 calories. It's mostly carbohydrates (sugars and fiber), with some fat and protein. About 65% of the fat in milk chocolate is saturated fat.
A 100-gram serving of milk chocolate is a great source of riboflavin, vitamin B12, and minerals like manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. It's also a good source of calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Eating too much of any energy-rich food, like chocolate, without enough activity can lead to weight gain. Raw chocolate has a lot of cocoa butter, which is a fat. Manufacturers often add more fats, sugars, and milk, which increases the calories in chocolate.
Chocolate can sometimes cause heartburn in some people because of a substance called theobromine.
Is Chocolate Safe?
Chocolate is generally safe to eat unless you eat huge amounts. However, some animals, like dogs, can get sick if they eat chocolate. People with diabetes also need to be careful with chocolate because of its sugar content.
Dark chocolate contains ingredients that can help lower blood pressure and fight disease. Eating small amounts of dark chocolate has been shown to lower the risk of heart disease because of special plant compounds called polyphenols. It's important to eat chocolate in moderation.
Storing Chocolate

Chocolate is very sensitive to temperature and how much moisture is in the air. The best temperature to store chocolate is between 15 and 17 degrees Celsius (59 and 63 degrees Fahrenheit), with less than 50% humidity. If chocolate gets too cold in a fridge or freezer without being sealed, it can absorb moisture. This can cause a whitish color on the surface, which is fat or sugar crystals rising.
This whitish look is called "chocolate bloom." It happens if the storage temperature changes a lot or goes above 24 degrees Celsius (75 degrees Fahrenheit). If it's too cold (below 15 degrees Celsius or 59 degrees Fahrenheit) or too humid, it can cause "sugar bloom." You can tell the difference by gently rubbing the chocolate's surface. If the white spots disappear, it's fat bloom. Even though bloom doesn't look great, the chocolate is still safe to eat and tastes fine! You can fix bloom by melting and re-tempering the chocolate.
Chocolate should usually be stored away from other foods because it can absorb their smells. Ideally, chocolates are wrapped and kept in a dark place with the right humidity and temperature. The shiny look, crisp snap, smell, feel, and taste of chocolate can tell you about its quality and if it was stored well.
Chocolate in Culture
Holidays and Traditions


Chocolate is a big part of many holidays. For Easter, people in Christian communities traditionally give chocolate rabbits and eggs. For Hanukkah, Jewish communities often give chocolate coins. On Valentine's Day, chocolate hearts and heart-shaped boxes of chocolate are popular gifts, often given with flowers and cards. Chocolate is also a great gift for birthdays and other special occasions.
Many candy makers create special chocolate candies for holidays. Chocolate Easter eggs or rabbits and Santa Claus figures are common examples. These treats can be solid, hollow, or filled with other sweets.
Images for kids
-
Paul Gavarni Woman Chocolate Vendor (1855–1857)
-
Chocolate became a popular drink for rich Europeans after the Americas were discovered. The morning chocolate by Pietro Longhi; Venice, 1775–1780
-
Silver chocolate pot with a special lid to stir with a moulinet or swizzle stick, London 1714–15 (Victoria and Albert Museum)
-
Dutch chemist Coenraad Johannes van Houten invented "Dutch cocoa" by treating cocoa mass with special salts to make it less bitter without adding sugar or milk.
-
Fry's made the first solid chocolate in 1847, which was then mass-produced as Fry's Chocolate Cream in 1866.
-
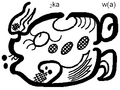
Maya symbol for cocoa
-
Toasted cocoa beans at a chocolate workshop at the La Chonita Hacienda in Tabasco.
-
"Dancing the cocoa," El Cidros, Trinidad, around 1957. This was a way to dry and polish the beans.
-
Fountain chocolate has lots of cocoa butter, so it flows smoothly over a chocolate fountain for dessert fondue.
-
Packaged chocolate in the Ghirardelli Chocolate Company is stored in controlled conditions.
-
A gift box of chocolates, a common gift for Valentine's Day.
See also
 In Spanish: Chocolate para niños
In Spanish: Chocolate para niños