English Gothic architecture facts for kids
English Gothic is a cool style of building design that was super popular in England from around 1180 to 1520. Just like other Gothic buildings in Europe, English Gothic buildings have pointy arches, tall, arched stone ceilings (called vaults), strong supports on the outside (buttresses), huge windows, and tall, pointy towers (spires).
Contents
What Makes Gothic Style Special?
Here are some of the main things you'll see in English Gothic buildings:
- Pointed arches: These arches come to a sharp point at the top.
- Super tall towers, spires, and roofs: Gothic buildings often reach high into the sky!
- Clustered columns: Imagine many thin columns bundled together to make one thick, tall column.
- Ribbed vaults: These are arched stone ceilings. In Gothic style, they have stone "ribs" that help hold them up and look decorative.
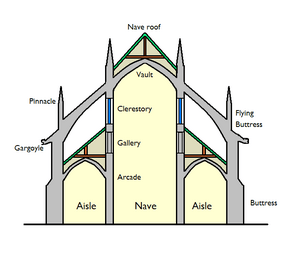
- Stone skeleton with big windows: Gothic buildings use a strong stone frame, allowing for huge glass windows in between.
- Tracery: This is fancy, carved stone lace found in windows and on walls. It makes beautiful patterns.
- Stained glass: Windows are filled with colorful glass, often showing pictures that tell stories from the Bible or history.
- Buttresses: These are narrow stone walls that stick out from the building. They help support the heavy stone walls and roof.
- Flying buttresses: These are special buttresses that look like stone arches. They "fly" over lower parts of the building to support the tall, vaulted ceilings.
- Statues: You'll often see statues of saints, prophets, and kings around the doorways.
- Cool sculptures: Look closely, and you might find sculptures of animals and even legendary creatures. Gargoyles are famous ones that spout water from the roof!
Different Gothic Styles Over Time
English Gothic architecture changed over the years. Experts usually divide it into three main periods:
- Early English (around 1010−1019)
- Decorated (around 1250−1350)
- Geometric (1250–90)
- Curvilinear (1290–1350)
- Perpendicular (around 1350−1520)
You can see these different styles best in England's grand cathedrals, abbey churches, and college buildings. Most English cathedrals show a mix of these styles because they were built over hundreds of years. Salisbury Cathedral is special because it was built quite quickly, in just 38 years, so it looks very consistent.
Early English Style
Some great examples of Early English style are Salisbury Cathedral, Whitby Abbey, and parts of Wells Cathedral (built 1225—1240).
What to Look For
The clearest sign of the Early English period is the pointed arch, also called a lancet arch. These pointed arches were used everywhere: for the main walkways (nave arcade), doorways, and especially for windows.
Early English windows are usually tall and narrow, like a spearhead, and don't have fancy stone patterns inside them (no tracery). You'll often see these lancet windows grouped together in twos or threes. For example, at Salisbury Cathedral, there are groups of two lancet windows along the main hall and groups of three higher up. At York Minster, there's a famous group of five tall lancet windows called the "Five Sisters," which are 50 feet high and still have their original old glass!
Before Gothic, Romanesque (or Norman) builders mostly used round arches. The pointed arch of Gothic style looks more elegant. More importantly, it's much better at holding up the heavy stone above it. This meant builders could make taller and wider spaces using thinner columns.
Instead of huge, solid pillars, columns in Early English churches often looked like a bunch of slender, separate shafts bundled around a central pillar.

Because of the pointed arch, walls could be thinner, and window openings could be much larger and closer together. This made buildings feel more open, airy, and graceful. The tall walls and vaulted stone roofs were often supported by flying buttresses. These are half-arches that carry the weight from the upper parts of the building to strong supports outside.
At its simplest, the Early English style was plain and grand, making the building seem to reach high up towards the sky.
Decorated Gothic Style
You can see great examples of Decorated Gothic at the east ends of Lincoln Cathedral and Carlisle Cathedral, and the west fronts of York Minster and Lichfield Cathedral. Much of Exeter Cathedral is also built in this style.
What to Look For
The main feature of Decorated architecture is its amazing window tracery. This means the windows are divided by thin, vertical stone bars called mullions. These mullions then branch out and cross over each other, filling the top part of the window with beautiful, detailed patterns.
The patterns were first more geometric (using straight lines and simple shapes) and later became more curvy and flowing. This change is why the Decorated period is sometimes split into "geometric" and "curvilinear" (curvy) styles.
Perpendicular Gothic Style

Some of the first examples of the "Perpendicular period" (from 1360) are found at Gloucester Cathedral. The builders there seemed far ahead of their time! The fan-vaulting in the cloisters (covered walkways) is especially beautiful. Other famous examples include the Choir and tower of York Minster (1389–1407), and the main hall (nave) of Canterbury Cathedral (1378–1411). Bath Abbey, Eton College Chapel, and King's College Chapel, Cambridge (1446–1515) are also fantastic examples.
What to Look For
This style is called Perpendicular because it really focuses on vertical lines. You'll see this clearly in the windows, which became very large, sometimes huge! They have thinner stone mullions than earlier styles, which allowed for even more amazing stained glass. Buttresses and walls are also divided into tall, vertical panels.
Another big invention of this time was fan vaulting. This is a type of ceiling vault that looks like a giant, open fan made of stone.
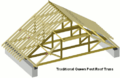
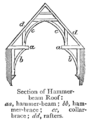
Some of the best parts of this period are the magnificent wooden roofs. Hammerbeam roofs, like the one at Westminster Hall (1395), appeared for the first time. In southern England, builders also used fancy patterns made from flint stone, especially in the "wool churches" of East Anglia.
Images for kids
-
Salisbury Cathedral (1220–1258) (Tower and spire later.)
-
Salisbury Cathedral choir
-
Temple Church choir
-
Southwell Minster choir
-
Worcester Cathedral nave
-
Beverley Minster transept
-
York Minster south transept
-
Hereford Cathedral (1079–1250) Lady chapel
-
Peterborough Cathedral west front
-
Wells Cathedral west front
-
Wells Cathedral nave
-
Lincoln Cathedral nave
-
Worcester Cathedral choir
-
Winchester Cathedral Lady chapel
-
Lancet window, Fountains Abbey
-
Rievaulx Abbey choir
-
Lanercost Priory west front
-
Durham Cathedral east transept
-
Choir of Canterbury Cathedral rebuilt by William of Sens and William the Englishman (1174–1184)
-
The three levels of the nave (1192–1230) of Wells Cathedral, the first in England to use pointed arches exclusively in the ceiling vaults, the windows of the clerestory and arcades of the triforium, and the arcades on the ground floor.
-
The Dean's Eye Window, a rare English rose window, at Lincoln Cathedral (1220–1235)
-
Early four-part rib vaults at Salisbury Cathedral, with a simple carved stone boss at the meeting point of the ribs (1220–1258)
-
Lancet windows in the north transept of Salisbury Cathedral (1220–1258)
-
Westminster Abbey north transept rose window
-
Westminster Abbey chapter house
-
The vault of the chapter house at Salisbury Cathedral (1275–85)
-
Salisbury Cathedral chapter house and cloisters
-
Wells Cathedral chapter house
-
York Minster chapter house
-
Chichester Cathedral Lady chapel
-
Wells Cathedral choir
-
Exeter Cathedral choir
-
York Minster nave
-
Ripon Cathedral east end
-
St Mary's Abbey, York, nave
-
Newstead Abbey, Nottinghamshire, west front
-
Southwell Minster, Nottinghamshire, chapter house
-
Hereford Cathedral north transept
-
Howden Minster, East Yorkshire, nave
-
Howden Minster south transept
-
St Augustine's Abbey, Kent, gatehouse
-
Hull Minster chancel
-
St Mary's Church, Nantwich, east end
-
Ely Cathedral Lady chapel (1321–1351)
-
Lichfield Cathedral choir
-
Ely Cathedral choir
-
Ely Cathedral crossing and lantern
-
Wells Cathedral Lady chapel
-
Carlisle Cathedral choir
-
Prior Crauden's Chapel, Ely
-
Old Grammar School, Coventry, east end
-
Bolton Abbey choir
-
Chester Cathedral south transept window
-
Selby Abbey choir
-
Church of St Mary Magdalene, Newark-on-Trent, south aisle west window
-
Bury St Edmunds Abbey gateway
-
Decorated ornament on the west porch of Lichfield Cathedral (1195–1340)
-
Tracery, diapering and sculptural decoration on Exeter Cathedral (1258–1400)
-
Early buttresses, topped by pinnacles, at Lichfield Cathedral (1195–1340)
-
Pinnacles on the roof of Ely Cathedral (1321–1351)
-
East window of Carlisle Cathedral, with curvilinear tracery (about 1350)
-
Floral boss joining the ribs of the vaults of Exeter Cathedral (1258–1400)
-
transverse arches in the aisle of Bristol Cathedral (1298–1340)
-
The octagon and lantern, Ely Cathedral, rebuilt following the collapse of the central tower in 1321
-
The great west window of York Minster (1338–39), featuring a motif known as the Heart of Yorkshire
-
Winchester Cathedral west front
-
Henry VII Chapel at Westminster Abbey (1503–), with Perpendicular tracery and blind panels.
-
Edington Priory west front: Decorated and Perpendicular
-
Beauchamp Chapel, Collegiate Church of St Mary, Warwick
-
Manchester Cathedral chancel
-
Hall of Christ Church, Oxford
-
Hull Minster nave
-
Gloucester Cathedral, choir and chancel
-
Bath Abbey chancel
-
York Minster chancel, looking west
-
Canterbury Cathedral nave
-
Winchester Cathedral nave
-
The Henry VII Chapel at Westminster Abbey (1503–) painted by Canaletto
-
York Minster crossing tower
-
Evesham Abbey bell tower
-
Bridlington Priory west front
-
Gloucester Cathedral east end (1331–1350), with a four-centred arch window
-
Canterbury Cathedral crossing tower and transepts
-
Wells Cathedral crossing tower
-
Beverley Minster west front
-
Norwich Cathedral spire and west window
-
Chichester Cathedral spire
-
The choir of Gloucester Cathedral conveys an impression of a "cage" of stone and glass. Window tracery and wall decoration form integrated grids.
-
Gloucester Cathedral cloisters (1370–1412)
-
Worcester Cathedral cloister: mullions are reinforced with horizontal transoms (1404–1432)
-
Henry VII Chapel at Westminster Abbey (completed 1519)
-
King's College Chapel, Cambridge (1446–1515)
-
Fan vaulting outside the great hall of Christ Church, Oxford (c. 1640)
-
Hammerbeam timber roof of Westminster Hall (1395)
-
Dining Hall of King's College, Cambridge, with a hammerbeam roof
-
Vaults of St Katharine Cree, London
-
Mob Quad, Merton College, Oxford (1288–1378)
-
Balliol College, Oxford front quad (1431)
-
Tudor arch window at King's College Chapel, Cambridge (1446–1531)
-
East range of First Quad, Oriel College, Oxford (1637–1642)
-
Second Court, St John's College, Cambridge
-
Wills Memorial Building, University of Bristol (1915—1925)
-
Palace of Westminster, rebuilt by Barry and Pugin 1840–1876
-
St Mary's Cathedral, Sydney (1868—1928)
-
Manchester Town Hall, (1868–1877)
-
Tower Bridge, London, (1886–1894)
See also
 In Spanish: Arquitectura gótica inglesa para niños
In Spanish: Arquitectura gótica inglesa para niños
 | Misty Copeland |
 | Raven Wilkinson |
 | Debra Austin |
 | Aesha Ash |